线程是程序的执行单元,执行路径。是程序使用CPU的最基本单位
多线程 -- 程序有多条执行路径,提高应用进程的使用率
进程中线程越多,抢到CPU执行权概率越高。线程的执行有随机性
Java程序的运行原理:
由Java命令启动JVM,JVM启动就相当于启动了一个进程,接着由该程序创建了一个主线程去调用main方法
JVM的启动是多线程的,因为垃圾回收线程也要启动,否则容易出现内存溢出。(GC线程和主线程)
Java多线程程序:
方法1:继承Thread类,并重写run()方法,创建对象,执行对象。
run()方法: Thread类中的run()用来包含那些被线程执行的代码(封装被线程执行的代码)(不单独调用run方法(直接调用是普通方法),调用start())
start()方法:首先启动了线程,然后再由JVM去调用该线程的run()方法
方法2:实现runnable接口
A:自定义类实现runnable
B:重写run()方法
C:创建MyRunnable类的对象
D:创建Thread类的对象,把C步骤的对象作为构造参数传递
解决了java单继承的局限性,适合多个相同程序代码去处理同一个资源的情况,把线程相同的代码,数据有效分离
一些内建方法:
public final String getName() //获取线程名称
public final String setName(): //设置线程名称
public static Thread currentThread(): //返回当前正在执行的线程对象
抢占式调度模型(Java):优先让优先级高的线程使用CPU
public final int getPriority(): //返回线程对象的优先级 public final void setPriority(): //设置线程优先级
优先级范围1-10,默认为5,最低为1,最高为5
线程控制:
public static void sleep(long millis) //线程休眠
public final void join(): //线程加入 (等待线程终止)
public static void yield(): //线程礼让 暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程
//让多个线程的执行更加和谐,但不能保证
public final void setDaemon(boolean on): //设置守护线程 //当正在运行的线程都是守护线程时,JVM退出,该方法必须在启动线程前调用
public void interrupt(): //中断线程,把线程的状态终止,并抛出一个InterruptException
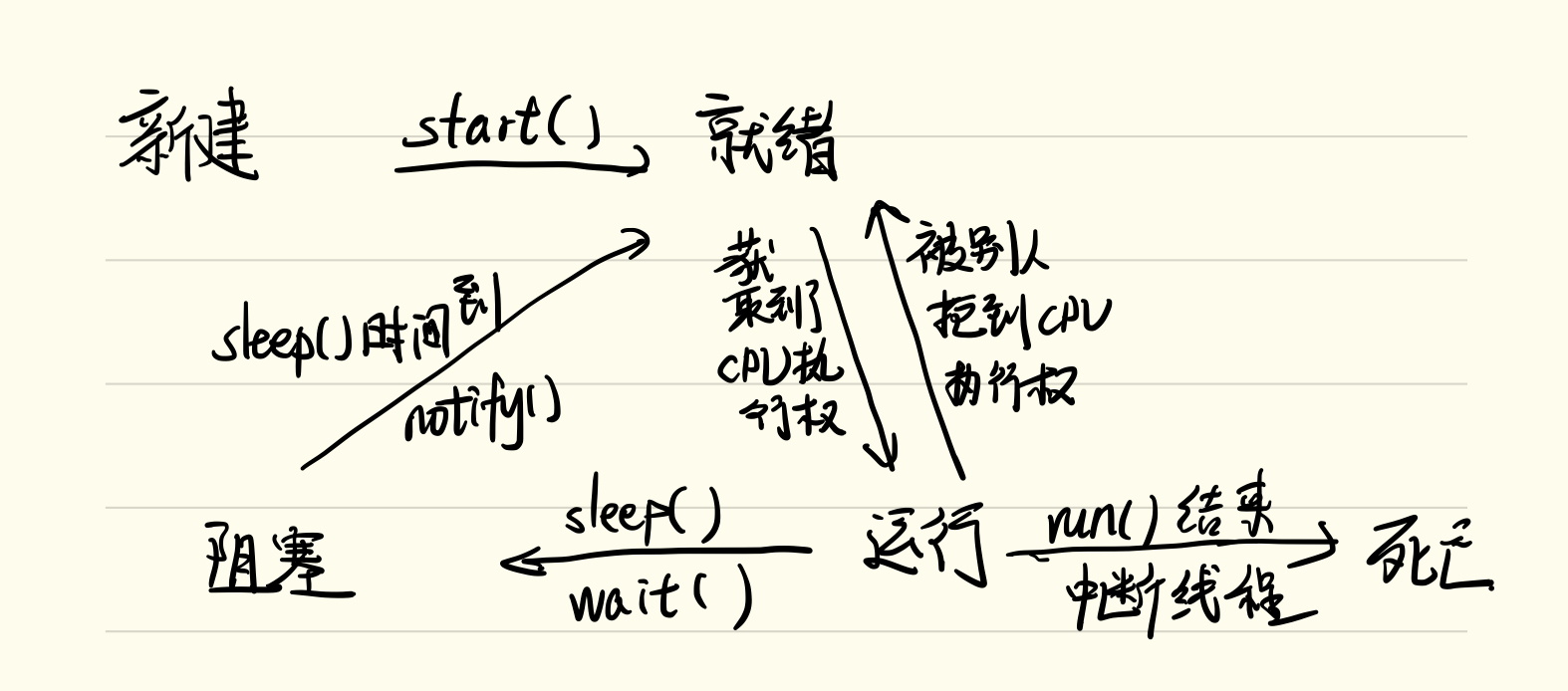
线程的生命周期:(图解)
线程同步:synchronized关键字
将多条语句操作的共享数据代码包成一个整体,让某个线程在执行的时候别人不执行
前提:多个线程; 注意:多个线程使用同一个锁对象
优点:解决了多线程的安全问题
缺点:当线程相当时,因为每个线程都会去判断同步上的锁,很耗费资源,无形中降低了程序的运行效率,容易产生死锁
使用同步代码块或者同步方法
死锁:
死锁代码举例:
1 public class MyLock { 2 // 创建两把锁对象 3 public static final Object objA = new Object(); 4 public static final Object objB = new Object(); 5 }
1 public class DeadLock extends Thread { 2 3 private boolean flag; 4 5 public DeadLock(boolean flag) { 6 this.flag = flag; 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public void run() { 11 if (flag) { 12 synchronized (MyLock.objA) { 13 System.out.println("if objA"); 14 synchronized (MyLock.objB) { 15 System.out.println("if objB"); 16 } 17 } 18 } else { 19 synchronized (MyLock.objB) { 20 System.out.println("else objB"); 21 synchronized (MyLock.objA) { 22 System.out.println("else objA"); 23 } 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 }
1 public class DieLockDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 DeadLock dl1 = new DeadLock(true); 4 DeadLock dl2 = new DeadLock(false); 5 6 dl1.start(); 7 dl2.start(); 8 } 9 }
等待唤醒机制:
Object类提供三个方法:
wait() :等待
notify():唤醒单个线程
notifyAll():唤醒所有线程
为什么不在Thread类中: 因为这些方法必须通过锁对象调用,而锁对象可以是任意锁对象,所以定义在object类中
Semaphore信号量:
信号量(Semaphore),又被称为信号灯,在多线程环境下用于协调各个线程, 以保证它们能够正确、合理的使用公共资源。信号量维护了一个许可集,我们在初始化Semaphore时需要为这个许可集传入一个数量值,该数量值代表同一时间能访问共享资源的线程数量。
线程可以通过acquire()方法获取到一个许可,然后对共享资源进行操作,注意如果许可集已分配完了,那么线程将进入等待状态,直到其他线程释放许可才有机会再获取许可,线程释放一个许可通过release()方法完成,"许可"将被归还给Semaphore。
多线程案例:
电影院卖票:电影院一共有100张票,有三个窗口卖票,模拟电影院售票:
使用同步代码块:
public class SellTicket implements Runnable { // 定义100张票 private int tickets = 100; //创建锁对象 private Object obj = new Object(); @Override public void run() { while (true) { synchronized (obj) { if (tickets > 0) { try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "正在出售第" + (tickets--) + "张票"); } } } } }
public class SellTicketDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建资源对象 SellTicket st = new SellTicket(); // 创建三个线程对象 Thread t1 = new Thread(st, "窗口1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(st, "窗口2"); Thread t3 = new Thread(st, "窗口3"); // 启动线程 t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } }
使用同步方法:
1 package lab2; 2 3 public class SellTicket implements Runnable { 4 5 // 定义100张票 6 private static int tickets = 100; 7 8 @Override 9 public void run() { 10 while (true) { 11 sellTicket(); 12 } 13 } 14 15 private synchronized void sellTicket() { 16 if (tickets > 0) { 17 try { 18 Thread.sleep(100); 19 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() 23 + "正在出售第" + (tickets--) + "张票 "); 24 } 25 } 26 }
使用锁方法:
1 import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; 2 import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; 3 4 public class SellTicket implements Runnable { 5 6 // 定义票 7 private int tickets = 100; 8 9 // 定义锁对象 10 private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 11 12 @Override 13 public void run() { 14 while (true) { 15 try { 16 // 加锁 17 lock.lock(); 18 if (tickets > 0) { 19 try { 20 Thread.sleep(100); 21 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } 24 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() 25 + "正在出售第" + (tickets--) + "张票"); 26 } 27 } finally { 28 // 释放锁 29 lock.unlock(); 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 34 }
Ornamental Garden Problem:(使用Bakery class) 花园有两个旋转门,可进可出,监控花园内的人数
volatile关键字: Specifying a variable as volatile instructs the compiler to load and store the value of the variable at each use. 另外更多说明可以参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/daxin/p/3364014.html
Bakery Algorithm面包店算法
Bakery.java
1 package lab2; 2 3 public class Bakery { 4 public int nThreads; 5 6 private volatile int[] ticket; 7 private volatile boolean[] choosing; 8 9 Bakery(int nTh) { 10 nThreads = nTh; 11 ticket = new int[nThreads]; 12 choosing = new boolean[nThreads]; 13 14 for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i++) { 15 System.out.println(i + ticket[1]); 16 ticket[i] = 0; 17 choosing[i] = false; 18 } 19 } 20 21 private int getNextNumber() { 22 int largest = 0; 23 for (int i = 0; i < nThreads; i++) { 24 if (ticket[i] > largest) 25 largest = ticket[i]; 26 } 27 return largest + 1; 28 } 29 30 private boolean isFavouredThread(int i, int j) { 31 if ((ticket[i] == 0) || (ticket[i] > ticket[j])) 32 return false; 33 else { 34 if (ticket[i] < ticket[j]) 35 return true; 36 else 37 return (i < j); 38 } 39 } 40 41 void wantToEnterCS(int threadID) { 42 choosing[threadID] = true; 43 ticket[threadID] = getNextNumber(); 44 choosing[threadID] = false; 45 46 for (int otherThread = 0; otherThread < nThreads; otherThread++) { 47 while(choosing[otherThread]) { 48 // busy-wait 49 } 50 // Break any ties between threads 51 while (isFavouredThread(otherThread,threadID)) { 52 // busy-wait 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 57 void exitCS(int threadID) { 58 // Leave critical section 59 ticket[threadID] = 0; 60 } 61 }
Couter.java
1 package lab2; 2 3 public class Counter { 4 volatile int value = 0; 5 6 Counter() { 7 System.out.println("TOTAL: " + value); 8 } 9 10 boolean increment() { 11 int temp = value; //read[v] 12 Simulate.HWinterrupt(); 13 value = temp + 1; //write[v+1] 14 System.out.println("TOTAL: " + value); 15 return true; 16 } 17 18 boolean decrement() { 19 int temp = value; //read[v] 20 Simulate.HWinterrupt(); 21 if (temp == 0) return false; 22 Simulate.HWinterrupt(); 23 value = temp - 1; //write[v+1] 24 System.out.println("TOTAL: " + value); 25 return true; 26 } 27 } 28 29 class Simulate { 30 public static void HWinterrupt() { 31 if (Math.random() < 0.5) 32 try{ 33 Thread.sleep(200); 34 } catch(InterruptedException ie) {}; 35 } 36 }
Turnstile.java
1 package lab2; 2 3 /* Notes: 4 * No modifications need be made to the bakery class. Instead, the turnstile 5 * class and counter classes are adjusted to allow for "exit" turnstiles as well 6 * as entrance turnstiles. This solution incorporates a system to prevent the 7 * number of people in the gardens from being negative, so the sleep call in 8 * this class can be commented out. Study the code in the Counter and Turnstile 9 * classes to see how how this works. 10 * */ 11 12 public class Gardens { 13 static Turnstile west; 14 static Turnstile east; 15 static Turnstile westExit; 16 static Turnstile eastExit; 17 static Counter people; 18 static Bakery bakery; 19 20 public static void main(String[] args) { 21 people = new Counter(); 22 bakery = new Bakery(4); 23 24 west = new Turnstile(0, true, people, bakery); 25 east = new Turnstile(1, true, people, bakery); 26 27 westExit = new Turnstile(2, false, people, bakery); 28 eastExit = new Turnstile(3, false, people, bakery); 29 30 west.start(); 31 east.start(); 32 33 /* 34 try { 35 Thread.sleep(5000); 36 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 37 } 38 */ 39 40 westExit.start(); 41 eastExit.start(); 42 } 43 }
Garden.java
1 package lab2; 2 3 public class Gardens { 4 static Turnstile west; 5 static Turnstile east; 6 static Turnstile westExit; 7 static Turnstile eastExit; 8 static Counter people; 9 static Bakery bakery; 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 people = new Counter(); 13 bakery = new Bakery(4); 14 15 west = new Turnstile(0, true, people, bakery); 16 east = new Turnstile(1, true, people, bakery); 17 18 westExit = new Turnstile(2, false, people, bakery); 19 eastExit = new Turnstile(3, false, people, bakery); 20 21 west.start(); 22 east.start(); 23 24 /* 25 try { 26 Thread.sleep(5000); 27 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 28 } 29 */ 30 31 westExit.start(); 32 eastExit.start(); 33 } 34 }
生产者消费者,操作列表:
Buffer.java
1 import java.util.LinkedList; 2 import java.util.NoSuchElementException; 3 4 class Buffer { 5 LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>(); 6 7 public synchronized void write(int i) { 8 queue.add(i); 9 } 10 11 public synchronized int read() { 12 try { 13 return queue.removeFirst(); 14 } catch(NoSuchElementException e) { 15 // the buffer is empty!? 16 return -1; 17 } 18 } 19 }
Producer.java
1 class Producer implements Runnable { 2 Buffer buffer; 3 4 public Producer(Buffer b) { 5 buffer = b; 6 } 7 8 public void run() { 9 for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 10 buffer.write(i); 11 System.out.println("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + 12 " writes " + i); 13 } 14 } 15 }
Consumer.java
1 class Consumer implements Runnable { 2 Buffer buffer; 3 4 public Consumer(Buffer b) { 5 buffer = b; 6 } 7 8 public void run() { 9 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 10 try { 11 Thread.sleep(10); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 } 14 int x = buffer.read(); 15 System.err.println("Thread " + Thread.currentThread().getId() + 16 " reads " + x); 17 } 18 } 19 }
InfBuffer.java
1 public class InfBuffer { 2 public static void main(String args[]) { 3 Buffer b = new Buffer(); 4 Consumer c1 = new Consumer(b); 5 Consumer c2 = new Consumer(b); 6 Producer p = new Producer(b); 7 (new Thread(c1)).start(); 8 (new Thread(c2)).start(); 9 (new Thread(p)).start(); 10 } 11 }
生产者消费者,修改学生姓名和年龄并获取:(只能一打一大片,无法实现生产者生产后等待消费者消费后再产生)
1 public class Student { 2 String name; 3 int age; 4 }
1 public class SetThread implements Runnable { 2 3 private Student s; 4 private int x = 0; 5 6 public SetThread(Student s) { 7 this.s = s; 8 } 9 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 while (true) { 13 synchronized (s) { 14 if (x % 2 == 0) { 15 s.name = "Student1"; 16 s.age = 27; 17 } else { 18 s.name = "Student2"; 19 s.age = 30; 20 } 21 x++; 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 }
1 public class GetThread implements Runnable { 2 private Student s; 3 4 public GetThread(Student s) { 5 this.s = s; 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public void run() { 10 while (true) { 11 synchronized (s) { 12 System.out.println(s.name + "---" + s.age); 13 } 14 } 15 } 16 }
1 public class StudentDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 //创建资源 4 Student s = new Student(); 5 6 //设置和获取的类 7 SetThread st = new SetThread(s); 8 GetThread gt = new GetThread(s); 9 10 //线程类 11 Thread t1 = new Thread(st); 12 Thread t2 = new Thread(gt); 13 14 //启动线程 15 t1.start(); 16 t2.start(); 17 } 18 }
生产者消费者,修改学生姓名和年龄并获取:(使用等待唤醒机制改进)
1 public class Student { 2 String name; 3 int age; 4 boolean flag; //添加一个标记,默认为false,表示生产者是否生成值 5 }
1 public class SetThread implements Runnable { 2 3 private Student s; 4 private int x = 0; 5 6 public SetThread(Student s) { 7 this.s = s; 8 } 9 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 while (true) { 13 synchronized (s) { 14 //判断有没有 15 if(s.flag) { 16 try { 17 s.wait(); 18 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 } 22 23 if (x % 2 == 0) { 24 s.name = "Student1"; 25 s.age = 27; 26 } else { 27 s.name = "Student2"; 28 s.age = 30; 29 } 30 x++; 31 32 //修改标记 33 s.flag = true; 34 //唤醒线程 35 s.notify(); 36 } 37 } 38 } 49 }
1 public class GetThread implements Runnable { 2 private Student s; 3 4 public GetThread(Student s) { 5 this.s = s; 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public void run() { 10 while (true) { 11 synchronized (s) { 12 if (!s.flag) { 13 try { 14 s.wait(); 15 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 } 19 System.out.println(s.name + "---" + s.age); 20 21 //修改标记 22 s.flag = false; 23 //唤醒线程 24 s.notify(); 25 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 }
public class StudentDemo { //同上 public static void main(String[] args) { //创建资源 Student s = new Student(); //设置和获取的类 SetThread st = new SetThread(s); GetThread gt = new GetThread(s); //线程类 Thread t1 = new Thread(st); Thread t2 = new Thread(gt); //启动线程 t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
厕所排队(使用信号量)
1 import java.util.Random; 2 import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; 3 4 class Wc extends Thread { 5 private String name; 6 private Semaphore wc; 7 8 public Wc(String name, Semaphore wc) { 9 this.name = name; 10 this.wc = wc; 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public void run() { 15 int availablePermit = wc.availablePermits(); 16 if (availablePermit > 0) { 17 System.out.println(name+",好开心啊,我终于有坑了"); 18 }else { 19 System.out.println(name+"怎么没有坑了。。。"); 20 } 21 22 try { 23 wc.acquire(); 24 System.out.println(name+",好开心啊,我终于抢到了!"); 25 Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000)); 26 System.out.println(name+",好爽啊,终于上完了!"); 27 wc.release(); 28 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 29 30 } 31 } 32 } 33 34 public class Demo { 35 public static void main(String[] args) { 36 Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3); 37 38 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 39 Wc wc = new Wc("第"+i+"个人", semaphore); 40 wc.start(); 41 } 42 } 43 }
The Sleeping Barber (生产者消费者,信号量)
1 import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; 2 3 public class Barber implements Runnable{ 4 5 Semaphore customerWaiting, seats, barberSleeping; 6 7 Barber(Semaphore customerWaiting, Semaphore seats, Semaphore barberSleeping) { 8 this.customerWaiting = customerWaiting; 9 this.seats = seats; 10 this.barberSleeping = barberSleeping; 11 } 12 13 public void run() { 14 15 while (true){ 16 17 // Get a customer, sleep otherwise 18 try { 19 customerWaiting.acquire(); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) {} 21 22 // Cut the hair of the customer 23 System.out.println("Cutting Hair"); 24 barberSleeping.release(); 25 26 } 27 } 28 }
1 import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; 2 3 public class Customer implements Runnable{ 4 5 Semaphore customerWaiting, seats, barberSleeping; 6 7 boolean cut = false; 8 Customer(Semaphore customerWaiting, Semaphore seats, Semaphore barberSleeping) { 9 this.customerWaiting = customerWaiting; 10 this.seats = seats; 11 this.barberSleeping = barberSleeping; 12 13 } 14 15 public void run() { 16 while (!cut) { 17 18 // A random delay 19 // Don't want all the threads trying at once! 20 try { 21 Thread.sleep((long)(Math.random()*100)); 22 } catch (InterruptedException e1) {} 23 24 // Try to get a seat in the waiting room 25 try { 26 seats.acquire(); 27 } catch (InterruptedException e) {} 28 System.out.println(seats.availablePermits()); 29 30 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" is sitting down"); 31 // Try and wake barber 32 customerWaiting.release(); 33 34 35 // Get hair cut 36 try { 37 barberSleeping.acquire(); 38 } catch (InterruptedException e) {} 39 cut = true; 40 seats.release(); 41 42 } 43 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" has had hair cut"); 44 } 45 }
1 import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore; 2 3 public class Runner { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Semaphore barberSleeping = new Semaphore(1); 8 Semaphore customerWaiting = new Semaphore(1); 9 try { 10 customerWaiting.acquire(); 11 barberSleeping.acquire(); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 } 14 15 Semaphore seats = new Semaphore(3); 16 17 Barber bar = new Barber(customerWaiting,seats,barberSleeping); 18 Thread bThread = new Thread(bar); 19 bThread.start(); 20 21 int nCust = 30; 22 Customer customers[] = new Customer[nCust]; 23 Thread cThread[] = new Thread[nCust]; 24 25 for (int i=0;i<nCust;i++) { 26 customers[i] = new Customer(customerWaiting,seats,barberSleeping); 27 cThread[i] = new Thread(customers[i]); 28 cThread[i].start(); 29 } 30 } 31 }
线程池:
程序启动一个新线程成本是比较高的,因为它涉及到要与操作系统进行交互,而使用线程池可以很好的提高性能,尤其是当程序中要创建大量生存期很短的线程时,更应该考虑使用线程池
线程池里的每一个线程代码结束后,并不会死亡,而是再次回到线程池中成为空闲状态,等待下一个对象来使用。
1 public class ExecutorsDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 // 创建一个线程池对象,控制要创建几个线程对象。 4 // public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) 5 ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); //直接通过类名调用 6 7 // 可以执行Runnable对象或者Callable对象代表的线程 8 pool.submit(new MyRunnable()); 9 pool.submit(new MyRunnable()); 10 11 //结束线程池 12 pool.shutdown(); 13 } 14 }
使用Callable方法
public class MyCallable implements Callable { @Override public Object call() throws Exception { for (int x = 0; x < 100; x++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + x); } return null; } }
public class CallableDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建线程池对象 ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); //可以执行Runnable对象或者Callable对象代表的线程 pool.submit(new MyCallable()); pool.submit(new MyCallable()); //结束 pool.shutdown(); } }
Callable带返回值:
1 public class CallableDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { 3 // 创建线程池对象 4 ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); 5 6 // 可以执行Runnable对象或者Callable对象代表的线程 7 Future<Integer> f1 = pool.submit(new MyCallable(100)); 8 Future<Integer> f2 = pool.submit(new MyCallable(200)); 9 10 // V get() 11 Integer i1 = f1.get(); 12 Integer i2 = f2.get(); 13 14 System.out.println(i1); 15 System.out.println(i2); 16 17 // 结束 18 pool.shutdown(); 19 } 20 }
1 public class MyCallable implements Callable<Integer> { 2 3 private int number; 4 5 public MyCallable(int number) { 6 this.number = number; 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public Integer call() throws Exception { 11 int sum = 0; 12 for (int x = 1; x <= number; x++) { 13 sum += x; 14 } 15 return sum; 16 } 17 18 }
匿名内部类实现多线程:
1 public class ThreadDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 // 继承Thread类来实现多线程 4 new Thread() { 5 public void run() { 6 for (int x = 0; x < 100; x++) { 7 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" 8 + x); 9 } 10 } 11 }.start(); 12 13 // 实现Runnable接口来实现多线程 14 new Thread(new Runnable() { 15 @Override 16 public void run() { 17 for (int x = 0; x < 100; x++) { 18 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" 19 + x); 20 } 21 } 22 }) { 23 }.start(); 24 25 // 更有难度的 26 new Thread(new Runnable() { 27 @Override 28 public void run() { 29 for (int x = 0; x < 100; x++) { 30 System.out.println("hello" + ":" + x); 31 } 32 } 33 }) { 34 public void run() { //走的是这边的run方法 35 for (int x = 0; x < 100; x++) { 36 System.out.println("world" + ":" + x); 37 } 38 } 39 }.start(); 40 } 41 }