在学习c++基础总结了笔记,并分享出来。有问题请及时联系博主:Alliswell_WP,转载请注明出处。
04-c++day08
目录:
一、C++模板
1、函数模板基本使用
2、课堂练习-实现通用的数组排序
3、函数模板和普通函数区别
4、函数模板和普通函数在一起调用规则
5、模板机制
6、函数模板的局限性
7、类模板的基本使用
8、成员函数创建时机
9、类模板做函数的参数
10、类模板碰到继承的问题以及解决
11、类模板的类外实现成员函数
12、类模板的分文件编写问题以及解决
13、友元碰到类模板——友元函数类内实现
14、友元碰到类模板——友元函数类外实现
15、类模板的应用——数组类的封装
二、总结
一、C++模板
c++提供了函数模板(function template.)所谓函数模板,实际上是建立一个通用函数,其函数类型和形参类型不具体制定,用一个虚拟的类型来代表。这个通用函数就成为函数模板。凡是函数体相同的函数都可以用这个模板代替,不必定义多个函数,只需在模板中定义一次即可。在调用函数时系统会根据实参的类型来取代模板中的虚拟类型,从而实现不同函数的功能。
>c++提供两种模板机制:函数模板和类模板
>类属 - 类型参数化,又称参数模板
总结:
>模板把函数或类要处理的数据类型参数化,表现为参数的多态性,成为类属。
>模板用于表达逻辑结构相同,但具体数据元素类型不同的数据对象的通用行为。
1、函数模板基本使用
用模板是为了实现泛型,可以减轻编程的工作量,增强函数的重用性。
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 //交换int类型两个数字 6 void mySwapInt(int& a, int& b) 7 { 8 int temp = a; 9 a = b; 10 b = temp; 11 } 12 //交换double类型两个数字 13 void mySwapDouble(double& a, double& b) 14 { 15 double temp = a; 16 a = b; 17 b = temp; 18 } 19 20 //类型、逻辑又非常相似 21 //类型参数化,泛型编程——模板技术 22 template<class T>//告诉编译器,下面如果出现T不要报错,T是一个通用的类型 23 void mySwap(T& a, T& b) 24 { 25 T tmp = a; 26 a = b; 27 b = tmp; 28 } 29 30 //template<typename T> //等价于 template<class T> 31 template<typename T> 32 void mySwap2() 33 {} 34 35 36 void test01() 37 { 38 int a = 10; 39 int b = 20; 40 char c1 = 'c'; 41 42 //mySwapInt(a, b); 43 //1.自动类型推导,必须有参数类型才可以推导 44 mySwap(a, b); 45 mySwap(a, c1);//推导不出来T,所以不能运行 46 47 //2.显式指定类型 48 mySwap<int>(a, b); 49 50 //模板必须要指定出T才可以使用 51 mySwap2<double>();//mySwap2();报错 52 53 cout << "a = " << a << endl; 54 cout << "b = " << b << endl; 55 56 double a2 = 10; 57 double b2 = 20; 58 //mySwapInt(a2, b2); 59 mySwap(a2, b2); 60 61 62 } 63 64 int main() 65 { 66 test01(); 67 68 system("pause"); 69 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 70 }
2、课堂练习-实现通用的数组排序
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 //对char和int数组进行排序,排序规则:从大到小,利用选择排序 6 template<class T> 7 void mySwap(T& a, T& b) 8 { 9 T tmp = a; 10 a = b; 11 b = tmp; 12 } 13 14 15 template<class T> 16 void mySort(T arr[], int len) 17 { 18 for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) 19 { 20 int max = i; 21 for(int j = i + 1; j < len; j++) 22 { 23 if(arr[max] < arr[j]) 24 { 25 //交换下标 26 max = j; 27 } 28 } 29 if(max != i) 30 { 31 //交换数据 32 mySwap(arr[max], arr[i]); 33 } 34 35 } 36 } 37 //输出数组元素的模板 38 template<class T> 39 void printArray(T arr[], int len) 40 { 41 for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) 42 { 43 cout << arr[i] << " "; 44 } 45 cout << endl; 46 } 47 48 void test01() 49 { 50 char charArr[] = "helloworld"; 51 int num = sizeof(charArr) / sizeof(char); 52 mySort(charArr, num); 53 printArray(charArr, num); 54 55 int intArr[] = {1, 4, 100, 34, 55}; 56 int num2 = sizeof(intArr) / sizeof(int);//比较通用的方式求长度 57 mySort(intArr, num2); 58 printArray(intArr, num2); 59 } 60 61 int main() 62 { 63 test01(); 64 65 system("pause"); 66 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 67 }
3、函数模板和普通函数区别
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 //1.普通函数与函数模板区别 6 template<class T> 7 T myPlus(T a, T b) 8 { 9 return a + b; 10 } 11 12 int myPlus2(int a, int b) 13 { 14 return a + b; 15 } 16 17 18 void test01() 19 { 20 int a = 10; 21 int b = 20; 22 char c = 'c'; 23 24 myPlus(a, b); 25 //myPlus(a, c);//类型推导不出来,函数模板不可以进行隐式类型转换 26 myPlus2(a, b); 27 cout << myPlus2(a, c) << endl;//10 + 99,普通函数,可以进行隐式类型转换 28 29 } 30 31 //2.普通函数和函数模板的调用规则 32 template<class T> 33 void myPrint(T a, T b) 34 { 35 cout << "模板调用的myPrint(a, b)" << endl; 36 } 37 38 template<class T> 39 void myPrint(T a, T b, T c) 40 { 41 cout << "模板调用的myPrint(a, b, c)" << endl; 42 } 43 44 void myPrint(int a, int b) 45 { 46 cout << "普通函数调用的myPrint" << endl; 47 } 48 49 void test02() 50 { 51 int a = 10; 52 int b = 20; 53 54 //(1)如果出现重载,优先使用普通函数调用,如果没有实现,那就出现错误 55 myPrint(a, b); 56 57 //(2)如果想强制调用模板,那么可以使用空参数列表 58 myPrint<>(a, b); 59 60 //(3)函数模板可以发生重载 61 int c = 30; 62 myPrint(a, b, c); 63 64 //(4)如果函数模板可以产生更好的匹配,那么优先调用函数模板 65 char c2 = 'c'; 66 char d = 'd'; 67 68 myPrint(c2, d); 69 } 70 71 int main() 72 { 73 test01(); 74 75 system("pause"); 76 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 77 }
4、函数模板和普通函数在一起调用规则
1)c++编译器优先考虑普通函数
2)可以通过空模板实参列表的语法限定编译器只能通过模板匹配
3)函数模板可以像普通函数那样可以被重载
4)如果函数模板可以产生一个更好的匹配,那么选择模板
5、模板机制
思考:为什么函数模板可以和普通函数放在一起?c++编译器是如何实现函数模板机制的?
hello.cpp程序是高级c语言程序,这种程序易于被人读懂。为了在系统上运行hello.c程序,每一条c语句都必须转化为低级的机器指令。然后将这些机器指令打包成可执行目标文件格式,并以二进制形式存储于磁盘中。
预处理(Pre-processing) -> 编译(Compiling) ->汇编(Assembling) -> 链接(Linking)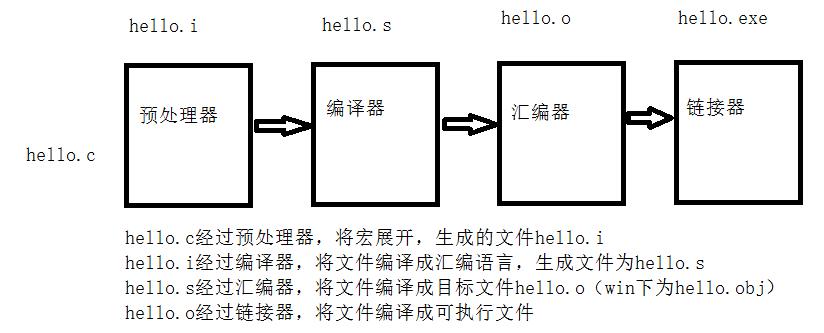
函数模板机制结论:
1)编译器并不是把函数模板处理成能够处理任何类型的函数
2)函数模板通过具体类型产生不同的函数
3)编译器会对函数模板进行两次编译,在声明的地方对模板代码本身进行编译,在调用的地方对参数替换后的代码进行编译。
6、函数模板的局限性
模板不能解决所有的类型,如果出现不能解决的类型,可以通过第三地具体化来解决问题。
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Person 7 { 8 public: 9 Person(string name, int age) 10 { 11 this->m_Name = name; 12 this->m_Age = age; 13 } 14 15 16 string m_Name; 17 int m_Age; 18 }; 19 20 template<class T> 21 bool myCompare(T& a, T& b) 22 { 23 if(a == b) 24 { 25 return true; 26 } 27 return false; 28 } 29 30 //通过(第三代)具体化自定义数据类型,解决上述问题 31 //如果具体化能够优先匹配,那么就选择具体化 32 //语法:template<> 返回值 函数名<具体类型>(参数) 33 template<> bool myCompare<Person>(Person& a, Person& b) 34 { 35 if(a.m_Age == b.m_Age) 36 { 37 return true; 38 } 39 return false; 40 } 41 42 void test01() 43 { 44 int a = 10; 45 int b = 20; 46 47 int ret = myCompare(a, b); 48 49 cout << "ret = " << ret << endl; 50 51 Person p1("Tom", 10); 52 Person p2("Jerry", 10); 53 54 int ret2 = myCompare(p1, p2); 55 56 cout << "ret2 = " << ret << endl; 57 } 58 59 int main() 60 { 61 test01(); 62 63 system("pause"); 64 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 65 }
7、类模板的基本使用
与函数模板区别,可以有默认类型参数; 函数模板可以进行自动类型推导,而类模板不可以
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //类模板 7 template<class NameType, class AgeType = int>//类模板可以有默认类型 8 class Person 9 { 10 public: 11 Person(NameType name, AgeType age) 12 { 13 this->m_Name = name; 14 this->m_Age = age; 15 } 16 17 void showPerson() 18 { 19 cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name << "年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl; 20 } 21 22 NameType m_Name; 23 AgeType m_Age; 24 }; 25 26 void test01() 27 { 28 //自动类型推导,类模板,不支持 29 //Person p("孙悟空", 100); 30 31 //显示指定类型 32 Person<string, int> p("孙悟空", 100); 33 p.showPerson(); 34 } 35 36 int main() 37 { 38 test01(); 39 40 system("pause"); 41 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 42 }
8、成员函数创建时机
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //类模板 7 template<class NameType, class AgeType>//类模板可以有默认类型 8 class Person 9 { 10 public: 11 Person(NameType name, AgeType age) 12 { 13 this->m_Name = name; 14 this->m_Age = age; 15 } 16 17 void showPerson() 18 { 19 cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name << "年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl; 20 } 21 22 NameType m_Name; 23 AgeType m_Age; 24 }; 25 26 void test01() 27 { 28 //自动类型推导,类模板,不支持 29 //Person p("孙悟空", 100); 30 31 //显示指定类型 32 Person<string, int> p("孙悟空", 100); 33 p.showPerson(); 34 } 35 36 class Person1 37 { 38 public: 39 void showPerson1() 40 { 41 cout << "Person1的调用" << endl; 42 } 43 }; 44 45 class Person2 46 { 47 public: 48 void showPerson1() 49 { 50 cout << "Person2的调用" << endl; 51 } 52 }; 53 54 template<class T> 55 class myClass 56 { 57 public: 58 T obj; 59 void func1() 60 { 61 obj.showPerson1(); 62 } 63 void func2() 64 { 65 obj.showPerson2(); 66 } 67 68 }; 69 70 //成员函数一开始不会创建出来,而是在运行时才去创建 71 72 void test02() 73 { 74 myClass<Person1> m; 75 76 m.func1(); 77 78 //m.func2(; 79 } 80 81 82 int main() 83 { 84 test01(); 85 86 system("pause"); 87 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 88 }
9、类模板做函数的参数
三种方式?
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //类模板 7 template<class NameType, class AgeType = int>//类模板可以有默认类型 8 class Person 9 { 10 public: 11 Person(NameType name, AgeType age) 12 { 13 this->m_Name = name; 14 this->m_Age = age; 15 } 16 17 void showPerson() 18 { 19 cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name << "年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl; 20 } 21 22 NameType m_Name; 23 AgeType m_Age; 24 }; 25 26 //1.指定传入类型 27 void doWork(Person<string, int>& p) 28 { 29 p.showPerson(); 30 } 31 32 void test01() 33 { 34 Person<string, int> p("MT", 10); 35 doWork(p); 36 } 37 38 //2.参数模板化 39 template<class T1, class T2> 40 void doWork2(Person<T1, T2>& p) 41 { 42 //如何查看类型? 43 cout << typeid(T1).name() << endl; 44 cout << typeid(T2).name() << endl; 45 p.showPerson(); 46 } 47 48 void test02() 49 { 50 Person<string, int> p("呆贼", 18); 51 doWork2(p); 52 } 53 54 //3.整体模板化 55 template<class T> 56 void doWork3(T& p) 57 { 58 cout << typeid(T).name() << endl; 59 p.showPerson(); 60 } 61 62 void test03() 63 { 64 Person<string, int> p("劣人", 18); 65 doWork3(p); 66 } 67 68 int main() 69 { 70 test01(); 71 72 system("pause"); 73 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 74 }
10、类模板碰到继承的问题以及解决
基类如果是模板类,必须让子类告诉编译器 基类中的T到底是什么类型;如果不告诉,那么无法分配内存,编译不过。
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 template<class T> 6 class Base 7 { 8 public: 9 T m_A;//double类型 10 11 }; 12 13 //child继承于base,必须告诉base中T的类型,否则T无法分配内存 14 class Child:public Base<int> 15 { 16 17 18 }; 19 20 //child2也是模板类 21 template<class T1, class T2> 22 class Child2:public Base<T2> 23 { 24 public: 25 Child2() 26 { 27 cout << typeid(T1).name() << endl; 28 cout << typeid(T2).name() << endl; 29 } 30 31 public: 32 T1 m_B;//int类型 33 }; 34 35 void test01() 36 { 37 Child2<int, double>child;//由用户指定类型 38 39 } 40 41 int main() 42 { 43 test01(); 44 45 system("pause"); 46 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 47 }
11、类模板的类外实现成员函数
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 template<class T1, class T2> 7 class Person 8 { 9 public: 10 Person(T1 name, T2 age); 11 /*{ 12 this->m_Name = name; 13 this->m_Age = age; 14 } 15 */ 16 17 void showPerson(); 18 /*{ 19 cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name << "年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl; 20 } 21 */ 22 23 T1 m_Name; 24 T2 m_Age; 25 }; 26 27 //类外实现成员函数 28 template<class T1, class T2> 29 Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1 name, T2 age) 30 { 31 this->m_Name = name; 32 this->m_Age = age; 33 } 34 35 template<class T1, class T2> 36 void Person<T1, T2>::showPerson() 37 { 38 cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name << "年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl; 39 } 40 41 void test01() 42 { 43 Person<string, int>p1("Mt", 100); 44 p1.showPerson(); 45 } 46 47 int main() 48 { 49 test01(); 50 51 system("pause"); 52 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 53 }
12、类模板的分文件编写问题以及解决
解决方案 保护 .cpp文件 (不推荐);不要进行分文件编写,写到同一个文件中,进行声明和实现,后缀名改为.hpp; 约定俗成的。
类模板的分文件编写.cpp
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 #include"Person.hpp" 6 7 //建议模板不要做分文件编写,写到一个类中即可,类内进行声明和实现,最后把后缀名改为.hpp(约定俗成) 8 9 void test01() 10 { 11 Person<string, int>("猪八戒", 10); 12 p.showPerson(); 13 14 } 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 test01(); 19 20 system("pause"); 21 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 22 }
Person.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 template<class T1, class T2> 7 class Person 8 { 9 public: 10 Person(T1 name, T2 age); 11 12 void showPerson(); 13 14 T1 m_Name; 15 T2 m_Age; 16 }; 17 18 template<class T1, class T2> 19 Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1 name, T2 age) 20 { 21 this->m_Name = name; 22 this->m_Age = age; 23 } 24 25 template<class T1, class T2> 26 void Person<T1, T2>::showPerson() 27 { 28 cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name << "年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl; 29 }
Person.h(不用)
1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 template<class T1, class T2> 7 class Person 8 { 9 public: 10 Person(T1 name, T2 age); 11 12 void showPerson(); 13 14 T1 m_Name; 15 T2 m_Age; 16 };
Person.cpp(不用)
1 #include"Person.h" 2 3 4 template<class T1, class T2> 5 Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1 name, T2 age) 6 { 7 this->m_Name = name; 8 this->m_Age = age; 9 } 10 11 template<class T1, class T2> 12 void Person<T1, T2>::showPerson() 13 { 14 cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name << "年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl; 15 }
13、友元碰到类模板——友元函数类内实现
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 template<class T1, class T2> 7 class Person 8 { 9 //友元函数类内实现 10 friend void printPerson(Person<T1, T2>& p) 11 { 12 cout << "姓名:" << p.m_Name << "年龄:" << p.m_Age << endl; 13 14 } 15 16 17 public: 18 Person(T1 name, T2 age) 19 { 20 this->m_Name = name; 21 this->m_Age = age; 22 } 23 24 private: 25 T1 m_Name; 26 T2 m_Age; 27 }; 28 29 void test01() 30 { 31 Person<string, int> p("Tom", 10); 32 printPerson(p); 33 } 34 35 int main() 36 { 37 test01(); 38 39 system("pause"); 40 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 41 }
14、友元碰到类模板——友元函数类外实现
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //让编译器提前看到printPerson声明 7 //让编译器看到Person类声明 8 template<class T1, class T2>class Person; 9 template<class T1, class T2>void printPerson(Person<T1, T2>& p); 10 11 template<class T1, class T2> 12 class Person 13 { 14 //友元函数类内实现,利用空参数列表<>,告诉编译器,模板函数的声明 15 friend void printPerson<>(Person<T1, T2>& p);//普通函数的声明 16 /*{ 17 cout << "姓名:" << p.m_Name << "年龄:" << p.m_Age << endl; 18 19 } 20 */ 21 22 public: 23 Person(T1 name, T2 age) 24 { 25 this->m_Name = name; 26 this->m_Age = age; 27 } 28 29 private: 30 T1 m_Name; 31 T2 m_Age; 32 }; 33 34 //类外实现 35 template<class T1, class T2> 36 void printPerson(Person<T1, T2>& p) 37 { 38 cout << "姓名:" << p.m_Name << "年龄:" << p.m_Age << endl; 39 40 } 41 42 void test01() 43 { 44 Person<string, int> p("Tom", 10); 45 printPerson(p); 46 } 47 48 int main() 49 { 50 test01(); 51 52 system("pause"); 53 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 54 }
15、类模板的应用——数组类的封装
类模板的应用—数组类封装.cpp
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 #include"MyArray.hpp" 6 7 //输出int类型数组 8 void printIntArray(MyArray arr) 9 { 10 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 11 { 12 cout << arr[i] << " " << endl; 13 } 14 } 15 16 17 18 class Person 19 { 20 public: 21 Person(){} 22 23 Person(string name, int age) 24 { 25 this->m_Name = name; 26 this->m_Age = age; 27 } 28 29 string m_Name; 30 int m_Age; 31 32 }; 33 34 //输出Person类型数组 35 void printPersonArray(MyArray<Person>& array) 36 { 37 for(int i = 0; i < array.getSize(); i++) 38 { 39 cout << "姓名:" << array[i].m_Name << "年龄:" << array[i].m_Age << endl; 40 } 41 } 42 43 int main() 44 { 45 MyArray<int>arr(10); 46 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 47 { 48 arr.push_Back(i + 100); 49 } 50 51 printIntArray(arr); 52 53 Person p1("MT", 10); 54 Person p2("呆贼", 12); 55 Person p3("傻慢", 14); 56 Person p4("劣人", 15); 57 58 MyArray<Person>arr2(10); 59 arr2.push_Back(p1); 60 arr2.push_Back(p2); 61 arr2.push_Back(p3); 62 arr2.push_Back(p4); 63 64 printPersonArray(arr2); 65 66 system("pause"); 67 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 68 }
MyArray.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 template<class T> 6 class MyArray 7 { 8 public: 9 //构造 10 explicit MyArray(int capacity)//防止隐式类型转换,防止MyArray arr = 10;这样的写法,加上explicit 11 { 12 this->m_Capacity = capacity; 13 this->m_Size = 0; 14 this->pAddress = new T[this->m_Capacity]; 15 } 16 17 MyArray(const MyArray& array) 18 { 19 this->m_Capacity = array.m_Capacity; 20 this->m_Size = array.m_Size; 21 this->pAddress = new T[this->m_Capacity]; 22 for(int i = 0; i < m_Size; i++) 23 { 24 this->pAddress[i] = array[i]; 25 } 26 } 27 28 ~MyArray() 29 { 30 if(this->pAddress != NULL) 31 { 32 delete[] this->pAddress; 33 this->pAddress = NULL; 34 } 35 36 } 37 38 //赋值操作符重载 39 MyArray& operator=(MyArray& array) 40 { 41 //先判断原始数据,有就清空 42 if(this->pAddress != NULL) 43 { 44 delete[] this->pAddress; 45 this->pAddress = NULL; 46 } 47 48 this->m_Capacity = array.m_Capacity; 49 this->m_Size = array.m_Size; 50 this->pAddress = new T[this->m_Capacity]; 51 for(int i = 0; i < m_Size; i++) 52 { 53 this->pAddress[i] = array[i]; 54 } 55 } 56 57 //[]重载 58 //MyArray arr(10) 59 //arr[0] = 100; 60 T& operator[](int index) 61 { 62 return this->pAddress[index]; 63 } 64 65 //尾插法 66 void push_Back(T val) 67 { 68 this->pAddress[this->m_Size] = val; 69 this->m_Size++; 70 } 71 72 //获取大小 73 int getSize() 74 { 75 return m_Size; 76 } 77 78 //获取容量 79 int getCapacity() 80 { 81 return this->m_Capacity; 82 } 83 84 private: 85 T* pAddress;//指向堆区指针 86 int m_Capacity;//容量 87 int m_Size; 88 };
二、总结
1 函数模板基本使用
1.1 template < class / typename T> 告诉编译器紧跟的代码里出现T不要报错
1.2 mySwap( T &a T &b ) 类型也需要传入 ,类型参数化
1.3 myswap(a,b) 自动类型推导 按照a b的类型 来替换T
1.4 myswap<int>(a,b) 显示指定类型
2 函数模板与普通函数的区别以及调用规则
2.1 区别 普通函数可以进行隐式类型转换 模板不可以
2.2 调用规则
2.2.1 c++编译器优先考虑普通函数
2.2.2 可以通过空模板实参列表的语法限定编译器只能通过模板匹配
2.2.3 函数模板可以像普通函数那样可以被重载
2.2.4 如果函数模板可以产生一个更好的匹配,那么选择模板
2.3 模板的机制
2.3.1 模板并不是万能的,不能通用所有的数据类型
2.3.2 模板不能直接调用,生成后的模板函数才可以调用
2.3.3 二次编译,第一次对模板进行编译,第二次对替换T类型后的代码进行二次编译
3 模板局限性
3.1 模板不能解决所有的类型
3.2 如果出现不能解决的类型,可以通过第三地具体化来解决问题
3.3 template<> 返回值 函数名<具体类型>(参数)
4 类模板
4.1 写法template <T…> 紧跟着是类
4.2 与函数模板区别,可以有默认类型参数
4.3 函数模板可以进行自动类型推导,而类模板不可以
4.4 类模板中的成员函数 一开始不会创建出来,而是在运行时才去创建
5 类模板做函数的参数
5.1 三种方式
5.1.1 显示指定类型
5.1.2 参数模板化
5.1.3 整体模板化
5.2 查看类型名称
5.2.1 cout << typeid(T).name() << endl;
6 当类模板碰到继承
6.1 基类如果是模板类,必须让子类告诉编译器 基类中的T到底是什么类型
6.2 如果不告诉,那么无法分配内存,编译不过
6.3 利用参数列表class Child :public Base<int>
7 类模板的类外实现成员函数
template <class T1, class T2>
7.1 Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1 name, T2 age)
8 类模板的分文件编写问题以及解决
8.1 .h .cpp分别写声明和实现
8.2 但是由于 类模板的成员函数运行阶段才去创建,导致包含.h头文件,不会创建函数的实现,无法解析外部命令
8.3 解决方案 保护 .cpp文件 (不推荐)
8.4 不要进行分文件编写,写到同一个文件中,进行声明和实现,后缀名改为.hpp
8.5 约定俗成的
9 类模板碰到友元函数
9.1 友元函数类内实现
9.2 friend void printPerson( Person<T1 ,T2> & p )
9.3 友元函数类外实现
9.4 friend void printPerson<>(Person<T1, T2> & p); //没有<>普通函数 声明 加上 <>模板函数声明
9.5 让编译器看到 函数 并且看到这个Person类型
10 类模板的应用——数组类的封装
在学习c++基础总结了笔记,并分享出来。有问题请及时联系博主:Alliswell_WP,转载请注明出处。