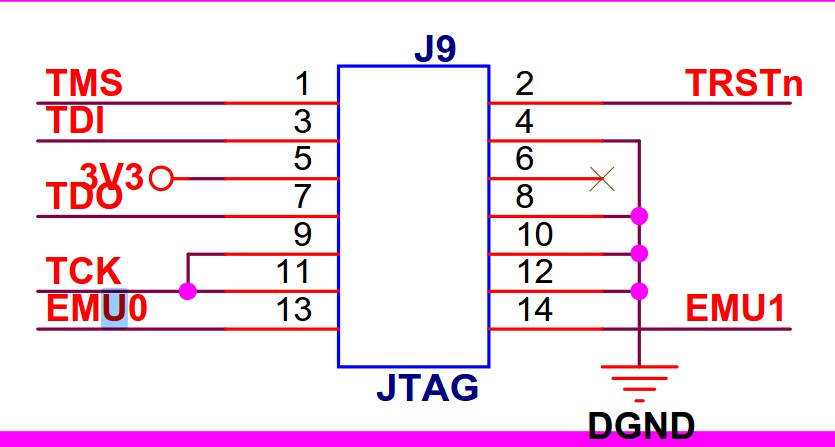
1. 本次以三兄弟的DSP28335开发板为例,看下JTAG接口,EMU0,EMU1的用途,不是很懂,不深入研究,用到再说
EMU0/1是TI芯片的JTAG才有的信号,本身不属于JTAG标准里的信号,有两个作用。
(1)设定芯片是仿真模式(上拉)还是边界扫描模式(下拉)。
(2)用做高速实时数据交换RTDX及TRACE等功能时。这个一般用户可能用不到。
所以这两个信号是双向的,这个信号一般来说不需加要buffer,直接连起来就好了,不用管他是单向还是双向。
2. 打开工程,E:dspSXD_C28335SXD28335_PRO_1_V2Example_2833x_LEDBlink,建立一个CCXML文件,编译一下工程
3. 看下引脚原理图,28335有3组GPIO,每组GPIO最多有32个引脚,但是28335是16位的,所以每组GPIO有高低寄存器

4. GPIO寄存器

5. 代码研究一下,看了一下底层用的是C2000WARE里面的库函数。
1 #include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File 2 3 // Prototype statements for functions found within this file. 4 interrupt void cpu_timer0_isr(void); 5 6 void main(void) 7 { 8 9 // Step 1. Initialize System Control: 10 // PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks 11 // This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file. 12 InitSysCtrl(); 13 14 // Step 2. Initalize GPIO: 15 // This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and 16 // illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state. 17 // InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example 18 19 20 // Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table: 21 // Disable CPU interrupts 22 DINT; 23 24 // Initialize the PIE control registers to their default state. 25 // The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags 26 // are cleared. 27 // This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file. 28 InitPieCtrl(); 29 30 // Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags: 31 IER = 0x0000; 32 IFR = 0x0000; 33 34 // Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt 35 // Service Routines (ISR). 36 // This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt 37 // is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes. 38 // The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c. 39 // This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c. 40 InitPieVectTable(); 41 42 // Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to 43 // ISR functions found within this file. 44 EALLOW; // This is needed to write to EALLOW protected registers 45 PieVectTable.TINT0 = &cpu_timer0_isr; 46 EDIS; // This is needed to disable write to EALLOW protected registers 47 48 // Step 4. Initialize the Device Peripheral. This function can be 49 // found in DSP2833x_CpuTimers.c 50 InitCpuTimers(); // For this example, only initialize the Cpu Timers 51 #if (CPU_FRQ_150MHZ) 52 // Configure CPU-Timer 0 to interrupt every 500 milliseconds: 53 // 150MHz CPU Freq, 50 millisecond Period (in uSeconds) 54 ConfigCpuTimer(&CpuTimer0, 150, 500000); 55 #endif 56 #if (CPU_FRQ_100MHZ) 57 // Configure CPU-Timer 0 to interrupt every 500 milliseconds: 58 // 100MHz CPU Freq, 50 millisecond Period (in uSeconds) 59 ConfigCpuTimer(&CpuTimer0, 100, 500000); 60 #endif 61 62 // To ensure precise timing, use write-only instructions to write to the entire register. Therefore, if any 63 // of the configuration bits are changed in ConfigCpuTimer and InitCpuTimers (in DSP2833x_CpuTimers.h), the 64 // below settings must also be updated. 65 66 CpuTimer0Regs.TCR.all = 0x4001; // Use write-only instruction to set TSS bit = 0 67 68 // Step 5. User specific code, enable interrupts: 69 70 // Configure GPIO32 as a GPIO output pin 71 EALLOW; 72 GpioCtrlRegs.GPBMUX2.bit.GPIO53 = 0; 73 GpioCtrlRegs.GPBDIR.bit.GPIO53 = 1; 74 GpioCtrlRegs.GPAMUX1.bit.GPIO0 = 0; 75 GpioCtrlRegs.GPADIR.bit.GPIO0 = 1; 76 EDIS; 77 78 // Enable CPU INT1 which is connected to CPU-Timer 0: 79 IER |= M_INT1; 80 81 // Enable TINT0 in the PIE: Group 1 interrupt 7 82 PieCtrlRegs.PIEIER1.bit.INTx7 = 1; 83 84 // Enable global Interrupts and higher priority real-time debug events: 85 EINT; // Enable Global interrupt INTM 86 ERTM; // Enable Global realtime interrupt DBGM 87 88 // Step 6. IDLE loop. Just sit and loop forever (optional): 89 for(;;); 90 } 91 92 interrupt void cpu_timer0_isr(void) 93 { 94 CpuTimer0.InterruptCount++; 95 GpioDataRegs.GPBTOGGLE.all = 0x40000004; // Toggle GPIO32 once per 500 milliseconds 96 GpioDataRegs.GPBTOGGLE.bit.GPIO53 = 1; 97 GpioDataRegs.GPATOGGLE.bit.GPIO0 = 1; 98 // Acknowledge this interrupt to receive more interrupts from group 1 99 PieCtrlRegs.PIEACK.all = PIEACK_GROUP1; 100 }
6. 看下GPIO的全局变量volatile struct GPIO_CTRL_REGS GpioCtrlRegs;,volatile 确保本条指令不会被编译器优化,从下面看的出来,函数库将GPIOA,GPIOB,GPIOC,的控制寄存器全部写在一起了。数据寄存器也是一样的GpioDataRegs.GPATOGGLE.bit.GPIO0 = 1;
1 struct GPIO_CTRL_REGS { 2 union GPACTRL_REG GPACTRL; // GPIO A Control Register (GPIO0 to 31) 3 union GPA1_REG GPAQSEL1; // GPIO A Qualifier Select 1 Register (GPIO0 to 15) 4 union GPA2_REG GPAQSEL2; // GPIO A Qualifier Select 2 Register (GPIO16 to 31) 5 union GPA1_REG GPAMUX1; // GPIO A Mux 1 Register (GPIO0 to 15) 6 union GPA2_REG GPAMUX2; // GPIO A Mux 2 Register (GPIO16 to 31) 7 union GPADAT_REG GPADIR; // GPIO A Direction Register (GPIO0 to 31) 8 union GPADAT_REG GPAPUD; // GPIO A Pull Up Disable Register (GPIO0 to 31) 9 Uint32 rsvd1; 10 union GPBCTRL_REG GPBCTRL; // GPIO B Control Register (GPIO32 to 63) 11 union GPB1_REG GPBQSEL1; // GPIO B Qualifier Select 1 Register (GPIO32 to 47) 12 union GPB2_REG GPBQSEL2; // GPIO B Qualifier Select 2 Register (GPIO48 to 63) 13 union GPB1_REG GPBMUX1; // GPIO B Mux 1 Register (GPIO32 to 47) 14 union GPB2_REG GPBMUX2; // GPIO B Mux 2 Register (GPIO48 to 63) 15 union GPBDAT_REG GPBDIR; // GPIO B Direction Register (GPIO32 to 63) 16 union GPBDAT_REG GPBPUD; // GPIO B Pull Up Disable Register (GPIO32 to 63) 17 Uint16 rsvd2[8]; 18 union GPC1_REG GPCMUX1; // GPIO C Mux 1 Register (GPIO64 to 79) 19 union GPC2_REG GPCMUX2; // GPIO C Mux 2 Register (GPIO80 to 95) 20 union GPCDAT_REG GPCDIR; // GPIO C Direction Register (GPIO64 to 95) 21 union GPCDAT_REG GPCPUD; // GPIO C Pull Up Disable Register (GPIO64 to 95) 22 };
7. 还有一些汇编指令,以后再研究吧
1 #define EINT asm(" clrc INTM") 2 #define DINT asm(" setc INTM") 3 #define ERTM asm(" clrc DBGM") 4 #define DRTM asm(" setc DBGM") 5 #define EALLOW asm(" EALLOW") 6 #define EDIS asm(" EDIS") 7 #define ESTOP0 asm(" ESTOP0")