Matrices are 2-dimensional arrays:

It's a 4*2 matrix
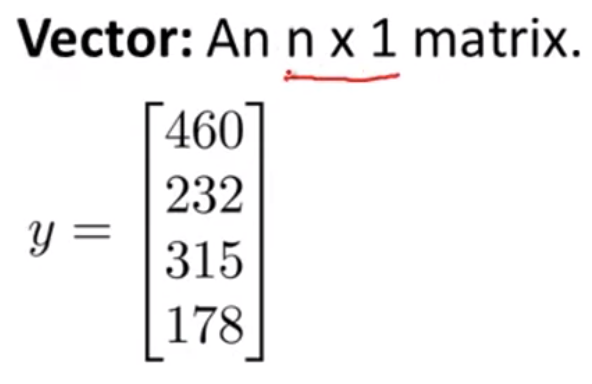
1 column's matrice is called Vector;

% The ; denotes we are going back to a new row. A = [1, 2, 3; 4, 5, 6; 7, 8, 9; 10, 11, 12] % Initialize a vector v = [1;2;3] % Get the dimension of the matrix A where m = rows and n = columns [m,n] = size(A) % You could also store it this way dim_A = size(A) % Get the dimension of the vector v dim_v = size(v) % Now let's index into the 2nd row 3rd column of matrix A A_23 = A(2,3)
/* A = 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 v = 1 2 3 m = 4 n = 3 dim_A = 4 3 dim_v = 3 1 A_23 = 6 */