上一篇我们学习了服务的注册与发现,本篇博客是在上一篇的基础上学习服务的调用。上一博客主要创建了Eureka的服务端和一个Client,该Client包含了一个Controller用来提供对外服务供外部调用,可以作为生产者。
一、引入依赖
前面创建了EurekaClient的项目,在项目中引入了spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client用来注册服务,是生产者,这里调用属于消费者,同样也需要引入spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client,这里还使用了openfeign来调用生产者提供的服务。具体pom.xml如下,主要引入spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client、spring-boot-starter-web、spring-cloud-starter-openfeign、spring-cloud-openfeign-core。

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.6.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>EurekaConsumer</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>EurekaConsumer</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> <spring-cloud.version>Greenwich.SR1</spring-cloud.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.cloud/spring-cloud-openfeign-core --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-openfeign-core</artifactId> <version>2.1.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <dependencyManagement> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId> <version>${spring-cloud.version}</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> </dependencyManagement> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> <packaging>war</packaging> </project>
二、在main类中引入@EnableDiscoveryClient、@EnableFeignClients注解

package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient; import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients; @SpringBootApplication @EnableDiscoveryClient @EnableFeignClients public class EurekaConsumerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(EurekaConsumerApplication.class, args); } }
@EnableDiscoveryClient :启用服务注册与发现
@EnableFeignClients:启用feign进行远程调用
Feign是一个声明式Web Service客户端。使用Feign能让编写Web Service客户端更加简单, 它的使用方法是定义一个接口,然后在上面添加注解,同时也支持JAX-RS标准的注解。Feign也支持可拔插式的编码器和解码器。Spring Cloud对Feign进行了封装,使其支持了Spring MVC标准注解和HttpMessageConverters。Feign可以与Eureka和Ribbon组合使用以支持负载均衡。
三、配置文件
spring.application.name=spring-cloud-consumer server.port=9001 eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8088/eureka/
四、feign调用实现
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; @FeignClient(name= "spring-cloud-producer") public interface HelloRemote { @RequestMapping(value = "/hello") public String hello(@RequestParam(value = "name") String name); }
name:远程服务名,及spring.application.name配置的名称,此类中的方法和远程服务中contoller中的方法名和参数需保持一致。
五、web层调用远程服务
这里使用@Autowired将远程访问类注入到Controller中用来调用服务。
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class ConsumerController { @Autowired HelloRemote HelloRemote; @RequestMapping("/hello") public String index(@RequestParam String name) { return HelloRemote.hello(name); } }
六、测试
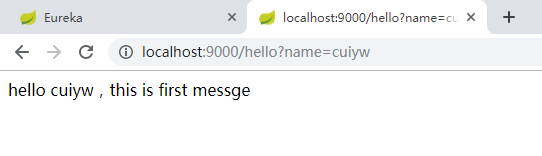
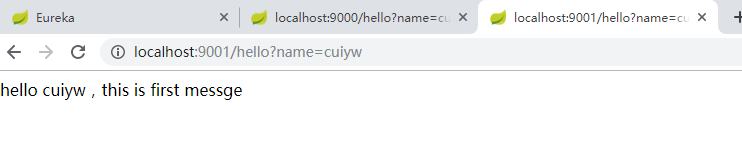
分别启动Server、Client、Consumer,依次输入http://localhost:8088/、http://localhost:9000/hello?name=cuiyw、http://localhost:9001/hello?name=cuiyw。端口8088是Eureka Server端,9000是Eureka Client,作为生产者,端口9001也是Eureka Client,作为消费者,在端口9001中消费者调用生产者9000提供的服务。

七、负载均衡
修改EurekaClient项目中的Controller和配置文件。在Controller中的index方法增加了修改了return的值,用来区分生产者。在application.properties中修改了端口号。
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String index(@RequestParam String name) { return "hello "+name+",this is first messge 2"; } }
spring.application.name=spring-cloud-producer server.port=9002 eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://localhost:8088/eureka/
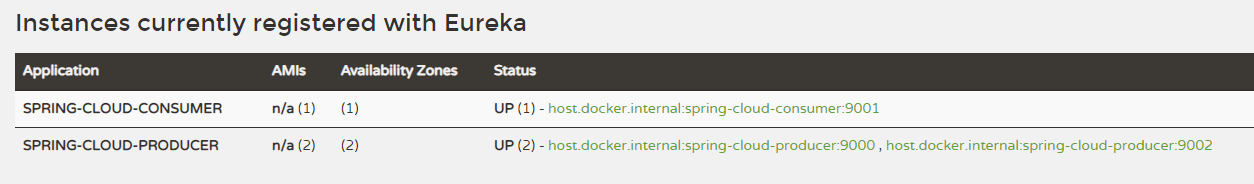
启动该Client,这时在Eureka Server中可以看到两个生产者。
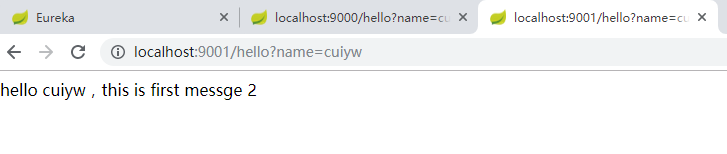
在浏览器中数次刷新url:http://localhost:9001/hello?name=cuiyw,可以看到不同的响应结果。

八、小结
本篇主要学习了下服务的调用以及简单的使用openfeign进行的负载均衡,后面会参考纯洁的微笑的博文学习熔断器Hystrix。
本篇博客参考:http://www.ityouknow.com/springcloud/2017/05/12/eureka-provider-constomer.html
九、号外
本人的新书已出版上架,书名Spring快速入门,天猫、京东也都能搜得到,这里也算是王婆卖瓜自卖自夸一下,大家如果感兴趣可以了解一下,个人感觉对初学者来说还是值得一读的。

