对于一开始的队列的存储结构混了半天脑袋
后来还是乖乖参考严奶奶里面的代码修改了一下。。终于没错了
回头要梳理这个结构体和结构体指针关系!
1、队列的链式存储
实际上是一个同时带有队头指针和队尾指针的单链表
头指针指向队头结点,尾指针指向队尾结点。
特别适于数据元素变动比较大的情形,如果程序中要使用多个队列,最好使用链式队列
有一个很大的优点是不会出现队列满和溢出的问题
2、代码实现
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdlib> 3 using namespace std; 4 #define ture 1 5 #define false 0 6 #define maxsize 50 7 #define listincreament 10 8 #define ok 1 9 #define error -3 10 #define overflow -2 11 typedef int Status; 12 typedef int ElemType; 13 /*存储类型的定义*/ 14 typedef struct LNode 15 { 16 int data; 17 struct LNode *next; 18 } Queue; 19 typedef struct ptr //链式队列的队头指针和队尾指针的定义 20 { 21 Queue *fron,*rear; 22 } LinkQueue; 23 24 /*队列的初始化*/ 25 void InitQueue(LinkQueue *Q) 26 { 27 Queue *q; 28 q=(Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue)); 29 q->next=NULL; 30 Q->fron=q; 31 Q->rear=q; 32 } 33 /*队判空*/ 34 bool isEmpty(LinkQueue *Q) 35 { 36 if(Q->fron==Q->rear)return true; 37 else return false; 38 } 39 /*入队*/ 40 int EnQueue(LinkQueue *Q,int x) 41 { 42 Queue *s=(Queue *)malloc(sizeof(Queue));//对谁处理用谁 43 s->next=NULL; 44 s->data=x; 45 Q->rear->next=s; 46 Q->rear=s; 47 return ok; 48 } 49 /*出队*/ 50 int DeQueue(LinkQueue *Q,int &x) 51 { 52 if(isEmpty(Q)) return error; 53 x=Q->fron->next->data; 54 Queue *p; 55 p=Q->fron->next; 56 Q->fron->next=p->next; 57 58 if(Q->rear==p) 59 Q->rear=Q->fron; 60 //自己打的时候忘了加上这句了 作用是:如果原队列中只有一个结点,删除了以后就变空 61 62 free(p); 63 return ok; 64 } 65 66 int main() 67 { 68 LinkQueue *Q=(LinkQueue*)malloc(sizeof(LinkQueue));//链表结点在使用前一定要为他分配存储空间!!忘了好多次了 69 InitQueue(Q); 70 int x; 71 cin>>x; 72 while(x!=0) 73 { 74 EnQueue(Q,x); 75 cin>>x; 76 } 77 cout<<endl; 78 cout<<"Now show you the data in the queue:"; 79 while(!isEmpty(Q)) 80 { 81 int ans; 82 DeQueue(Q,ans); 83 cout<<ans<<" "; 84 } 85 86 return 0; 87 }
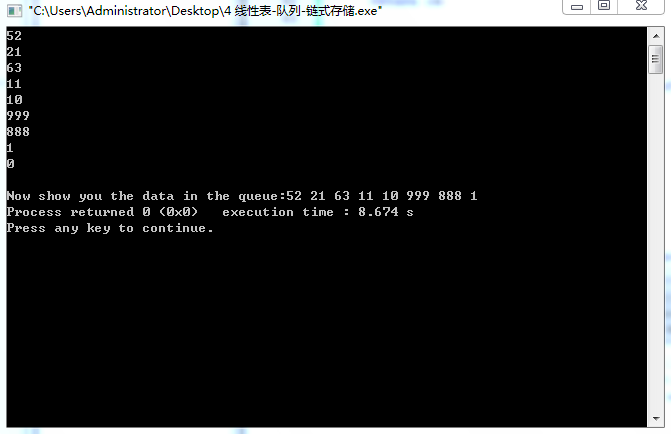
3、实现截图