源地址(相关案例在视频下方):http://cookdata.cn/auditorium/course_room/10020/
《机器学习十讲》——第九讲(深度学习)
应用
图像识别:IMAGENET。
机器翻译:Google神经机器翻译系统。
语音识别:
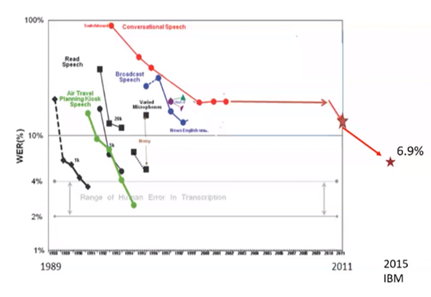
以往GMM-HMM传统方法一直未有突破,2011年使用DNN后获得较大突破,2015年,IBM再次将错误率降低到6.9%,接近人类的平均水平(4%)
游戏:DeepMind团队开发的自我学习玩游戏的系统。
发展原因
大规模高质量标注数据集出现:IMAGENET
并行运算(如GPU)的发展
更好的非线性激活函数的使用:ReLU代替Logistic
更多优秀的网络结构的发明:ResNet,GoogleNet和AlexNet
深度学习开发平台的发展:TensorFlow,PyTorch和MXNet等
新的正则化技术出现:批标准化,Dropout等
更多稳健的优化算法:SGD的变种:RMSprop,Adam等。
概念
神经元与感知机:

由输入空间到输出空间的如下函数: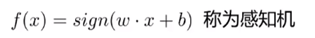
多层感知机(MLP)
定义:多个神经元以全连接层次相连,也称为前馈神经网络。
万能逼近原理:MLP能够逼近任何函数
函数逼近:![]()
误差函数:

由于深度学习的数据量非常大,所以之前的一些算法不能使用,可以使用随机梯度下降法SGD的一些变种。
梯度计算:后向传播BP

困境:
目标函数通常为非凸函数;极容易陷入局部最优解;随着网络层数增加,容易发生梯度消失或梯度爆炸问题。
机器学习与深度学习的区别:

机器学习需要人工选取特征;深度学习会自动学习有用的特征。
三个·思想:
特征学习(图像识别为例):深度学习通过层次化的学习方式得到图像特征。
可以将深度学习视为非线性函数逼近器:
深度学习通过一种深层网络结构,实现复杂函数逼近。
万能逼近原理:当隐层节点数目足够多时,具有一个隐层的神经网络,可以以任意精度逼近任意具有有限间断点的函数。
网络层数越多,需要的隐含节点数目指数减小。
端到端学习:从原始输入直接学习到目标,中间的函数和参数都是可学习。
典型网络结构:
卷积神经网络(VGG / GoogleNet / AlexNet / ResNet)
循环神经网络(RNN)
自编码器(Autoencoder)
生成对抗网络(GAN)
卷积神经网络(CNN):
适合处理网格型数据:物体识别,图片分类,2维网格。
全连接网络不适用于图像:像素大(参数爆炸)
CNN:卷积。(稀疏连接;参数共享;等变表示)
操作:
卷积操作: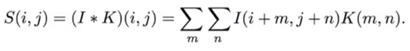
卷积和:
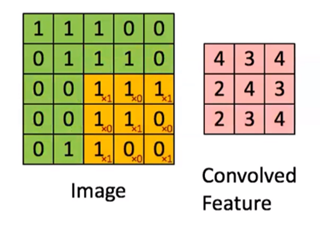
池化
对于局部转换不敏感;在局部节点内进行操作;池化->降采样
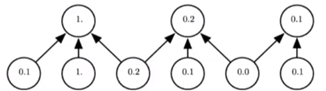
不敏感:图中下方最左0.1改成0.2,0.3不会影响上方1.的变动
最大池化

CNN完整结构:

AlexNet:

VGG:
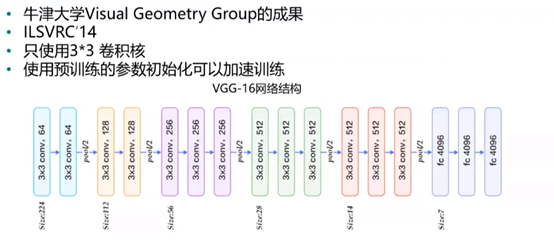
GoogleNet:
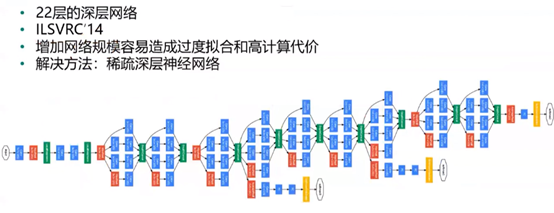
ResNet:

RNN:
适合处理训练型数据:自然语言处理等领域。
GAN:

案例——基于卷积神经网络的人脸识别
#使用sklearn的datasets模块在线获取Olivetti Faces数据集。 from sklearn.datasets import fetch_olivetti_faces faces = fetch_olivetti_faces() #打印 faces

该数据集包括四个部分:DESCR主要介绍数据来源;data以一维向量的形式存储了数据集中的400张图像;images以二维矩阵的形式存储了数据集中的400张图像;target存储了数据集中400张图像的类别信息,类别为0-39
#数据结构与类型 print("The shape of data:",faces.data.shape, "The data type of data:",type(faces.data)) print("The shape of images:",faces.images.shape, "The data type of images:",type(faces.images)) print("The shape of target:",faces.target.shape, "The data type of target:",type(faces.target))

#使用matshow输出部分人脸图片 import numpy as np rndperm = np.random.permutation(len(faces.images)) #将数据的索引随机打乱 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt %matplotlib inline plt.gray() fig = plt.figure(figsize=(9,4) ) for i in range(0,18): ax = fig.add_subplot(3,6,i+1 ) plt.title(str(faces.target[rndperm[i]])) #类标 ax.matshow(faces.images[rndperm[i],:]) #图片内容 plt.box(False) #去掉边框 plt.axis("off")#不显示坐标轴 plt.tight_layout()

#查看同一个人的不同人脸特点 labels = [2,11,6] #选取三个人 %matplotlib inline plt.gray() fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12,4) ) for i in range(0,3): faces_labeli = faces.images[faces.target == labels[i]] for j in range(0,10): ax = fig.add_subplot(3,10,10*i + j+1 ) ax.matshow(faces_labeli[j]) plt.box(False) #去掉边框 plt.axis("off")#不显示坐标轴 plt.tight_layout()

#将数据集划分为训练集和测试集两部分,注意要按照图像标签进行分层采样 # 定义特征和标签 X,y = faces.images,faces.target # 以5:5比例随机地划分训练集和测试集 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.5,stratify = y,random_state=0) # 记录测试集中出现的类别,后期模型评价画混淆矩阵时需要 #index = set(test_y)
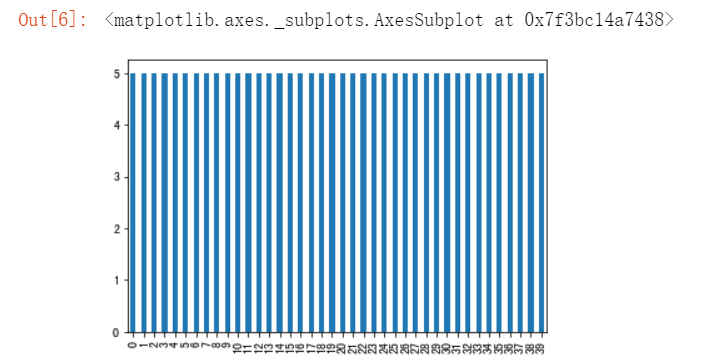
#使用柱状图显示训练集中40人每个人有几张图片 import pandas as pd pd.Series(train_y).value_counts().sort_index().plot(kind="bar")
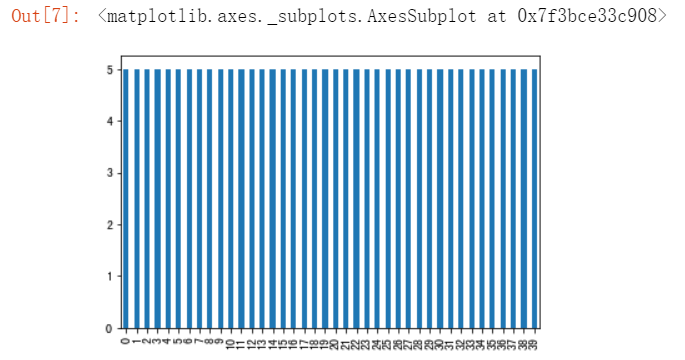
#在测试集中每个人有几张图片 pd.Series(test_y).value_counts().sort_index().plot(kind="bar")
# 转换数据维度,模型训练时要用 train_x = train_x.reshape(train_x.shape[0], 64, 64, 1) test_x = test_x.reshape(test_x.shape[0], 64, 64, 1)
建立卷积神经网络人脸识别模型——CNN网络结构

