张季跃 201771010139《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十八周学习总结
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 综合掌握java基本程序结构;
(2) 综合掌握java面向对象程序设计特点;
(3) 综合掌握java GUI 程序设计结构;
(4) 综合掌握java多线程编程模型;
(5) 综合编程练习。
2、实验内容和步骤
任务1:填写课程课后调查问卷,网址:https://www.wjx.cn/jq/33108969.aspx。
任务2:综合编程练习
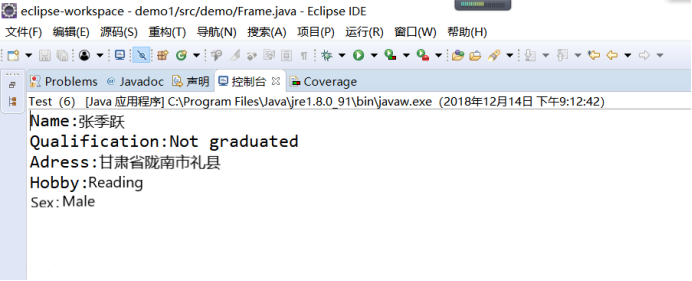
练习1:设计一个用户信息采集程序,要求如下:
(1) 用户信息输入界面如下图所示:
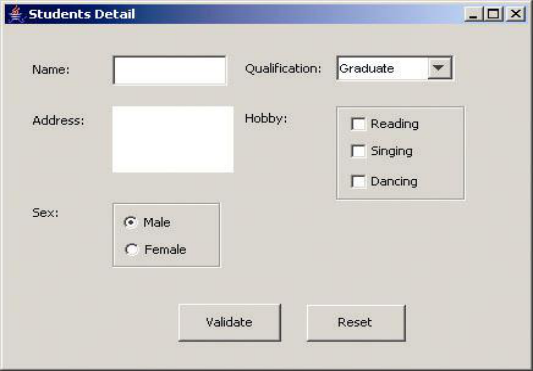
(1)用户点击提交按钮时,用户输入信息显示控制台界面;
(2)用户点击重置按钮后,清空用户已输入信息;
(3)点击窗口关闭,程序退出。
程序代码:
package 测试程序5; import java.awt.EventQueue; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class Mian { public static void main(String[] args) { EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { demo page = new demo(); }); } }
package 测试程序5; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.Toolkit; import java.awt.Window; public class WinCenter { public static void center(Window win){ Toolkit tkit = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); Dimension sSize = tkit.getScreenSize(); Dimension wSize = win.getSize(); if(wSize.height > sSize.height){ wSize.height = sSize.height; } if(wSize.width > sSize.width) { wSize.width = sSize.width; } win.setLocation((sSize.width - wSize.width)/ 2, (sSize.height - wSize.height)/ 2); } }
package 测试程序5; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import javax.swing.*; import javax.swing.border.*; public class demo extends JFrame { public demo() { JPanel panel1 = new JPanel(); panel1.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 45)); panel1.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4)); JLabel label1 = new JLabel("Name:"); JTextField j1 = new JTextField(""); JLabel label2 = new JLabel("Qualification:"); JComboBox<Object> j2 = new JComboBox<>(); j2.addItem("Graduate"); j2.addItem("Not Graduate"); panel1.add(label1); panel1.add(j1); panel1.add(label2); panel1.add(j2); JPanel panel2 = new JPanel(); panel2.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 50)); panel2.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 4)); JLabel label3 = new JLabel("Address:"); JTextArea j3 = new JTextArea(); JLabel label4 = new JLabel("Hobby:"); JPanel p = new JPanel(); p.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 1)); p.setBorder(BorderFactory.createLineBorder(null)); JCheckBox c1 = new JCheckBox("Reading"); JCheckBox c2 = new JCheckBox("Singing"); JCheckBox c3 = new JCheckBox("Dancing"); p.add(c1); p.add(c2); p.add(c3); panel2.add(label3); panel2.add(j3); panel2.add(label4); panel2.add(p); JPanel panel3 = new JPanel(); panel3.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150)); FlowLayout flowLayout1 = new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT, 20, 40); panel3.setLayout(flowLayout1); JLabel label5 = new JLabel("Sex:"); JPanel p1 = new JPanel(); p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1)); p1.setBorder(BorderFactory.createLineBorder(null)); ButtonGroup bu = new ButtonGroup(); JRadioButton jr1 = new JRadioButton("Male"); JRadioButton jr2 = new JRadioButton("Female"); bu.add(jr1); bu.add(jr2); p1.add(jr1); p1.add(jr2); panel3.add(label5); panel3.add(p1); add(panel1); add(panel2); add(panel3); JPanel panel4 = new JPanel(); panel4.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(700, 150)); JButton b1 = new JButton("Validate"); panel4.add(b1); JButton b2 = new JButton("Reset"); panel4.add(b2); add(panel4); FlowLayout flowLayout = new FlowLayout(); this.setLayout(flowLayout); this.setTitle("Students Detail"); this.setBounds(200, 200, 800, 400); this.setVisible(true); this.setDefaultCloseOperation(DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE); b1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 String xueli = j2.getSelectedItem().toString(); System.out.println("Name:" + j1.getText()); System.out.println("Qualification:" + xueli); String hobbystring = "Hobby:"; if (c1.isSelected()) { hobbystring += "Reading"; } if (c2.isSelected()) { hobbystring += "Singing"; } if (c3.isSelected()) { hobbystring += "Dancing"; } System.out.println("Address:" + j3.getText()); if (jr1.isSelected()) { System.out.println("Sex:Male"); } if (jr2.isSelected()) { System.out.println("Sex:Female"); } System.out.println(hobbystring); } }); b2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { // TODO 自动生成的方法存根 j1.setText(null); j3.setText(null); j2.setSelectedIndex(0); c1.setSelected(false); c2.setSelected(false); c3.setSelected(false); bu.clearSelection(); } }); } public static void main(String args[]) { new demo(); } }
运行结果:
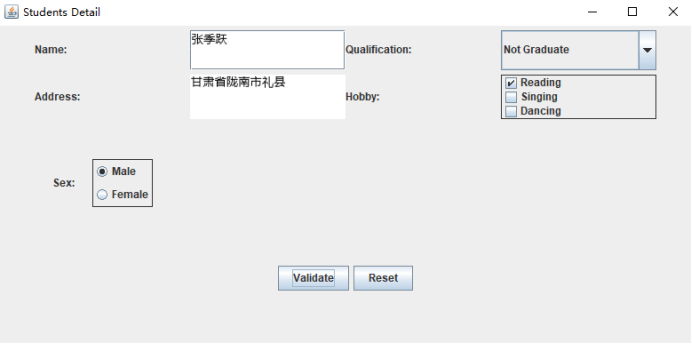
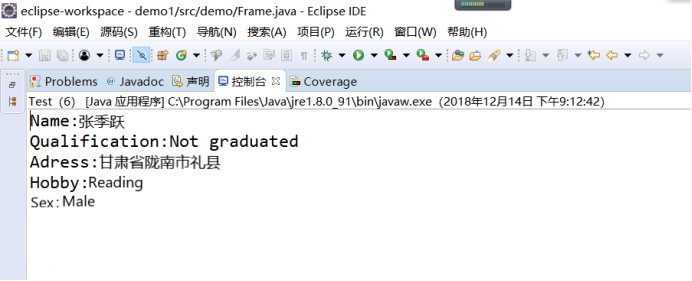
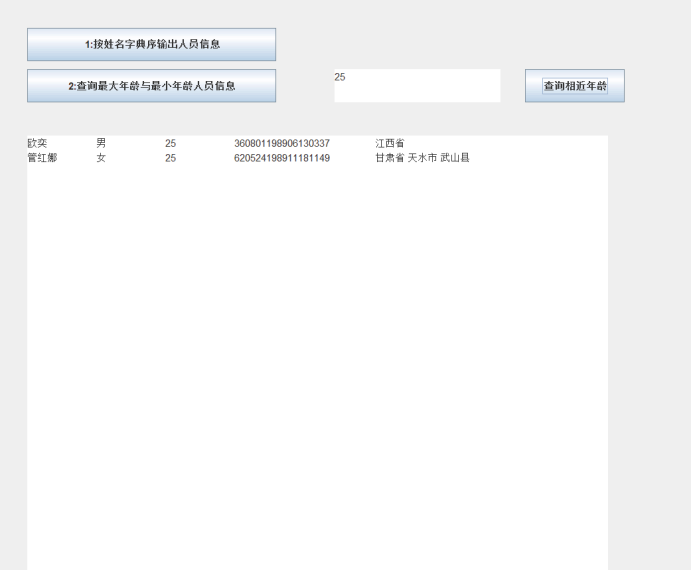
练习2:采用GUI界面设计以下程序:
编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中;
按姓名字典序输出人员信息;
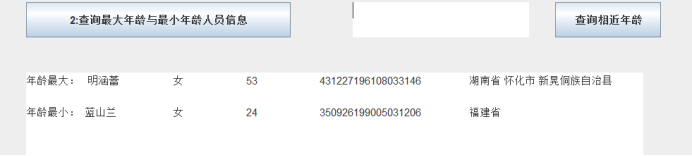
查询最大年龄的人员信息;
查询最小年龄人员信息;
输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;
查询人员中是否有你的同乡。
输入身份证信息,查询所提供身份证号的人员信息,要求输入一个身份证数字时,查询界面就显示满足查询条件的查询结果,且随着输入的数字的增多,查询匹配的范围逐渐缩小。
程序代码:
package IDcard; import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.*; import java.util.Timer; import javax.swing.*; public class Main1 extends JFrame { private static ArrayList<Person> Personlist; Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); File file = new File("C:\Users\张季跃\Desktop\第十周实验报告\身份证号.txt"); private JPanel Panel; private JLabel JLabel1; private JButton Button,Button2,Button3; private JTextArea text,text1,text2,text3; boolean tru=true; public Main1() { Panel = new JPanel();Panel.setLayout(null); Button = new JButton("1:按姓名字典序输出人员信息"); Button2 = new JButton("2:查询最大年龄与最小年龄人员信息"); Button3 = new JButton("查询相近年龄"); JLabel1 = new JLabel("输入身份证号或者地址查询"); JLabel1.setBounds(900, 50, 400, 30); text=new JTextArea(30,80);text.setBounds(50, 180, 700, 700); text1=new JTextArea(1,30);text1.setBounds(900, 80, 400, 30); text2=new JTextArea(30,80);text2.setBounds(900,180,700, 700); text3=new JTextArea(30,80);text3.setBounds(420,100,200,40); Button.addActionListener(new Action());Button.setBounds(50,50,300,40); Button2.addActionListener(new Action1());Button2.setBounds(50,100,300,40); Button3.addActionListener(new Action2());Button3.setBounds(650,100,120,40); Panel.add(JLabel1); Panel.add(Button); Panel.add(Button2); Panel.add(Button3); Panel.add(text); Panel.add(text2); Panel.add(text1); Panel.add(text3); add(Panel); Timer timer = new Timer(); TimerTask timeTask=new TimerTask() { @Override public void run() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub text2.setText(null); String place=text1.getText().toString().trim(); for (int i = 0; i <Personlist.size(); i++) { String Str=(String)Personlist.get(i).getbirthplace(); if(Str.contains(place)&&!place.equals("")) { text2.append(Personlist.get(i).toString()); } } for (int i = 0; i <Personlist.size(); i++) { String Str=(String)Personlist.get(i).getID(); if(Str.contains(place)&&!place.equals("")) { text2.append(Personlist.get(i).toString()); } } } };timer.schedule(timeTask, 0,100); Personlist = new ArrayList<>(); try { FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis)); String temp = null; while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" "); String name = linescanner.next(); String ID = linescanner.next(); String sex = linescanner.next(); String age = linescanner.next(); String place =linescanner.nextLine(); Person Person = new Person(); Person.setname(name); Person.setID(ID); Person.setsex(sex); int a = Integer.parseInt(age); Person.setage(a); Person.setbirthplace(place); Personlist.add(Person); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { System.out.println("查无此人"); e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { System.out.println("读取出错"); e.printStackTrace(); } } private class Action implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { text.setText(null); Collections.sort(Personlist); text.append(Personlist.toString()); } } private class Action1 implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { text.setText(null); int max=0,min=100;int j,k1 = 0,k2=0; for(int i=1;i<Personlist.size();i++) { j=Personlist.get(i).getage(); if(j>max) { max=j; k1=i; } if(j<min) { min=j; k2=i; } } text.append("年龄最大: "+Personlist.get(k1)+" "+"年龄最小: "+Personlist.get(k2)); } } private class Action2 implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { text.setText(null); int a = Integer.parseInt(text3.getText().toString().trim()); int d_value=a-Personlist.get(agenear(a)).getage(); for (int i = 0; i < Personlist.size(); i++) { int p=Personlist.get(i).getage()-a; if(p==d_value||-p==d_value) text.append(Personlist.get(i).toString()); } } } public static int agenear(int age) { int j=0,min=53,d_value=0,k=0; for (int i = 0; i < Personlist.size(); i++) { d_value=Personlist.get(i).getage()-age; if(d_value<0) d_value=-d_value; if (d_value<min) { min=d_value; k=i; } } return k; } }
package IDcard; public class Person implements Comparable<Person> { private String name; private String ID; private int age; private String sex; private String birthplace; public String getname() { return name; } public void setname(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getID() { return ID; } public void setID(String ID) { this.ID= ID; } public int getage() { return age; } public void setage(int age) { this.age= age; } public String getsex() { return sex; } public void setsex(String sex) { this.sex= sex; } public String getbirthplace() { return birthplace; } public void setbirthplace(String birthplace) { this.birthplace= birthplace; } public int compareTo(Person o) { return this.name.compareTo(o.getname()); } public String toString() { return name+" "+sex+" "+age+" "+ID+" "+birthplace+" "; } }
package IDcard; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.EventQueue; import java.awt.Toolkit; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class Out { public static void main (String args[]) { Toolkit t=Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); Dimension s=t.getScreenSize(); EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new Main1(); frame.setBounds(0, 0,(int)s.getWidth(),(int)s.getHeight()); frame.setTitle("第四组"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
运行结果:

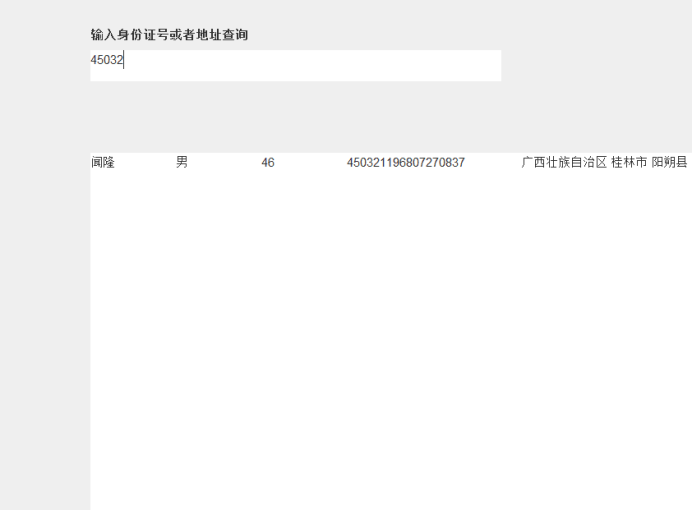
练习3:采用GUI界面设计以下程序
编写一个计算器类,可以完成加、减、乘、除的操作
利用计算机类,设计一个小学生100以内数的四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt。
程序代码:
package test; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.EventQueue; import java.awt.Toolkit; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class New { public static void main (String args[]) { Toolkit t=Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(); Dimension s=t.getScreenSize(); EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> { JFrame frame = new Demo(); frame.setBounds(0, 0,(int)s.getWidth()/2,(int)s.getHeight()/2); frame.setTitle("第四组"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.setVisible(true); }); } }
package test; import java.awt.Font; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.Scanner; import javax.swing.*; import java.math.*; public class Demo extends JFrame { private String[] c=new String[10]; private String[] c1=new String[10]; private int[] list=new int[10]; int i=0,i1=0,sum = 0; private PrintWriter out = null; private JTextArea text,text1; private int counter; public Demo() { JPanel Panel = new JPanel(); Panel.setLayout(null); JLabel JLabel1=new JLabel(""); JLabel1.setBounds(500, 800, 400, 30); JLabel1.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); JButton Button = new JButton("生成题目"); Button.setBounds(50,150,150,50); Button.