四则运算
(3)可定制数量,输入大的数量值,测试系统是否崩溃。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
package day02;import java.util.Random;import java.util.Scanner;public class Test { public static void main(String args[]) { Random rand = new Random(); boolean[] bool = new boolean[101]; String[] fuhao = new String[] { "+", "-", "*", "/" }; // variable initialization int first = 0; int second = 0; String fh = " "; int length = 0; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("您想练习题目的个数为:"); length=scan.nextInt(); for (int i = 0; i <length ; i++) { do { first = rand.nextInt(101); second = rand.nextInt(101); fh = fuhao[rand.nextInt(4)]; } while (bool[first] && bool[second]); bool[first] = true; bool[second] = true; System.out.println(i+1+"、"+first + fh + second + "="); } }} |

当输入100000后,系统崩溃。

(4)定制操作数的个数
package day02;import java.util.Random;import java.util.Scanner;public class Test { public static void main(String args[]) { Random rand = new Random(); boolean[] bool = new boolean[101]; String[] fuhao = new String[] { "+", "-", "*", "/" }; int n = 0; int length = 0; @SuppressWarnings("resource") Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("您想练习题目的个数为:"); length = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print("操作数的个数为:"); n = scan.nextInt(); int[] Number = new int[n]; String[] Fh = new String[n]; for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { do { Number[j] = rand.nextInt(101); Fh[j] = String.valueOf(fuhao[rand.nextInt(4)]); } while (bool[Number[j]]); bool[Number[j]] = true; if (j != n - 1) { System.out.print(Number[j] + Fh[j]); } else { System.out.print(Number[j]); } } System.out.println(); } }} |

最初我将数组 Fh 定义为:String[] Fh = new String[n-1]; 结果出现了溢出现象
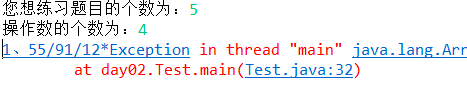
经过修改,改成了 String[] Fh = new String[n]; 运行成功
其中,由于我并没有考虑最后一组数字与符号的问题,导致在随机生成的计算题后面出现符号。经过修改,加了一个判断语句,判断它是否为最后一组,得以正确输出。
还有一个很大的收获是:我学习了如何给字符串数组中的元素赋值
Fh[j] = String.valueOf(fuhao[rand.nextInt(4)]); |