实验四 类与对象的定义及使用
实验时间 2018-9-20
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解用户自定义类的定义;
类是具有相同属性和行为的一组对象的集合。java中,用构造器构造并初始化对象。
类是构造对象的基本单元。
构造器是类中一个特殊的方法,其方法名与类名相同。
(2) 掌握对象的声明;
对象是客观事物的抽象,类是对对象的抽象。类是一种抽象的数据类型,其定义为:class 类名{ } 他们的关系是对象是类的实例,类是对象的模板。
对象的声明:
类名 对象名 = new 类名();
对象的调用
访问属性:对象名.属性名;
访问方法:对象名.方法名;
(3) 学会使用构造函数初始化对象;
构造函数的特点:构造函数名与类名相同;构造函数不返回任何值,也没有返回类型;每一类可以有零个或多个构造方法;构造方法在创建对象时自动执行,一般不用显示的直接调用。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1 测试以下程序,掌握文件输入输出程序设计技术(文件输入输出,教材61-62).
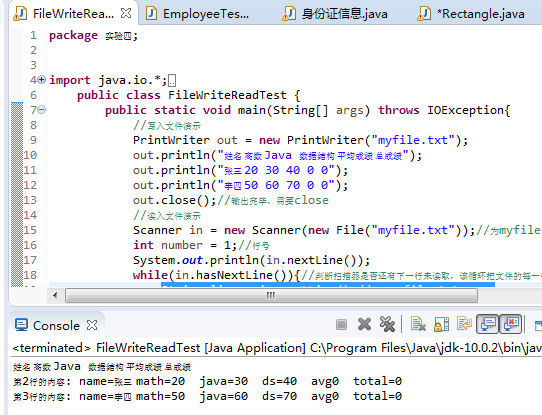
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class FileWriteReadTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ //写入文件演示 PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter("myfile.txt"); out.println("姓名 高数 Java 数据结构 平均成绩 总成绩"); out.println("张三 20 30 40 0 0"); out.println("李四 50 60 70 0 0"); out.close();//输出完毕,需要close //读入文件演示 Scanner in = new Scanner(new File("myfile.txt"));//为myfile.txt这个File创建一个扫描器in int number = 1;//行号 System.out.println(in.nextLine()); while(in.hasNextLine()){//判断扫描器是否还有下一行未读取,该循环把文件的每一行都读出 String line = in.nextLine();//读出myfile.txt的下一行 System.out.print("第"+(++number)+"行的内容: "); Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(line);//行内容建立扫描器 linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");//使用空格作为分隔符 String name = linescanner.next(); String math = linescanner.next(); String java = linescanner.next(); String ds = linescanner.next(); String avg = linescanner.next(); String total = linescanner.next(); System.out.println("name="+name+" math="+math+" java="+java+" ds="+ds+" avg"+avg+" total="+total); } in.close();//读入完毕,最后需要对其进行close。 } }
实验2 导入第4章示例程序并测试。
测试程序1:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-2(教材104页);
l 结合程序运行结果,掌握类的定义与类对象的用法,并在程序代码中添加类与对象知识应用的注释;
l 尝试在项目中编辑两个类文件(Employee.java、 EmployeeTest.java ),编译并运行程序。
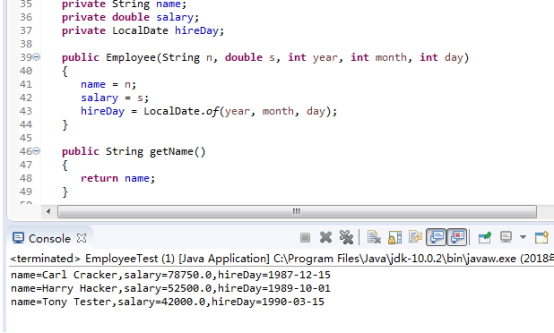
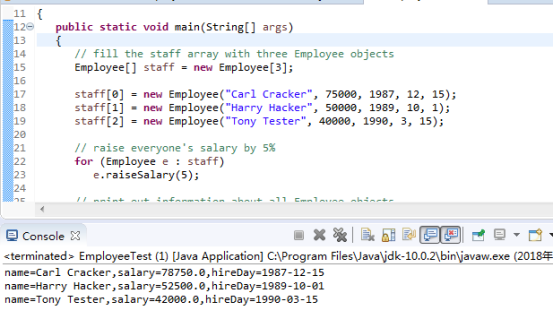
import java.time.*; /** * This program tests the Employee class. * @version 1.12 2015-05-08 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EmployeeTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // fill the staff array with three Employee objects Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; //构造一个数组,并填入如三个雇员对象。 staff[0] = new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); staff[1] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); staff[2] = new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15); // raise everyone's salary by 5% for (Employee e : staff) e.raiseSalary(5); // print out information about all Employee objects for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e.getHireDay()); } } class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String n, double s, int year, int month, int day) { name = n; salary = s; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
l 参考教材104页EmployeeTest.java,设计StudentTest.java,定义Student类,包含name(姓名)、sex(性别)、javascore(java成绩)三个字段,编写程序,从键盘输入学生人数,输入学生信息,并按以下表头输出学生信息表:
姓名 性别 java成绩
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class StudentTest{ private int number; private String name; private String sex; private int score; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getNumber() { return number; } public void setNumber(int number) { this.number = number; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } public int getScore() { return number; } public void setScore(int score) { this.number = number; } public StudentTest(){} public StudentTest(int number, String name) { this.number = number; this.name = name; this.sex = sex; } public StudentTest writeInfo(){ StudentTest st = new StudentTest(); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入学生的学号:"); number = in.nextInt(); st.setNumber(number); System.out.println("请输入学生的姓名:"); String name = in.next(); st.setName(name); System.out.println("请输入学生的性别:"); String sex = in.next(); st.setSex(sex); System.out.println("请输入学生的Java成绩:"); score = in.nextInt(); st.setNumber(score); return st; } public void readInfo(ArrayList list){ for(int i=0;i<=list.size()-1;i++){ StudentTest st = new StudentTest(); st = (StudentTest) list.get(i); System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"位学生的学号:" + st.getNumber()); System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"位学生的姓名:" + st.getName()); System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"位学生的性别:" + st.getSex()); System.out.println("第"+(i+1)+"位学生的成绩:" + st.getScore()); } } public static void main(String[]args){ ArrayList<StudentTest> list = new ArrayList<StudentTest>(); StudentTest st = new StudentTest(); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); while(true){ System.out.println("1、输入学生信息"); System.out.println("2、输出学生信息"); System.out.println("请选择:"); int option = in.nextInt(); switch (option) { case 1: list.add(st.writeInfo()); break; case 2: st.readInfo(list); break; default: break; } } } }
程序运行结果为:

测试程序2:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-3(教材116);
l 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握静态域(netxtId)与静态方法(getNextId)的用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
l 理解Java单元(类)测试的技巧。
/** * This program demonstrates static methods. * @version 1.01 2004-02-19 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class StaticTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // fill the staff array with three Employee objects Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; staff[0] = new Employee("Tom", 40000); staff[1] = new Employee("Dick", 60000); staff[2] = new Employee("Harry", 65000); // print out information about all Employee objects for (Employee e : staff) { e.setId(); System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",id=" + e.getId() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary()); } int n = Employee.getNextId(); // calls static method System.out.println("Next available id=" + n); } } class Employee { private static int nextId = 1; private String name; private double salary; private int id; public Employee(String n, double s) { name = n; salary = s; id = 0; } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId() { id = nextId; // set id to next available id nextId++; } public static int getNextId() { return nextId; // returns static field } public static void main(String[] args) // unit test { Employee e = new Employee("Harry", 50000); System.out.println(e.getName() + " " + e.getSalary()); } }
测试程序3:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-4(教材121);
l 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握掌握Java方法参数的用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
package 小陈1;
/**
* This program demonstrates parameter passing in Java.
* @version 1.00 2000-01-27
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ParamTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
/*
* Test 1: Methods can't modify numeric parameters
*/
System.out.println("Testing tripleValue:");
double percent = 10;
System.out.println("Before: percent=" + percent);
tripleValue(percent);
System.out.println("After: percent=" + percent);
/*
* Test 2: Methods can change the state of object parameters
*/
System.out.println("
Testing tripleSalary:");
Employee harry = new Employee("Harry", 50000);
System.out.println("Before: salary=" + harry.getSalary());
tripleSalary(harry);
System.out.println("After: salary=" + harry.getSalary());
/*
* Test 3: Methods can't attach new objects to object parameters
*/
System.out.println("
Testing swap:");
Employee a = new Employee("Alice", 70000);
Employee b = new Employee("Bob", 60000);
System.out.println("Before: a=" + a.getName());
System.out.println("Before: b=" + b.getName());
swap(a, b);
System.out.println("After: a=" + a.getName());
System.out.println("After: b=" + b.getName());
}
public static void tripleValue(double x) // doesn't work
{
x = 3 * x;
System.out.println("End of method: x=" + x);
}
public static void tripleSalary(Employee x) // works
{
x.raiseSalary(200);
System.out.println("End of method: salary=" + x.getSalary());
}
public static void swap(Employee x, Employee y)
{
Employee temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
System.out.println("End of method: x=" + x.getName());
System.out.println("End of method: y=" + y.getName());
}
}
class Employee // simplified Employee class
{
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee(String n, double s)
{
name = n;
salary = s;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
public double getSalary()
{
return salary;
}
public void raiseSalary(double byPercent)
{
double raise = salary * byPercent / 100;
salary += raise;
}
}
测试程序5:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-6、4-7(教材135);
l 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Java包的定义及用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
import java.time.*; /** * This program tests the Employee class. * @version 1.12 2015-05-08 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EmployeeTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // fill the staff array with three Employee objects Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; staff[0] = new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); staff[1] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); staff[2] = new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15); // raise everyone's salary by 5% for (Employee e : staff) e.raiseSalary(5); // print out information about all Employee objects for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e.getHireDay()); } } class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String n, double s, int year, int month, int day) { name = n; salary = s; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
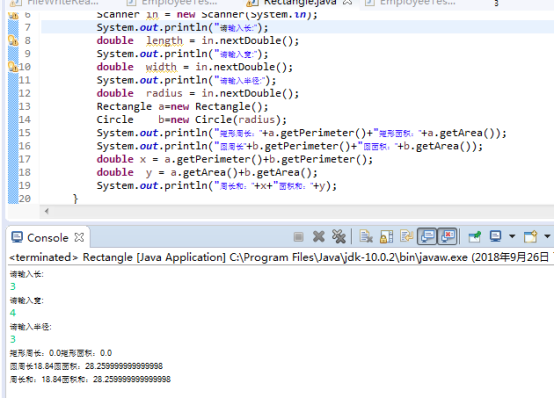
实验3 编写长方形类Rectangle与圆形类Circle,其中Rectangle类设置私有属性:width,length;Circle类设置私有属性radius。编写Rectangle类的带参构造函数Rectangle(int width,int length), Circle类的带参构造函数Circle(int radius),编写两个类的toString方法(Eclipse可自动生成)。上述2个类均定义以下方法:
求周长的方法public int getPerimeter()
求面积的方法public int getArea()
在main方法中完成以下任务:
(1) 输入1行长与宽,创建一个Rectangle对象;
(2) 输入1行半径,创建一个Circle对象;
(3) 将两个对象的周长加总输出,将两个对象的面积加总输出。
package 小陈4; import java.util.*; public class Rectangle{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入长:"); double length = in.nextDouble(); System.out.println("请输入宽:"); double width = in.nextDouble(); System.out.println("请输入半径:"); double radius = in.nextDouble(); Rectangle a=new Rectangle(); Circle b=new Circle(radius); System.out.println("矩形周长:"+a.getPerimeter()+"矩形面积:"+a.getArea()); System.out.println("圆周长"+b.getPerimeter()+"圆面积:"+b.getArea()); double x = a.getPerimeter()+b.getPerimeter(); double y = a.getArea()+b.getArea(); System.out.println("周长和:"+x+"面积和:"+y); } private double getArea() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 0; } private double getPerimeter() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return 0; } } class Rectangle1 { private double width; private double length; public Rectangle1(double w,double l) { width=w; length=l; } public double getPerimeter() { double Perimeter = (width+length)*2; return Perimeter; } public double getArea() { double Area = width*length; return Area; } } class Circle { private double R; double PI = 3.14; public Circle(double r) { R=r; } public double getPerimeter() { double Perimeter = 2*PI*R; return Perimeter; } public double getArea() { double Area = PI*R*R; return Area; } }