线程sleep方法:
单主线程使用sleep:
Main线程差了2000毫秒。
public class MainSleepThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { try { System.out.println(this.currentThread().getName() + " begin"); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println(this.currentThread().getName() + " end"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public class ThreadRunMain { public static void main(String[] args) { testMainSleepThread(); } public static void testMainSleepThread(){ MainSleepThread mst = new MainSleepThread(); System.out.println("begin = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); mst.run(); System.out.println("end = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); } }
运行结果:
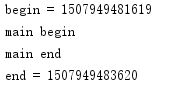
非Main线程使用sleep:
Main线开始和结束时间一样,而非主线程差了2000毫秒。
public class ThreadSleepThread extends Thread { @Override public void run() { try { System.out.println("run threadName= " + this.currentThread().getName() + " begin = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); Thread.sleep(2000); System.out.println("run threadName= " + this.currentThread().getName() + " end = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public class ThreadRunMain { public static void main(String[] args) { testThreadSleepThread(); } public static void testThreadSleepThread(){ ThreadSleepThread tst = new ThreadSleepThread(); System.out.println("begin = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); tst.start(); System.out.println("end = " + System.currentTimeMillis()); } }
运行结果:
