.ini 文件是Initialization File的缩写,即初始化文件,是windows的系统配置文件所采用的存储格式,来配置应用软件以实现不同用户的要求。配置文件有很多种如ini配置文件,XML配置文件,系统注册表等。在早期的windows桌面系统中主要是用ini文件作为系统的配置文件,从win95以后开始转向使用注册表,但是还有很多系统配置是使用INI文件的。其实INI文件就是简单的txt文件,只不过这种txt文件要遵循一定的INI文件格式。
ini文件由节、键、值组成:
节
[section]
参数(键=值)
name=value
注解
注解使用分号表示(;)。在分号后面的文字,直到该行结尾都全部为注解。
ini文件中可以存在多个小节(Section),每个小节的开始用包括在一对方括号中的小节名称指定,不同的小节不能重名,一个小节的内容从小节名称的下一行开始,直到下一个小节开始为止。用户程序可以按照自己的需求建立多个小节。因为ini文件可能是项目中共用的,所以使用[section]来区分不同用途的参数区。例如:[Section1 Name]表示传感器灵敏度参数区;[Section2 Name]表示测量通道参数区等等。INI所包含的最基本的“元素”就是parameter,每一个parameter都有一个name和一个value,name和value是由等号“=”隔开,name在等号的左边。如:name = value
Windows提供了一系列函数(包含winbase.h或windows.h头文件即可使用)来读写ini文件:
- 将信息写入.INI文件中
BOOL WritePrivateProfileStringA( LPCSTR lpAppName, // section name LPCSTR lpKeyName, // key name. If this parameter is NULL, the entire section, including all entries within the section, is deleted. LPCSTR lpString, // string to add. If this parameter is NULL, the key pointed to by the lpKeyName parameter is deleted. LPCSTR lpFileName // initialization file );
BOOL WritePrivateProfileSectionW( LPCWSTR lpAppName, LPCWSTR lpString, LPCWSTR lpFileName );
当这些参数全部指定为字符串的时候,函数将在指定INI文件的指定小节中写入“键名=键值”格式的行;当指定的INI文件、文件中的小节和小节中的键名都已经存在的时候,函数用新键值替换原来的键值;当指定的INI文件存在而小节不存在的时候,函数自动创建小节并将键写入;如果连指定的INI文件也不存在的话,函数会自动创建文件。总之,程序不必考虑INI文件是否存在,小节是否存在或键值定义是否存在等情况,只要调用WritePrivateProfileString函数就可以保证配置信息被正确保存。
WritePrivateProfileString函数也可以用来删除键或者小节,当lpAppName和lpKeyName参数指定了小节名称和键名,而lpString参数指定为NULL的时候,函数将指定的键删除。也可以将lpKeyName和lpString参数全部指定为NULL,而lpAppName参数指定小节名称,那么将会删除lpAppName参数指定的小节。
注意如果定义了UNICODE使用的函数实际上为WritePrivateProfileStringW。可以使用_T()宏或TEXT()宏:TEXT() 在定义 UNICODE 情况下使用 UNICODE 字符,否则使用 ANSI 字符。
#ifdef UNICODE #define WritePrivateProfileString WritePrivateProfileStringW #else #define WritePrivateProfileString WritePrivateProfileStringA #endif // !UNICODE
- 将信息从INI文件中读入程序中的变量
DWORD GetPrivateProfileString(
LPCTSTR lpAppName, // If this parameter is NULL, the GetPrivateProfileString function copies all section names in the file to the supplied buffer.
LPCTSTR lpKeyName, // If this parameter is NULL, all key names in the section specified by the lpAppNameparameter are copied to the buffer specified by the lpReturnedString parameter.
LPCTSTR lpDefault, // If the lpKeyName key cannot be found in the initialization file, GetPrivateProfileString copies the default string to the lpReturnedString buffer.
LPTSTR lpReturnedString, // destination buffer
DWORD nSize, // size of destination buffer
LPCTSTR lpFileName // The name of the initialization file
);