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20)); Button.addActionListener(new Action()); JButton Button2 = new JButton("确定答案"); Button2.setBounds(300,150,150,50); Button2.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20)); Button2.addActionListener(new Action1()); JButton Button3 = new JButton("读出文件"); Button3.setBounds(500,150,150,50); Button3.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20)); Button3.addActionListener(new Action2()); text=new JTextArea(30,80);text.setBounds(30, 50, 200, 50); text.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); text1=new JTextArea(30,80); text1.setBounds(270, 50, 200, 50); text1.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35)); Panel.add(text); Panel.add(text1); Panel.add(Button); Panel.add(Button2); Panel.add(Button3); Panel.add(JLabel1); add(Panel); } private class Action implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { text1.setText("0"); if(i<10) { int a = 1+(int)(Math.random() * 99); int b = 1+(int)(Math.random() * 99); int m= (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3); switch(m) { case 0: while(a<b){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } c[i]=(i+":"+a+"/"+b+"="); list[i]=Math.floorDiv(a, b); text.setText(i+":"+a+"/"+b+"="); i++; break; case 1: c[i]=(i+":"+a+"*"+b+"="); list[i]=Math.multiplyExact(a, b); text.setText(i+":"+a+"*"+b+"="); i++; break; case 2: c[i]=(i+":"+a+"+"+b+"="); list[i]=Math.addExact(a, b); text.setText(i+":"+a+"+"+b+"="); i++; break ; case 3: while(a<=b){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); } c[i]=(i+":"+a+"-"+b+"="); text.setText(i+":"+a+"-"+b+"="); list[i]=Math.subtractExact(a, b); i++; break ; } } } } private class Action1 implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { if(i<10) { text.setText(null); String daan=text1.getText().toString().trim(); int a = Integer.parseInt(daan); if(text1.getText()!="") { if(list[i1]==a) sum+=10; } c1[i1]=daan; i1++; } } } private class Action2 implements ActionListener { public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event) { try { out = new PrintWriter("text.txt"); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } for(int counter=0;counter<10;counter++) { out.println(c[counter]+c1[counter]); } out.println("成绩"+sum); out.close(); } } }
运行结果:

任务3:本学期课程已结束,请汇总《面向对象程序设计课程学习进度条》的数据,统计个人专业能力提升的数据。并从学习内容、学习方法、学习心得几个方面进行课程学习总结,也希望你对课程的不足提出建议和意见。
实验总结:
这一学期里我初次接触了Java这门特殊的编程语言,在我最初的想法里面,Java和c语言并没有太大的区别,就算有也只是在编程语法上面有不一样的地方。但在老师的讲解后我初步明白了这门语言与其它语言的不同之处和难学之处。不过虽然难,但在老师的教导和学长的帮助下我还是学到了许多知识的。说实话,刚开学发书的时候我还是有点被吓到了,这本Java教材可以说是我从小到大见到的最厚的教材了,对于能不能在一学期之内把这本书学完我是抱怀疑态度的。没想到一学期下来在老师和学长的帮助下虽然没有真正学完,但里面的东西也学了不少。在这个学习的过程中,老师和学长的帮助起到了很大的作用,不管是老师那特殊的教学方式还是学长每周晚上在QQ上的指导都很有用。
经过这一学期对Java的学习,我算是对Java这门语言有了一个初步的了解与认识,虽说不能像那些大神一样随手敲出一大堆代码搞出一个很NB的程序,但再怎么说也写过一些小程序了,虽然在这个过程中别人的帮助不可或缺,但自己写程序的经历到底是给了我不小的锻炼,相信在这一学期的学习之后,我不仅能学到现有的知识,在接下来的几个学期中这份经历也会带给我不小的帮助。