Unity3D ShaderLab 使用贴图对模型的高光进行遮罩
前面研究了高光效果的实现,再说说现很多游戏用到的高光贴图技术,因为它可以让3D美工更容易控制最终的视觉效果。
这也就为我们提供了另外的方式,我们可以在同一个着色器上实现垫型表面和光亮表面,也可以使用贴图来控制镜面高光的范围或者高光强度,
以实现一个表面是广泛的镜面高光而另一面确是细小的高光。
新建一个shader,一个材质球。老规矩双击shader脚本,在编辑器中编写代码吧。
1.Properties:
Properties { _MainTint("Diffuse Tint",Color) = (1,1,1,1) _MainTex ("Base (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {} _SpecularColor("Specular Tint",Color)=(1,1,1,1) _SpecularMask("Specular Texture",2D)="white"{} _SpecularPower("Specular Power",Range(1,100))=3 }
2.SubShader中修改CGPROGRAM,加入输出结构体SurfaceMyOutput,修改Input结构体:
CGPROGRAM #pragma surface surf TexPhong sampler2D _MainTex; float4 _MainTint; float4 _SpecularColor; sampler2D _SpecularMask; float _SpecularPower; struct SurfaceMyOutput{ fixed3 Albedo; fixed3 Normal; fixed3 Emission; fixed3 SpecularColor; half Specular; fixed Gloss; fixed Alpha; }; struct Input { float2 uv_MainTex; float2 uv_SpecularMask; };
3.实现自定义光照模型LightingTexPhong
inline fixed4 LightingTexPhong(SurfaceMyOutput s,fixed3 lightDir,half3 viewDir, fixed atten){ float diff = dot(s.Normal,lightDir); float3 reflection = normalize(3.0*s.Normal*diff-lightDir); float spec = pow(max(0,dot(reflection,viewDir)), _SpecularPower)*s.Specular; float3 finalSpec = s.SpecularColor * spec*_SpecularColor.rgb; fixed4 c; c.rgb = (s.Albedo*_LightColor0.rgb*diff)+(_LightColor0.rgb*finalSpec); c.a = s.Alpha; return c; }
4.修改surf函数
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceMyOutput o) { float4 c = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex)*_MainTint; float4 specMask = tex2D(_SpecularMask,IN.uv_SpecularMask)*_SpecularColor; o.Albedo = c.rgb; o.Specular = specMask.r; o.SpecularColor = specMask.rgb; o.Alpha = c.a; }
修改完毕后,返回unity设置参数,最终效果如下。
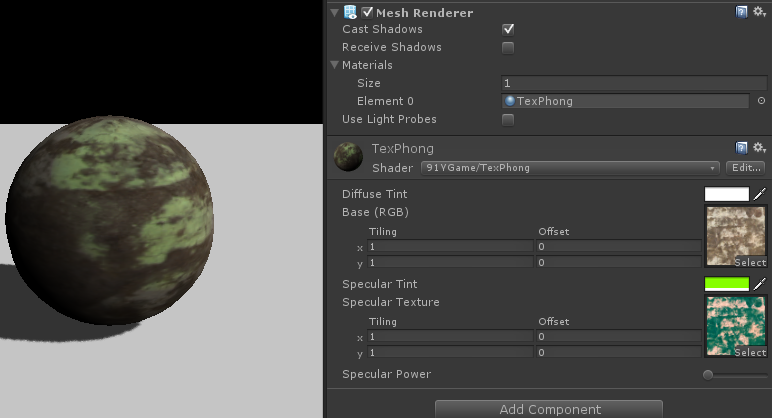
在上面的代码编写过程中,我们需要将表面函数的信息传递给给光照函数,因为我们在光照函数内部不能得到一个物体表面的uv,
所以我们需要通过input结构体来访问数据,唯一途径就是使用surf函数,为了建立数据关系,我们自定义了结构体SurfaceMyOutput,
用这个结构体作为容器存储表面着色器中所有最终数据。这样光照函数和surf函数都可以访问它的内部数据。
然后,我们告诉surf函数和光照函数使用output结构体是我们自定义的SurfaceMyOutput结构体,而不是着色器内置的。
最后我们只需要使用tex2D函数就可以访问纹理讯息返回值,直接传递给SurfaceMyOutput结构体,完成了这些,我们就可以在光照函数中访问讯息纹理。
code start --------------------------------------------------------------------------
Shader "91YGame/TexPhong" { Properties { _MainTint("Diffuse Tint",Color) = (1,1,1,1) _MainTex ("Base (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {} _SpecularColor("Specular Tint",Color)=(1,1,1,1) _SpecularMask("Specular Texture",2D)="white"{} _SpecularPower("Specular Power",Range(0.5,100))=3 } SubShader { Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" } LOD 200 CGPROGRAM #pragma surface surf TexPhong sampler2D _MainTex; float4 _MainTint; float4 _SpecularColor; sampler2D _SpecularMask; float _SpecularPower; struct SurfaceMyOutput{ fixed3 Albedo; fixed3 Normal; fixed3 Emission; fixed3 SpecularColor; half Specular; fixed Gloss; fixed Alpha; }; struct Input { float2 uv_MainTex; float2 uv_SpecularMask; }; inline fixed4 LightingTexPhong(SurfaceMyOutput s,fixed3 lightDir,half3 viewDir, fixed atten){ float diff = dot(s.Normal,lightDir); float3 reflection = normalize(3.0*s.Normal*diff-lightDir); float spec = pow(max(0,dot(reflection,viewDir)), _SpecularPower)*s.Specular; float3 finalSpec = s.SpecularColor * spec*_SpecularColor.rgb; fixed4 c; c.rgb = (s.Albedo*_LightColor0.rgb*diff)+(_LightColor0.rgb*finalSpec); c.a = s.Alpha; return c; } void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceMyOutput o) { float4 c = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex)*_MainTint; float4 specMask = tex2D(_SpecularMask,IN.uv_SpecularMask)*_SpecularColor; o.Albedo = c.rgb; o.Specular = specMask.r; o.SpecularColor = specMask.rgb; o.Alpha = c.a; } ENDCG } FallBack "Diffuse" }
code end ---------------------------------------------------------------------------