1.函数atoi
atoi (表示 alphanumeric to integer)是把字符串转换成整型数的一个函数。广泛的应用在计算机程序和办公软件中。atoi( ) 函数会扫描参数 nptr字符串,跳过前面的空白字符(例如空格,tab缩进等)。
原型:int atoi(const char *nptr),nptr:要进行转换的字符串;
功能:把字符串转换成整型数;
返回值:函数返回一个 int 值,此值由将输入字符作为数字解析而生成。 如果该输入无法转换为该类型的值,则atoi的返回值为 0。
说明:如果字符存在(如果是空格,会跳过,全是空格的话返回0),是数字或者正负号则开始做类型转换,当出现一个字符不能识别为数字时,函数将停止读入输入字符串,(包括结束符 �) 字符时停止转换,返回整型数。否则,返回零。
使用示例:
1 int main(void) 2 { 3 int s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6, s7; 4 char *str1 = "12345.67"; 5 char *str2 = " 12345.67"; 6 char *str3 = "�12345.67"; 7 char *str4 = "� 12345.67"; 8 char *str5 = "-12345"; 9 char *str6 = "abc-123"; 10 char *str7 = "-8362865623872387698"; 11 s1 = atoi(str1); 12 s2 = atoi(str2); 13 s3 = atoi(str3); 14 s4 = atoi(str4); 15 s5 = atoi(str5); 16 s6 = atoi(str6); 17 s7 = atoi(str7); 18 printf("s1=%d ", s1); 19 printf("s2=%d ", s2); 20 printf("s3=%d ", s3); 21 printf("s4=%d ", s4); 22 printf("s5=%d ", s5); 23 printf("s6=%d ", s6); 24 printf("s7=%d ", s7); 25 getchar(); 26 return 0; 27 }
输出结果:
2、模拟实现此函数
1 int my_atoi(const char* nptr) 2 { 3 int num = 0; 4 bool flag = false; 5 while (*nptr == ' ') 6 { 7 nptr++; 8 } 9 if (*nptr == '-' || *nptr == ' ') 10 { 11 if (*nptr++ == '-') 12 flag = true; 13 } 14 while (*nptr >= '0' && *nptr <= '9') 15 { 16 num = num * 10 + *nptr++ - '0'; 17 if (num < 0) 18 { 19 num = 2147483647; 20 break; 21 } 22 } 23 return num*(flag ? -1 : 1); 24 }
测试代码:
1 int main(void) 2 { 3 int mys1, mys2, mys3, mys4, mys5, mys6, mys7; 4 char *str1 = "12345.67"; 5 char *str2 = " 12345.67"; 6 char *str3 = "�12345.67"; 7 char *str4 = "� 12345.67"; 8 char *str5 = "-12345"; 9 char *str6 = "abc-123"; 10 char *str7 = "-8362865623872387698"; 11 mys1 = my_atoi(str1); 12 mys2 = my_atoi(str2); 13 mys3 = my_atoi(str3); 14 mys4 = my_atoi(str4); 15 mys5 = my_atoi(str5); 16 mys6 = my_atoi(str6); 17 mys7 = my_atoi(str7); 18 printf("s1=%d ", mys1); 19 printf("s2=%d ", mys2); 20 printf("s3=%d ", mys3); 21 printf("s4=%d ", mys4); 22 printf("s5=%d ", mys5); 23 printf("s6=%d ", mys6); 24 printf("s7=%d ", mys7); 25 getchar(); 26 return 0; 27 }
输出结果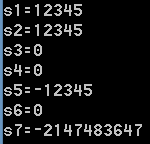
3、函数atof
atof(),是C 语言标准库中的一个字符串处理函数,功能是把字符串转换成浮点数,所使用的头文件为<stdlib.h>。该函数名是 “ascii to floating point numbers” 的缩写。
函数原型:double atof(const char *nptr ),nptr:要转换的字符串;
功 能: 把字符串转换成浮点数;
返回值:每个函数返回 double 值,此值由将输入字符作为数字解析而生成。 如果该输入无法转换为该类型的值,则返回值为 0.0。
函数说明 :atof()会扫描参数nptr字符串,跳过前面的空格字符,直到遇上数字或正负符号才开始做转换,而再遇到非数字或字符串结束时('�')才结束转换,并将结果返回,nptr字符串可包含正负号、小数点或E(e)来表示指数部分。
使用示例:
1 #include<stdlib.h> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 int main() 4 { 5 double c; 6 double d; 7 char*a = "-100.23"; 8 char*b = "200e-2"; 9 char str[] = "123.456"; 10 d = atof(str); 11 printf("str = %s double = %lf ", str, d); 12 c = atof(a) + atof(b); 13 printf("a = %.2lf b = %.2lf a + b = %.2lf ", atof(a), atof(b), c); 14 getchar(); 15 return 0; 16 }
输出结果为: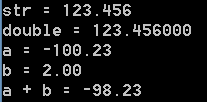
4、模拟实现此函数
1 double my_atof(const char* nptr) 2 { 3 double sum = 0.0; 4 double d = 10.0; 5 int num = 0; 6 bool flag = false; 7 while (*nptr == ' ')//当开始遇到空格时 8 { 9 nptr++; 10 } 11 if (*nptr == '-' || *nptr == '+') //记录数字正负 12 { 13 if (*nptr == '-') 14 flag = true; 15 nptr++; 16 } 17 if (!(*nptr >= '0' && *nptr <= '9'))//如果一开始就为非数字则退出,返回0.0 18 { 19 return sum; 20 } 21 while (*nptr >= '0' && *nptr <= '9' && *nptr != '.') //计算小数点前整数部分 22 { 23 sum = sum*10.0 + *nptr - '0'; 24 nptr++; 25 } 26 if (*nptr == '.') 27 { 28 nptr++; 29 } 30 while (*nptr >= '0' && *nptr <= '9')//计算小数部分 31 { 32 sum = sum + (*nptr - '0') / d; 33 d *= 10.0; 34 nptr++; 35 } 36 if (*nptr == 'e' || *nptr == 'E')//考虑科学计数法 37 { 38 nptr++; 39 char tmp = *nptr; 40 if (tmp == '-' || tmp == '+') 41 { 42 nptr++; 43 while (*nptr >= '0' && *nptr <= '9') 44 { 45 num = num * 10 + *nptr - '0'; 46 nptr++; 47 } 48 while (num > 0) 49 { 50 if (tmp == '-') 51 { 52 sum /= 10; 53 } 54 else if(tmp == '+') { 55 sum *= 10; 56 } 57 num--; 58 } 59 } 60 } 61 return sum*(flag ? -1.0 : 1.0); 62 }
测试代码:
1 int main() 2 { 3 char *s1 = " 123.456567567e+10"; 4 char *a1 = " 123.456567567e+10"; 5 char *s2 = "1234567.235e-10"; 6 char *a2 = "1234567.235e-10"; 7 char *s3 = " 123.45656�7567e-10"; 8 char *a3 = " 123.45656�7567e-10"; 9 10 double sum_1 = my_atof(s1); 11 double sum1 = atof(a1); 12 double sum_2 = my_atof(s2); 13 double sum2 = atof(a2); 14 double sum_3 = my_atof(s3);//遇到'�'结束 15 double sum3 = atof(a3); 16 17 printf("my_atof:%lf ", sum_1); 18 printf("atof :%lf ", sum1 ); 19 printf("my_atof:%lf ", sum_2); 20 printf("atof :%lf ", sum2 ); 21 printf("my_atof:%lf ", sum_3); 22 printf("atof :%lf ", sum3 ); 23 getchar(); 24 return 0; 25 }
测试结果: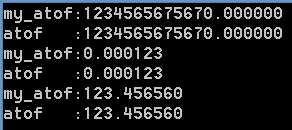
5、函数itoa
itoa(Integer to ASCII)是广泛应用的非标准C语言和C++语言扩展函数。由于它不是标准C/C++语言函数,所以不一定能在所有的编译器中使用。但是,大多数的编译器(如Windows上的)通常在<stdlib.h>/<cstdlib>头文件中包含这个函数。
原型:char *_itoa( int value, char *str, int radix );
原型说明:value:欲转换的数据,string:目标字符串的地址,radix:转换后的进制数,可以是10进制、16进制等,范围必须在 2-36。
功能:将整数value 转换成字符串存入string 指向的内存空间 ,radix 为转换时所用基数(保存到字符串中的数据的进制基数)。
返回值:函数返回一个指向 str,无错误返回。
注意:itoa并不是一个标准的C函数,它是Windows特有的,如果要写跨平台的程序,请用sprintf。
使用示例:
1 int main(void) 2 { 3 int number = 12345; 4 char string[25]; 5 _itoa(number, string, 10);//按十进制转换 6 printf("integer=%d string=%s ", number, string); 7 _itoa(number, string, 16);//按16进制转换 8 printf("integer=%d string=%s ", number, string); 9 getchar(); 10 return 0; 11 }
输出结果: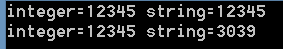
MSDN的例子:
1 /*ITOA.C:Thisprogramconvertsintegersofvarious 2 *sizestostringsinvariousradixes. 3 */ 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 #include<stdio.h> 6 int main(void) 7 { 8 char buffer[20]; 9 int i = 3445; 10 long l = -344115L; 11 unsigned long ul = 1234567890UL; 12 _itoa(i, buffer, 10); 13 printf("String of integer%d(radix10):%s ", i, buffer); 14 _itoa(i, buffer, 16); 15 printf("String of integer%d(radix16):0x%s ", i, buffer); 16 _itoa(i, buffer, 2); 17 printf("String of integer%d(radix2):%s ", i, buffer); 18 _ltoa(l, buffer, 16); 19 printf("String of long int%ld(radix16):0x%s ", l, buffer); 20 _ultoa(ul, buffer, 16); 21 printf("String of unsigned long%lu(radix16):0x%s ", ul, buffer); 22 getchar(); 23 return 0; 24 }
输出结果: 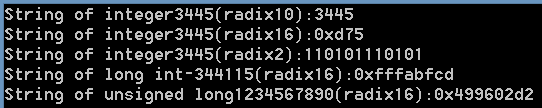
6、模拟实现此函数
1 char *my_itoa(int value, char *str, int radix) 2 { 3 int a[100] = { 0 }; 4 int sum = value; 5 char* cp = str; 6 int i = 0; 7 char zm[37] = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"; 8 if (radix < 2 || radix > 36)//增加了对错误的检测 9 { 10 printf("error!"); 11 return str; 12 } 13 if (sum < 0) //如果是负数,先转为正数 14 { 15 sum = -sum; 16 } 17 while (sum > 0)//从个位开始变为字符,直到最高位 18 { 19 a[i++] = zm[sum % radix]; 20 sum /= radix; 21 } 22 if (value < 0)//如果是负数,补上负号 23 { 24 *cp++ = '-'; 25 } 26 for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) 27 { 28 *cp++ = a[j]; //从高位到低位转换 29 } 30 *cp = '�';//最后加上字符串结束符 31 return str; 32 }
测试代码:
1 int main(void) 2 { 3 char buffer[20]; 4 int i = 3445; 5 long l = 344115L; 6 unsigned long ul = 1234567890UL; 7 my_itoa(i, buffer, 10); 8 printf("String of integer%d(radix10):%s ", i, buffer); 9 my_itoa(i, buffer, 16); 10 printf("String of integer%d(radix16):0x%s ", i, buffer); 11 my_itoa(i, buffer, 2); 12 printf("String of integer%d(radix2):%s ", i, buffer); 13 my_itoa(l, buffer, 16); 14 printf("String of long int%ld(radix16):0x%s ", l, buffer); 15 my_itoa(ul, buffer, 16); 16 printf("String of unsigned long%lu(radix16):0x%s ", ul, buffer); 17 getchar(); 18 return 0; 19 }
输出结果:
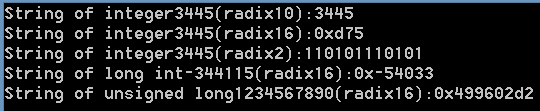
附:常用十进制的转换模拟函数
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 //反转字符串 3 char *reverse(char *s) 4 { 5 char temp; 6 char *p = s; //p指向s的头部 7 char *q = s; //q指向s的尾部 8 while(*q) 9 ++q; 10 q--; 12 //交换移动指针,直到p和q交叉 13 while(q > p) 14 { 15 temp = *p; 16 *p++ = *q; 17 *q-- = temp; 18 } 19 return s; 20 } 22 /* 23 * 功能:整数转换为字符串 24 * char s[] 的作用是存储整数的每一位 25 */ 26 char *my_itoa(int n) 27 { 28 int i = 0,isNegative = 0; 29 static char s[100]; //必须为static变量,或者是全局变量 30 if((isNegative = n) < 0) //如果是负数,先转为正数 31 { 32 n = -n; 33 } 34 do //从各位开始变为字符,直到最高位,最后应该反转 35 { 36 s[i++] = n%10 + '0'; 37 n = n/10; 38 }while(n > 0); 39 40 if(isNegative < 0) //如果是负数,补上负号 41 { 42 s[i++] = '-'; 43 } 44 s[i] = '�'; //最后加上字符串结束符 45 return reverse(s); 46 } 48 int main(void) 49 { 50 int m; 51 printf("请输入int型整数m:"); 52 scanf("%d",&m); 53 printf("整数=%d,字符串=%s ",m,my_itoa(m)); 54 return 0; 55 }
输出结果: