1、动机
2、基于内容的分类器
3、python实现
一、动机
在前面的文章中介绍了基于用户和基于物品的协同过滤推荐方法,其实无论是基于用户还是基于物品,都是通过群体效应来进行推荐,因为衡量相似度的向量都是基于一定群体用户的评分,所以推荐出来的物品都是热门的流行的物品,对于一些冷门物品可能就无法收到亲睐。
而一个好的推荐系统,不仅能为用户发现热门流行的感兴趣物品,也能为用户提供自己也不了解的但也会感兴趣的物品,即冷门的物品,这样既有益于用户,也照顾了内容提供商。
因此,本文将介绍一种基于内容即物品属性的分类方法来进行推荐,在机器学习中,称为有监督学习的方法。
二、基于内容(物品属性)的分类器
1、特征向量
与基于物品的协同顾虑类似,需要一个能够描述物品的特征向量,只是这里的特征向量与用户无关,只与物品的自身属性相关,如:
歌曲的属性:

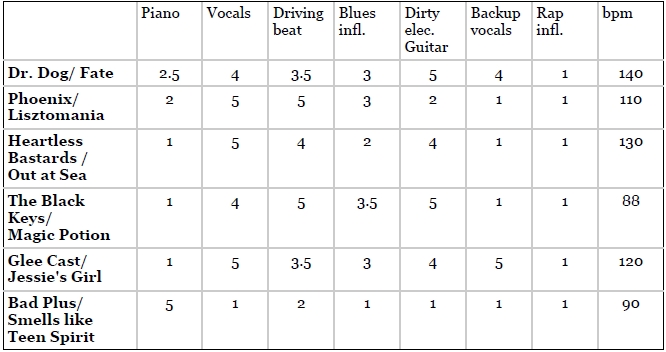
2、相似性度量
相似性度量方法与前面的介绍的一样,基本上采用距离公式,如曼哈顿距离,欧几里得距离等
有个问题在于不同特征属性的尺度不同,这样会导致距离的计算由某些特征主导,解决方法有两种:
A. 归一化
将特征属性都归一到[0,1]或[-1,1]之间

B. 标准化
将特征属性标准化为均值为0的高斯分布或其他分布


采用上面的标准化方法容易受离群点或奇异点(outliers)影响,因此一般采用如下方法:
将均值替换为中值,将标准差的计算方法替换为绝对标准差,如下:

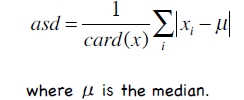
3、分类器
有了特征向量和相似度衡量方法,那么如何进行分类呢?
假设有一些用户和物品数据,我们知道用户听过一些音乐,知道他喜欢哪些,不喜欢哪些,那么来了一首新的歌曲,我们如何判断用户是否喜欢呢?这就是一个简单的分类问题,两个类别:喜欢or不喜欢。
其实很简单,这里介绍一种最简单的,前面也介绍过的方法,那就是最近邻分类或k近邻分类。
我们有了物品数据,即有了物品的特征向量,那么我们就可以在用户听过的歌曲中找到跟新歌曲相似度最高的歌曲,如果用户喜欢该歌曲,那么我们将猜测也喜欢这首新歌,否则反之。
总结一下:分类器就是利用一些已经标注过类别的物品数据,来预测新物品的类别。
4、训练集与测试集
训练集:用来训练模型参数的数据
测试集:用来测试模型好坏的数据
三、python实现
数据集下载:
- athletesTrainingSet.txt
- athletesTestSet.txt
- irisTrainingSet.data
- irisTestSet.data
- mpgTrainingSet.txt
- mpgTestSet.txt
代码:
## Each line of the file contains tab separated fields. ## The first line of the file describes how those fields (columns) should ## be interpreted. The descriptors in the fields of the first line are: ## ## comment - this field should be interpreted as a comment ## class - this field describes the class of the field ## num - this field describes an integer attribute that should ## be included in the computation. ## ## more to be described as needed ## ## ## So, for example, if our file describes athletes and is of the form: ## Shavonte Zellous basketball 70 155 ## The first line might be: ## comment class num num ## ## Meaning the first column (name of the player) should be considered a comment; ## the next column represents the class of the entry (the sport); ## and the next 2 represent attributes to use in the calculations. ## ## The classifer reads this file into the list called data. ## The format of each entry in that list is a tuple ## ## (class, normalized attribute-list, comment-list) ## ## so, for example ## ## [('basketball', [1.28, 1.71], ['Brittainey Raven']), ## ('basketball', [0.89, 1.47], ['Shavonte Zellous']), ## ('gymnastics', [-1.68, -0.75], ['Shawn Johnson']), ## ('gymnastics', [-2.27, -1.2], ['Ksenia Semenova']), ## ('track', [0.09, -0.06], ['Blake Russell'])] ## class Classifier: def __init__(self, filename): self.medianAndDeviation = [] # reading the data in from the file f = open(filename) lines = f.readlines() f.close() self.format = lines[0].strip().split(' ') self.data = [] for line in lines[1:]: fields = line.strip().split(' ') ignore = [] vector = [] for i in range(len(fields)): if self.format[i] == 'num': vector.append(float(fields[i])) elif self.format[i] == 'comment': ignore.append(fields[i]) elif self.format[i] == 'class': classification = fields[i] self.data.append((classification, vector, ignore)) self.rawData = list(self.data) # get length of instance vector self.vlen = len(self.data[0][1]) # now normalize the data for i in range(self.vlen): self.normalizeColumn(i) ################################################## ### ### CODE TO COMPUTE THE MODIFIED STANDARD SCORE def getMedian(self, alist): """return median of alist""" if alist == []: return [] blist = sorted(alist) length = len(alist) if length % 2 == 1: # length of list is odd so return middle element return blist[int(((length + 1) / 2) - 1)] else: # length of list is even so compute midpoint v1 = blist[int(length / 2)] v2 =blist[(int(length / 2) - 1)] return (v1 + v2) / 2.0 def getAbsoluteStandardDeviation(self, alist, median): """given alist and median return absolute standard deviation""" sum = 0 for item in alist: sum += abs(item - median) return sum / len(alist) def normalizeColumn(self, columnNumber): """given a column number, normalize that column in self.data""" # first extract values to list col = [v[1][columnNumber] for v in self.data] median = self.getMedian(col) asd = self.getAbsoluteStandardDeviation(col, median) #print("Median: %f ASD = %f" % (median, asd)) self.medianAndDeviation.append((median, asd)) for v in self.data: v[1][columnNumber] = (v[1][columnNumber] - median) / asd def normalizeVector(self, v): """We have stored the median and asd for each column. We now use them to normalize vector v""" vector = list(v) for i in range(len(vector)): (median, asd) = self.medianAndDeviation[i] vector[i] = (vector[i] - median) / asd return vector ### ### END NORMALIZATION ################################################## def manhattan(self, vector1, vector2): """Computes the Manhattan distance.""" return sum(map(lambda v1, v2: abs(v1 - v2), vector1, vector2)) def nearestNeighbor(self, itemVector): """return nearest neighbor to itemVector""" return min([ (self.manhattan(itemVector, item[1]), item) for item in self.data]) def classify(self, itemVector): """Return class we think item Vector is in""" return(self.nearestNeighbor(self.normalizeVector(itemVector))[1][0]) def unitTest(): classifier = Classifier('athletesTrainingSet.txt') br = ('Basketball', [72, 162], ['Brittainey Raven']) nl = ('Gymnastics', [61, 76], ['Viktoria Komova']) cl = ("Basketball", [74, 190], ['Crystal Langhorne']) # first check normalize function brNorm = classifier.normalizeVector(br[1]) nlNorm = classifier.normalizeVector(nl[1]) clNorm = classifier.normalizeVector(cl[1]) assert(brNorm == classifier.data[1][1]) assert(nlNorm == classifier.data[-1][1]) print('normalizeVector fn OK') # check distance assert (round(classifier.manhattan(clNorm, classifier.data[1][1]), 5) == 1.16823) assert(classifier.manhattan(brNorm, classifier.data[1][1]) == 0) assert(classifier.manhattan(nlNorm, classifier.data[-1][1]) == 0) print('Manhattan distance fn OK') # Brittainey Raven's nearest neighbor should be herself result = classifier.nearestNeighbor(brNorm) assert(result[1][2]== br[2]) # Nastia Liukin's nearest neighbor should be herself result = classifier.nearestNeighbor(nlNorm) assert(result[1][2]== nl[2]) # Crystal Langhorne's nearest neighbor is Jennifer Lacy" assert(classifier.nearestNeighbor(clNorm)[1][2][0] == "Jennifer Lacy") print("Nearest Neighbor fn OK") # Check if classify correctly identifies sports assert(classifier.classify(br[1]) == 'Basketball') assert(classifier.classify(cl[1]) == 'Basketball') assert(classifier.classify(nl[1]) == 'Gymnastics') print('Classify fn OK') def test(training_filename, test_filename): """Test the classifier on a test set of data""" classifier = Classifier(training_filename) f = open(test_filename) lines = f.readlines() f.close() numCorrect = 0.0 for line in lines: data = line.strip().split(' ') vector = [] classInColumn = -1 for i in range(len(classifier.format)): if classifier.format[i] == 'num': vector.append(float(data[i])) elif classifier.format[i] == 'class': classInColumn = i theClass= classifier.classify(vector) prefix = '-' if theClass == data[classInColumn]: # it is correct numCorrect += 1 prefix = '+' print("%s %12s %s" % (prefix, theClass, line)) print("%4.2f%% correct" % (numCorrect * 100/ len(lines))) ## ## Here are examples of how the classifier is used on different data sets ## in the book. # test('athletesTrainingSet.txt', 'athletesTestSet.txt') # test("irisTrainingSet.data", "irisTestSet.data") # test("mpgTrainingSet.txt", "mpgTestSet.txt") if __name__ == '__main__': # unitTest print ("-------------------UnitTest----------------") unitTest() print ("-------------------Athletes Test----------------") test("athletesTrainingSet.txt","athletesTestSet.txt") print ("-------------------Irises Data Test----------------") test("irisTrainingSet.data","irisTestSet.data") print ("-------------------mpg Test----------------") test("mpgTrainingSet.txt","mpgTestSet.txt")