Stack3.h的内容如下:
#ifndef STACK3_H #define STACK3_H #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <stdexcept> template <typename T, typename CONT = std::vector<T> > class Stack { private: CONT elems; public: void push(T const&); void pop(); T top() const; bool empty() const { return elems.empty(); } }; template <typename T, typename CONT> void Stack<T, CONT>::push(T const& elem) { elems.push_back(elem); } template <typename T, typename CONT> void Stack<T, CONT>::pop() { if (elems.empty()) { throw std::out_of_range("Stack<>::pop(): empty stack"); } elems.pop_back(); } template <typename T, typename CONT> T Stack<T, CONT>::top() const { if (elems.empty()) { throw std::out_of_range("Stack<>::top(): empty stack"); } return elems.back(); } #endif // STACK3_H
测试文件main.cpp的内容如下:
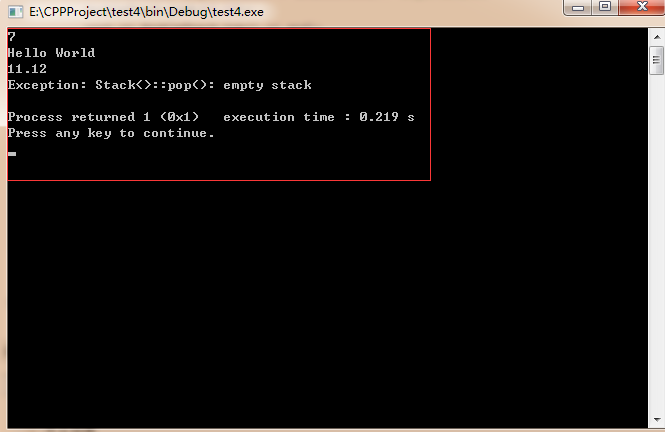
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <deque> #include <cstdlib> #include "Stack3.h" using namespace std; int main() { try { Stack<int> intStack;// vector<int> intStack.push(7); cout << intStack.top() << endl; intStack.pop(); Stack<string> stringStack;// vector<string> stringStack.push("Hello World"); cout << stringStack.top() << endl; Stack<double, deque<double> > doubleStack;// deque<double> doubleStack.push(11.12); cout << doubleStack.top() << endl; doubleStack.pop(); doubleStack.pop(); } catch (std::exception const& ex) { cerr << "Exception: " << ex.what() << endl; return EXIT_FAILURE;// n stdlib.h } return 0; }
结果: