IO
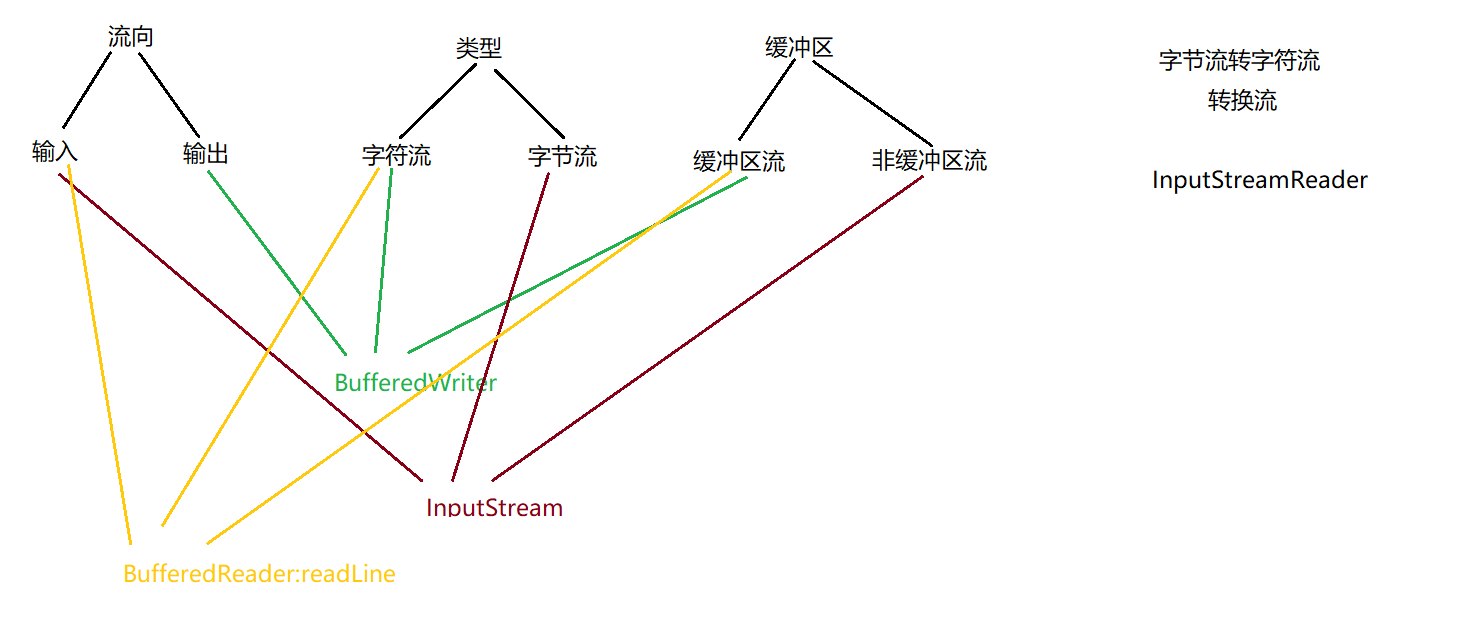
1. 流向
InputStream
OutputStream
2. 类型
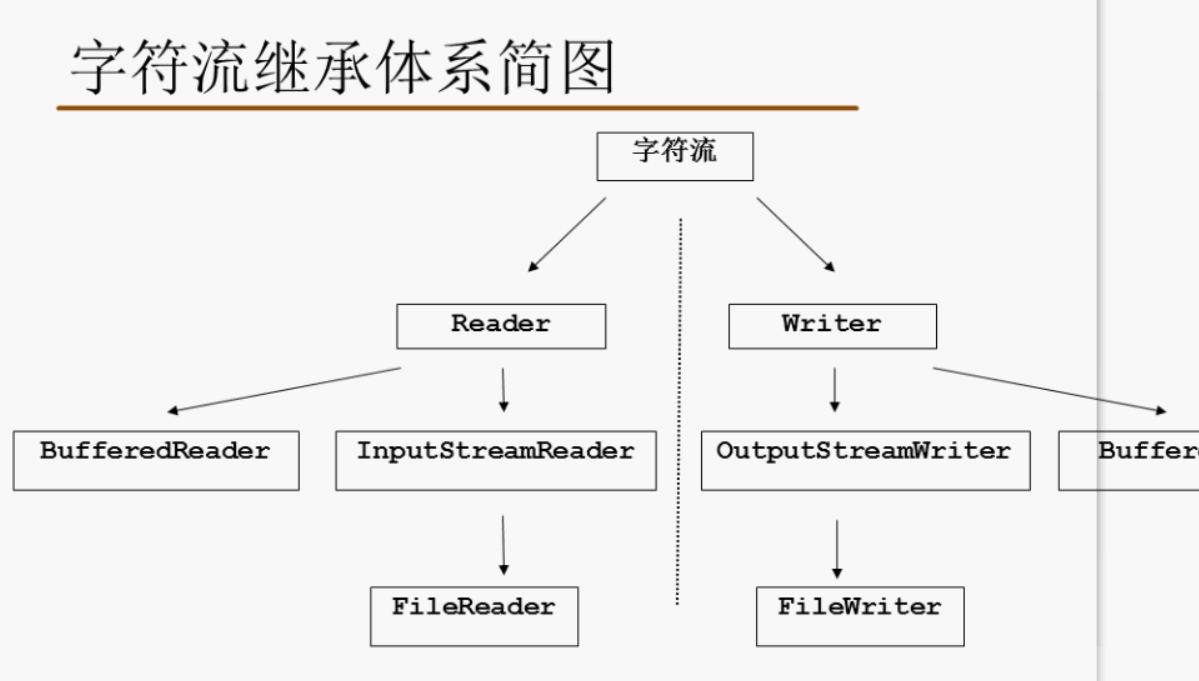
字符流:(文本文件)
Reader Writer
FileReader FileWriter
字节流:(任何文件)
InputStream OutputStream
FileInputStream FileOutputStream
3.性能划分
缓冲区流:
BufferedWriter:(装饰模式,flush清理)
BufferedReader:
readLine() LineNumberReader()
BufferedInputStream:
BufferedOutputStream:
非缓冲区流:
使用文本文件存储其他类型文件:
1 /** 2 * 使用文本文件存储其他类型的文件 3 * 4 */ 5 @Test 6 public void readOther() throws Exception{ 7 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("h:/a.txt"); 8 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("h:/testPicture/back_bg.png"); 9 int b = -1; 10 while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) { 11 fos.write((b + "").getBytes()); 12 fos.write(new byte[] {' ', ' '}); 13 } 14 fos.close(); 15 fis.close(); 16 }
还原文件:
1 /** 2 * 将文本文件还原为其他文件 3 */ 4 @Test 5 public void returnFile() { 6 FileOutputStream fos = null; 7 8 BufferedReader br = null; 9 try { 10 br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("h:\a.txt")); 11 fos = new FileOutputStream("h:/b.png"); 12 String str = null; 13 while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) { 14 byte c = (byte)Integer.parseInt(str); 15 fos.write(c); 16 } 17 } catch (Exception e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } finally { 20 if (br != null) { 21 try { 22 br.close(); 23 } catch (IOException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 if (fos != null) { 28 try { 29 fos.close(); 30 } catch (IOException e) { 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 36 }
缓冲区字节流
1 import java.io.BufferedInputStream; 2 import java.io.FileInputStream; 3 4 import org.junit.Test; 5 6 public class BufferedInputStreamDemo { 7 8 /** 9 * 缓冲区字节流 10 * @throws Exception 11 */ 12 @Test 13 public void bufferedInputStreamTest() throws Exception{ 14 BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("h:/a.txt")); 15 int i = -1; 16 while ((i = bis.read()) != -1) { 17 System.out.println(i); 18 } 19 bis.close(); 20 } 21 }
转换流
字节流到字符流的桥梁,使用特定字符集读取byte并解码成字符。
底层是字节流,如果需要将其转换成字符内容处理的还,就可以使用转换流。
- InputStreamReader
- new InputStreamReader(InputStream in, charset)
- OutputStreamWriter
1. new OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, charset)
1 import java.io.FileInputStream; 2 import java.io.InputStreamReader; 3 4 import org.junit.Test; 5 /** 6 * 使用转换流, 桥梁(文本->字节) 7 * 8 */ 9 public class InputStreamReaderDemo { 10 11 /** 12 * 使用转换流读取文本 13 * @throws Exception 14 */ 15 @Test 16 public void read() throws Exception { 17 InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("h:/b.txt"), "gbk"); 18 char[] cbuf = new char[1024]; 19 int len = -1; 20 while ((len = reader.read(cbuf)) != -1) { 21 System.out.println(new String(cbuf, 0, len)); 22 } 23 reader.close(); 24 } 25 }
打印流
改变系统默认的out流向
1 /** 2 * 改变系统默认out流向 3 * 默认是console 4 * @throws Exception 5 */ 6 @Test 7 public void sysoutTest() throws Exception { 8 PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("h:/log.log")); 9 System.setOut(ps); 10 System.out.println("helloworld"); 11 }
控制台读取输入
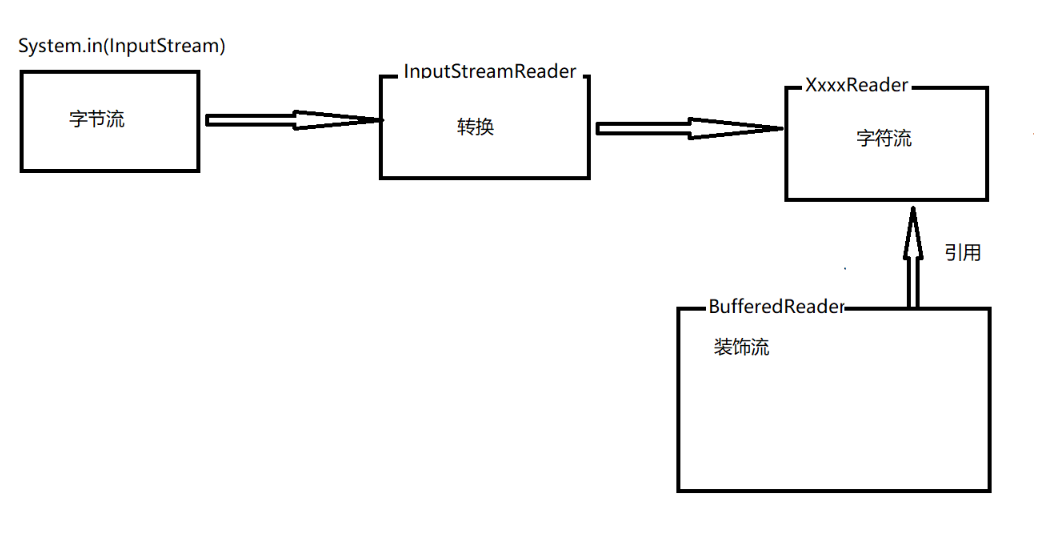
1 /** 2 * 从控制台读取 3 * @throws Exception 4 */ 5 @Test 6 public void systemin() throws Exception {
System.setIn(new FileInputStream("h:/log.log")); 7 BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); 8 while (true) { 9 String line = reader.readLine(); 10 if ("exit".equals(line)) { 11 System.exit(-1); 12 } 13 System.out.println(line); 14 } 15 16 }
文件
1 import java.io.File; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 5 public class FileTest { 6 @Test 7 public void file1() { 8 File f = new File("h:/a.txt"); 9 System.out.println(f.exists());//文件或文件夹是否存在 10 System.out.println(f.isDirectory());//是否为目录 11 12 //创建文件夹 13 String dir = "h:/testDir/a/b/c"; 14 f = new File(dir); 15 if(!f.exists()) { 16 f.mkdirs(); 17 } 18 19 //列出文件夹下所有文件和文件夹 20 f = new File("h:/testPicture"); 21 if(f.isDirectory()) { 22 File[] files = f.listFiles(); 23 for (File f0 : files) { 24 System.out.println(f0.getName()); 25 //f0.getAbsolutePath(); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 }
列出文件夹下所有文件和文件夹及所有子文件

1 import java.io.File; 2 3 public class FileRecursiveDemo { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 // showFiles("h:/txtFiles"); 6 showFiles(null); 7 } 8 9 /** 10 * 显示文件路径名 11 * 12 * @param dir 13 */ 14 public static void showFiles(String path) { 15 // 16 if (path != null) { 17 File f = new File(path); 18 if (f.exists()) { 19 // 是否是目录 20 if (f.isDirectory()) { 21 System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath()); 22 File[] files = f.listFiles(); 23 for (File f0 : files) { 24 String p0 = f0.getAbsolutePath(); 25 showFiles(p0); 26 } 27 } 28 // 是否是文件 29 else if (f.isFile()) { 30 System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath()); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 }
文件
1 @Test 2 public void FileTest() throws Exception { 3 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("h:/a.txt"); 4 System.out.println(fis.available()); 5 fis.close();//这个地方如果忘记关了无法renameTo 6 // 方法2 7 File f = new File("h:/a.txt"); 8 long len = f.length(); 9 System.out.println(len); 10 11 // 得到上级目录 12 String str = f.getParent(); 13 System.out.println(str); 14 15 System.out.println(f.canWrite()); 16 17 //重命名,相当于剪切 18 f.renameTo(new File("d://", "b.txt")); 19 20 // 21 f = new File("h:/ccc.txt"); 22 if (!f.exists()) { 23 f.createNewFile(); 24 } 25 26 // 列出文件系统的root 27 File[] fs = File.listRoots(); 28 for (File f0 : fs) { 29 System.out.println(f0.getAbsolutePath()); 30 } 31 }
实现复制文件夹(包含子文件)
1 import java.io.BufferedInputStream; 2 import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileInputStream; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 8 public class CopyDir { 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 copy("h:\txtFiles", "d:\"); 11 } 12 13 public static void copy(String srcDirPath, String destDirPath) { 14 // 1.创建新的根目录 15 File srcRootDir = new File(srcDirPath); 16 String srcDirName = srcRootDir.getName();// 原文件夹名称 17 String newDirPath = destDirPath + "\" + srcDirName;// 新文件夹路径 18 File newRootDir = new File(newDirPath); 19 if (!newRootDir.exists()) { 20 newRootDir.mkdir();// 创建新文件夹 21 } 22 23 // 2.处理子文件及子文件夹 24 File[] filesAndDirs = srcRootDir.listFiles(); 25 for (File f0 : filesAndDirs) { 26 // System.out.println(f0.getName()); 27 // 如果是文件夹,递归 28 if (f0.isDirectory()) { 29 copy(f0.getAbsolutePath(), newDirPath); 30 } 31 // 如果是文件,复制 32 else if (f0.isFile()) { 33 File newFile = new File(newDirPath + "\" + f0.getName()); 34 // 创建新文件 35 if (!newFile.exists()) { 36 try { 37 newFile.createNewFile(); 38 } catch (IOException e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 } 42 43 // 复制文件 44 BufferedInputStream bis = null; 45 BufferedOutputStream bos = null; 46 try { 47 bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(f0.getAbsolutePath())); 48 bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(newFile.getAbsolutePath())); 49 byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; 50 int len = -1; 51 while ((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1) { 52 // System.out.println(new String (buffer)); 53 bos.write(buffer); 54 } 55 bos.close(); 56 bis.close(); 57 } catch (Exception e) { 58 e.printStackTrace(); 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 63 } 64 65 }
根据绝对路径获取文件名
1 // 举例: 2 String fName =" G:\Java_Source\navigation_tigra_menu\demo1\img\lev1_arrow.gif "; 3 4 // 方法一: 5 6 File tempFile =new File( fName.trim()); 7 8 String fileName = tempFile.getName(); 9 10 System.out.println("方法一:fileName = " + fileName); 11 12 // 方法二: 13 14 fName = fName.trim(); 15 16 // fileName = fName.substring(fName.lastIndexOf("/")+1); 17 // 或者 18 fileName = fName.substring(fName.lastIndexOf("\")+1); 19 20 System.out.println("方法二:fileName = " + fileName); 21 22 // 方法三: 23 24 fName = fName.trim(); 25 26 String temp[] = fName.split("\\"); /**split里面必须是正则表达式,"\"的作用是对字符串转义*/ 27 28 //temp[] = [G:, Java_Source, navigation_tigra_menu, demo1, img, lev1_arrow.gif] 29 System.out.println("temp[] = " + Arrays.toString(temp)); 30 fileName = temp[temp.length-1]; 31 32 System.out.println("方法三:fileName = " + fileName);