函数的返回值是返回到缓冲区中的字符串长度。lpReturnedString参数指向一个缓冲区,函数在这里返回获取的键值字符串,缓冲区的长度用nSize参数指定,当缓冲区的长度太小以至于无法容纳返回的字符串时,字符串会被截止到nSize-1的长度后返回,余下的一个字节用来存放一个a null character(0字符:'�')做结尾。lpDefault参数指向一个默认字符串,当指定的键无法找到的时候,函数将这个字符串拷贝到返回缓冲区中。
GetPrivateProfileString还有两种特殊用法:
(1)当lpAppName参数指定为NULL的时候,函数在缓冲区中返回的是全部小节名称的列表,每个小节名以0结尾,全部的名称列表再以一个附加的0结束,返回到缓冲区中的数据格式如下所示:
小节名称1,0,小节名称2,0,…,小节名称n,0,0
(2)当lpAppName参数指定了小节名称,而lpKeyName参数指定为NULL的时候,函数在缓冲区中返回该小节的全部键名列表,每个键名以0结尾,全部列表后面再以一个附加的0结束,如下所示:
键名1,0,键名2,0,…,键名n,0,0
因此可以用这两种方式来枚举INI文件中的节名以及各个节中的键名。
下面代码在VS项目目录中创建了一个test.ini的文件:
#include <windows.h> int main() { WritePrivateProfileString(TEXT("Section1"), TEXT("FirstKey"), TEXT("Value1"), TEXT(".\test.ini")); WritePrivateProfileString(TEXT("Section1"), TEXT("SecondKey"), TEXT("Value2"), TEXT(".\test.ini")); // Test TCHAR inBuf[80]; int ret = GetPrivateProfileString(TEXT("Section1"), TEXT("FirstKey"), TEXT("Error: failed"), inBuf, 80, TEXT(".\test.ini")); _tprintf(TEXT("Key: %s "), inBuf); return 0; }
test.ini文件内容如下:
[Section1]
FirstKey=Value1
SecondKey=Value2
GetPrivateProfileString函数获取FirstKey的值Value后将其打印在屏幕上,输出为:
Key: Value1
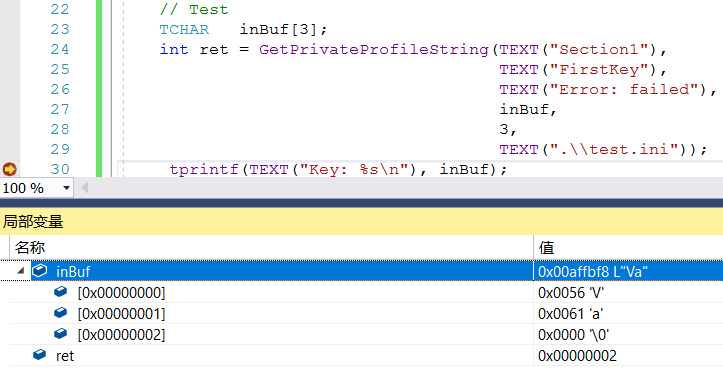
如果将接收数组长度改为3,可以看到结果被截断,GetPrivateProfileString函数返回值为3-1=2:
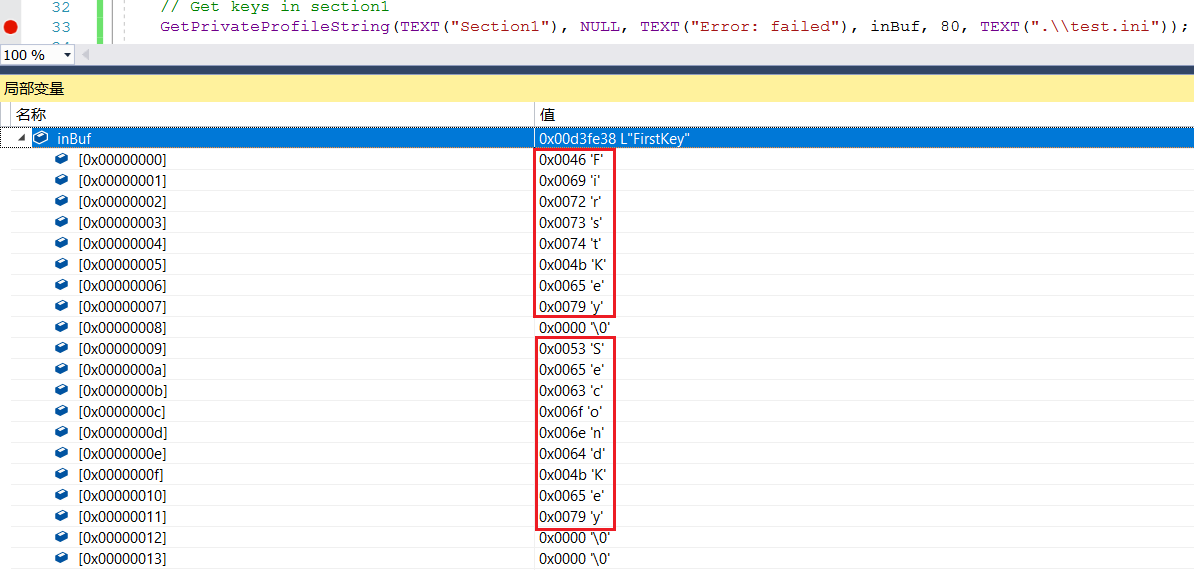
当lpKeyName参数指定为NULL的时候,函数在缓冲区中返回该小节的全部键名列表:
当lpAppName参数指定为NULL的时候,函数在缓冲区中返回的是全部小节名称的列表:

如果key的值为整数,那么还可以使用GetPrivateProfileInt函数来读取。该函数返回键值对应的整数
UINT GetPrivateProfileInt( LPCTSTR lpAppName, LPCTSTR lpKeyName, INT nDefault, //The default value to return if the key name cannot be found in the initialization file. LPCTSTR lpFileName );
比如下面的ini文件,可以用GetPrivateProfileInt函数获取Section2中AnotherKey的值,将返回整型数字2。如果获取其它section中的键值将返回默认值。
[Section1]
FirstKey=Value1
SecondKey=Value2
[Section2]
AnotherKey=2
代码如下:

#include <windows.h> int main() { WritePrivateProfileString(TEXT("Section1"), TEXT("FirstKey"), TEXT("Value1"), TEXT(".\test.ini")); WritePrivateProfileString(TEXT("Section1"), TEXT("SecondKey"), TEXT("Value2"), TEXT(".\test.ini")); WritePrivateProfileString(TEXT("Section2"), TEXT("AnotherKey"), TEXT("2"), TEXT(".\test.ini")); // Test TCHAR inBuf[80]; int ret = GetPrivateProfileString(TEXT("Section1"), TEXT("FirstKey"), TEXT("Error: failed"), inBuf, 80, TEXT(".\test.ini")); _tprintf(TEXT("Key: %s "), inBuf); // Get keys in section1 GetPrivateProfileString(TEXT("Section1"), NULL, TEXT("Error: failed"), inBuf, 80, TEXT(".\test.ini")); // Retrieves an integer associated with a key in the specified section of an initialization file. UINT i = GetPrivateProfileInt(TEXT("Section2"), TEXT("AnotherKey"), 0, TEXT(".\test.ini")); printf("integer value: %d", i); return 0; }
参考:
