扫描线分类两种,一种离散y轴,一种离散x轴。以离垂直x轴的直线为例:
将每个离散的线之间作为一个线段树的叶子节点,然后从最小与x轴平行的直线开始,区覆盖线段树的叶子节点,
也就是两根与y轴平行的直线之间所夹的空间,这段空间的长度乘以你的扫描线之间的距离(与x轴平行的直线),就是面积,
看图吧,图下的数字是代表覆盖的次数,矩形的下底线扫描覆盖节点时为 value +=1,上边线扫描 value -= 1;
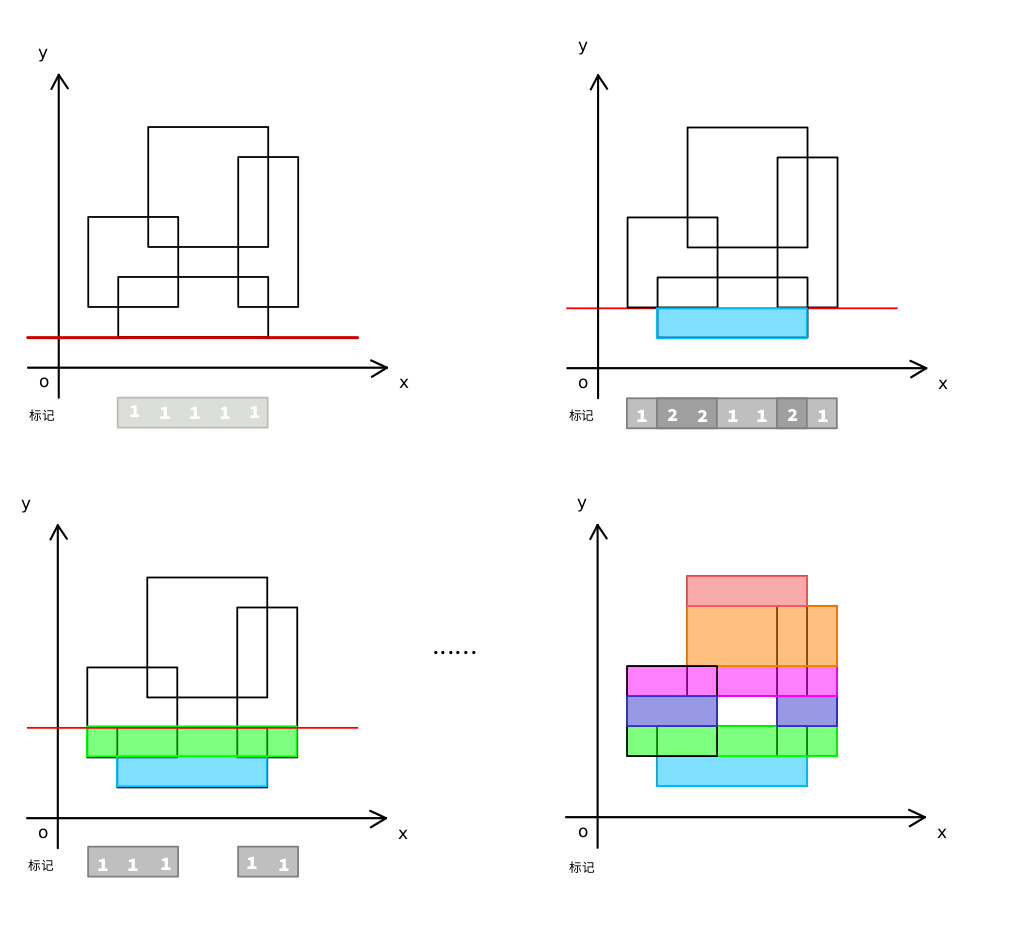
代码如下
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 205;
struct node
{
int r, l, lazy;
double dat;
}tr[maxn<<2];
struct bian
{
double x, a, b;
int k;
}egde[maxn<<1];
int n;
double yy[maxn << 1];
map<double, int> mp;
//注意节点为 l+1=r,离散化会丢失离散节点之间的信息
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p].dat = 0;
tr[p].l = l;tr[p].r = r;
tr[p].lazy = 0;
if (l == r - 1)return;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(p << 1, l, mid);
build(p << 1 | 1, mid, r);
}
inline void push(int p)
{
if (tr[p].lazy)tr[p].dat = yy[tr[p].r] - yy[tr[p].l];
else if (tr[p].l + 1 == tr[p].r)tr[p].dat = 0;
else tr[p].dat = tr[p << 1].dat + tr[p << 1 | 1].dat;
}
void updata(int p, int l, int r, int k)
{
if (tr[p].l > r || tr[p].r < l) return;
if (l <= tr[p].l && tr[p].r <= r)
{
tr[p].lazy += k;
push(p);
return;
}
int mid = (tr[p].l + tr[p].r) >> 1;
if (l <= mid) updata(p << 1, l, r, k);
if (mid < r) updata(p << 1 | 1, l, r, k);
push(p);
}
bool cmp(const bian& a, const bian& b)
{
if(a.x != b.x)return a.x < b.x;
return a.k > b.k;
}
int main(void)
{
/*freopen("atlantis.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("atlantis.out", "w", stdout);*/
for (int cas = 1;~scanf("%d", &n)&&n; ++cas)
{
double ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
double x, y, a, b;
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &x, &y, &a, &b);
egde[i << 1] = { x, y, b, 1 };
egde[i << 1 | 1] = { a, y, b, -1 };
yy[i << 1] = y;yy[i << 1 | 1] = b;
}
sort(yy, yy + (n << 1));sort(egde, egde + (n << 1), cmp);
int tot = unique(yy, yy + (n << 1)) - yy;
for (int i = 0; i < tot; ++i)mp[yy[i]] = i;
build(1, 0, tot - 1);
updata(1, mp[egde[0].a], mp[egde[0].b], egde[0].k);
for (int i = 1; i < (n << 1); ++i)
{
ans += (egde[i].x - egde[i - 1].x) * tr[1].dat;
updata(1, mp[egde[i].a], mp[egde[i].b], egde[i].k);
}
printf("Test case #%d
Total explored area: %.2lf
", cas, ans);
}
return 0;
}