Translated by:AcerWang 原文出自:customizing-android-listview-items-with-custom-arrayadapter
背景介绍
对于现实世界中的商业移动应用来说,Android的ListView默认的界面外观不是非常有吸引力。它只是使用了内部的TextView控件,在每个ListView的行(Row)里面传递了一个简单的字符串而已。大多数应用,你会想要创建出富含图形界面和呈现给用户视觉体验良好的应用。幸运地是,ListView 是一个非常强大的控件,由于有可定制的item 布局的帮助,它可以被定制从而轻松地适应你的需求。在本文中,我将向你展示怎样创建一个定制的ListView Item(有图标,自定义的header布局)以及怎样使用定制的ArrayAdapter将他们联系起来。我也会向你展示一些性能优化的小方法来优化你的ListView控件的内存占用。下面用一个例子来展示:
图1. 天气图 图2. 布局结构图

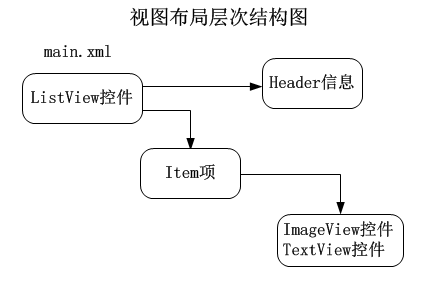
一、项目布局
在Eclipse中,创建一个新的Android项目,使用默认的Activity和main.xml布局文件。在main.xml文件中,声明一个ListView控件。
main.xml文件:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout 3 xmlns:android=http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android 4 android:orientation="vertical" 5 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 6 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 7 android:background="#FFFFFF"> 8 9 <ListView 10 android:id="@+id/listView1" 11 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 12 android:layout_height="fill_parent" /> 13 </LinearLayout>
上面的代码,使用了简单的线性布局方式,内部垂直排列。声明了一个ListView,占据整个父容器,他的android.layout_width和android.layout_width的属性都为fill_parent。ListView有一个唯一的id:listView1,在MainActivity中将用来引用ListView控件。
为了创建定制的header,先在你的工程中创建一个新的xml布局文件:listview_header_row.xml,在里面声明一个TextView控件,属性值见下面的代码。将会创建出一个白色字体,蓝色背景的header。
1 listview_header_row.xml文件: 2 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 3 <LinearLayout 4 xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 5 android:orientation="horizontal" 6 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 7 android:layout_height="fill_parent"> 8 9 <TextView android:id="@+id/txtHeader" 10 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 11 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 12 android:gravity="center_vertical" 13 android:layout_alignParentTop="true" 14 android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" 15 android:textStyle="bold" 16 android:textSize="22dp" 17 android:textColor="#FFFFFF" 18 android:padding="10dp" 19 android:text="Weather Photos" 20 android:background="#336699" /> 21 22 </LinearLayout>
为了创建定制的ListView的行样式,先在你的工程中创建另一个xml布局文件:listview_item_row.xml。Android 会将这个文件的内容传递给每个ListView的item,你将可以自由的声明任何你想添加进里面的控件。本文中,我使用了一个ImageView来显示天气图标和一个TextView来显示该条item的主题。下面是listview_item_row.xml文件的代码:
1 listview_item_row.xml文件: 2 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 3 <LinearLayout 4 xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 5 android:orientation="horizontal" 6 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 7 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 8 android:padding="10dp"> 9 10 <ImageView android:id="@+id/imgIcon" 11 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 12 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 13 android:gravity="center_vertical" 14 android:layout_alignParentTop="true" 15 android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" 16 android:layout_marginRight="15dp" 17 android:layout_marginTop="5dp" 18 android:layout_marginBottom="5dp" /> 19 20 <TextView android:id="@+id/txtTitle" 21 android:layout_width="fill_parent" 22 android:layout_height="fill_parent" 23 android:gravity="center_vertical" 24 android:layout_alignParentTop="true" 25 android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" 26 android:textStyle="bold" 27 android:textSize="22dp" 28 android:textColor="#000000" 29 android:layout_marginTop="5dp" 30 android:layout_marginBottom="5dp" /> 31 32 </LinearLayout>
本文中,我下载了一些32 X 32像素的PNG格式的图标。如果你愿意,你也可以使用你自己的图标。准备好你的图标,放到你工程的drawable-mdpi文件目录下。接下来,在工程中新建一个java类,命名为Weather.java,这个类将用于创建一个定制的ArrayAdapter来绑定对象到ListView中。下面是Weather.java文件的代码,它有两个简单的属性icon和title,一个普通的构造函数用于初始化属性。
二、项目程序开发
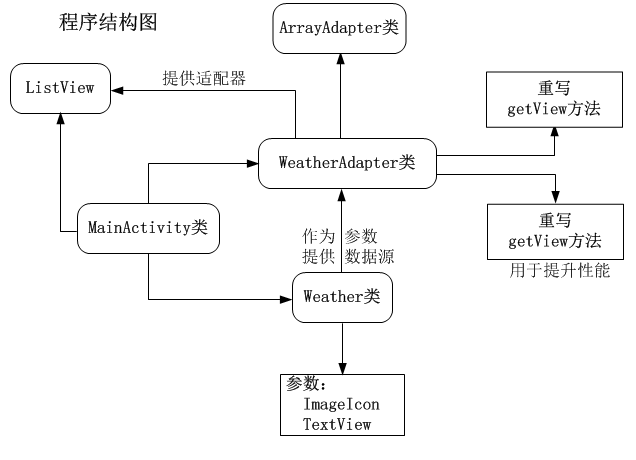
为了方便大家理解,我将程序结构流程画出来:
图3. 重要对象关系结构
1 Weather.java文件: 2 public class Weather { 3 public int icon; 4 public String title; 5 public Weather(){ 6 super(); 7 } 8 9 public Weather(int icon, String title) { 10 super(); 11 this.icon = icon; 12 this.title = title; 13 } 14 }
注意,上面listview_item_row.xml文件有两个View,对应于Weather类的两个属性。Weather类的属性值将被显示到这两个View中。为了将这两个View连接起来,你需要创建一个定制的ArrayAdapter,它继承了Android的ArrayAdapter类,并重写了getView方法。添加一个新的java类到你的工程中,命名为WeatherAdapter,具体的实现代码如下:
1 WeatherAdapter.java文件: 2 public class WeatherAdapter extends ArrayAdapter<Weather>{ 3 4 Context context; 5 int layoutResourceId; 6 Weather data[] = null; 7 8 public WeatherAdapter(Context context, int layoutResourceId, Weather[] data) { 9 super(context, layoutResourceId, data); 10 this.layoutResourceId = layoutResourceId; 11 this.context = context; 12 this.data = data; 13 } 14 15 @Override 16 public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) { 17 View row = convertView; 18 WeatherHolder holder = null; 19 20 if(row == null) 21 { 22 LayoutInflater inflater = ((Activity)context).getLayoutInflater(); 23 row = inflater.inflate(layoutResourceId, parent, false); 24 25 holder = new WeatherHolder(); 26 holder.imgIcon = (ImageView)row.findViewById(R.id.imgIcon); 27 holder.txtTitle = (TextView)row.findViewById(R.id.txtTitle); 28 29 row.setTag(holder); 30 } 31 else 32 { 33 holder = (WeatherHolder)row.getTag(); 34 } 35 36 Weather weather = data[position]; 37 holder.txtTitle.setText(weather.title); 38 holder.imgIcon.setImageResource(weather.icon); 39 40 return row; 41 } 42 43 static class WeatherHolder 44 { 45 ImageView imgIcon; 46 TextView txtTitle; 47 } 48 }
在上面的代码中,第一个比较重要的是类的构造函数有三个参数,第一个参数是Context对象(我们可以传递当前使用WeatherAdapter类的activity对象的引用,即MainActivity.this对象);第二个参数是resource的id(它是我们想用来呈现每个ListView的item的布局文件的id),在本文中我将传递我创建的listview_item_row.xml布局文件的id;第三个参数是一个Weather对象的数组,用于为Adapter适配器提供显示数据的数据源。
ArrayAdapter的getView方法被重写了。这个方法将被ListView每个 item项调用来创建视图View,它们的属性是我们设置的。getView方法也使用了一个临时的holder类(在WeatherAdapter类内部声明的内部类),这个类将被用于缓存ImageView和TextView,以便它们能够被ListView中的每行重用,这也会为我们带来巨大的性能的提升,由于我们不断地访问两个相同的views(ImageView和TextView)的属性,我们不必为每个ListView的Item查找这两个控件。上面的代码也是用了Android内置的LayoutInflator来解析xml布局文件(用于动态加载xml布局文件,以便能够查找其中的内容)。
最后一点代码是我们应用的MainActivity。里面,我们使用了所有上面声明的对象。下面是MainActivity.java文件的代码:
1 MainActivity.java文件: 2 public class MainActivity extends Activity { 3 4 private ListView listView1; 5 6 @Override 7 public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 8 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 9 setContentView(R.layout.main); 10 11 Weather weather_data[] = new Weather[] 12 { 13 new Weather(R.drawable.weather_cloudy, "Cloudy"), 14 new Weather(R.drawable.weather_showers, "Showers"), 15 new Weather(R.drawable.weather_snow, "Snow"), 16 new Weather(R.drawable.weather_storm, "Storm"), 17 new Weather(R.drawable.weather_sunny, "Sunny") 18 }; 19 20 WeatherAdapter adapter = new WeatherAdapter(this, 21 R.layout.listview_item_row, weather_data); 22 23 24 listView1 = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.listView1); 25 26 View header = (View)getLayoutInflater().inflate(R.layout.listview_header_row, null); 27 listView1.addHeaderView(header); 28 29 listView1.setAdapter(adapter); 30 }
MainActivity.java文件中有几个需要解释下的地方,以便你能更好的理解。首先,我们创建了一个Weather对象的数组,icon和title被作为参数传递给了它的构造函数;接下来,WeatherAdapter对象被创建,listview_item_row.xml文件的id和Weather对象数组被传递给了它的构造函数。再一次,我们使用了Android的LayoutInflator来解析listview_item_row.xml布局文件。通过ListView的addHeaderView方法设置ListView的header信息。最后,我们传递定制的Adapter给ListView的setAdapter方法。到现在就可以构建、运行工程了。如果一切实现正确,你会看到下面的内容。
图2. 运行效果

最近有一段时间没写东西了,真是罪过啊!翻译之中有不当之处在所难免,大家相互学习。尊重原创,尊重知识,相信分享的力量!