#从keras的相应模块引入需要的对象。 import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') #该行代码的作用是隐藏警告信息 import tensorflow as tf import tensorflow.keras.layers as layers import tensorflow.keras.backend as K K.clear_session() #逐层搭建卷积神经网络模型。此处使用了函数式api inputs = layers.Input(shape=(64,64,1), name='inputs') conv1 = layers.Conv2D(32,3,3,padding="same",activation="relu",name="conv1")(inputs) #卷积层32 maxpool1 = layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),name="maxpool1")(conv1) #池化层1 conv2 = layers.Conv2D(64,3,3,padding="same",activation="relu",name="conv2")(maxpool1) #卷积层64 maxpool2 = layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),name="maxpool2")(conv2) #池化层2 flatten1 = layers.Flatten(name="flatten1")(maxpool2) #拉成一维 dense1 = layers.Dense(512,activation="tanh",name="dense1")(flatten1) dense2 = layers.Dense(40,activation="softmax",name="dense2")(dense1) #40个分类 model = tf.keras.Model(inputs,dense2) #网络结构打印。 model.summary()

#模型编译,指定误差函数、优化方法和评价指标。使用训练集进行模型训练。 model.compile(loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', optimizer="Adam", metrics=['accuracy']) model.fit(train_x,train_y, batch_size=20, epochs=30, validation_data=(test_x,test_y),verbose=2)
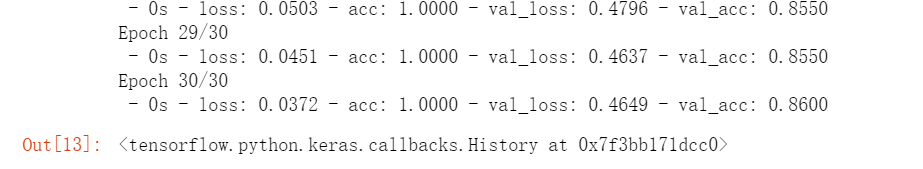
#评价 score = model.evaluate(test_x, test_y) print('Test loss:', score[0]) print('Test accuracy:', score[1])

使用TensorFlow进行数据增强,再进行一次训练
#数据增强——ImageDataGenerator from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator # 定义随机变换的类别及程度 datagen = ImageDataGenerator( rotation_range=0, # 图像随机转动的角度 width_shift_range=0.01, # 图像水平偏移的幅度 height_shift_range=0.01, # 图像竖直偏移的幅度 shear_range=0.01, # 逆时针方向的剪切变换角度 zoom_range=0.01, # 随机缩放的幅度 horizontal_flip=True, fill_mode='nearest')
#使用增强后的数据进行模型训练与评价 inputs = layers.Input(shape=(64,64,1), name='inputs') conv1 = layers.Conv2D(32,3,3,padding="same",activation="relu",name="conv1")(inputs) maxpool1 = layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),name="maxpool1")(conv1) conv2 = layers.Conv2D(64,3,3,padding="same",activation="relu",name="conv2")(maxpool1) maxpool2 = layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2,2),name="maxpool2")(conv2) flatten1 = layers.Flatten(name="flatten1")(maxpool2) dense1 = layers.Dense(512,activation="tanh",name="dense1")(flatten1) dense2 = layers.Dense(40,activation="softmax",name="dense2")(dense1) model2 = tf.keras.Model(inputs,dense2) model2.compile(loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', optimizer="Adam", metrics=['accuracy']) # 训练模型 model2.fit_generator(datagen.flow(train_x, train_y, batch_size=200),epochs=30,steps_per_epoch=16, verbose = 2,validation_data=(test_x,test_y)) # 模型评价 score = model2.evaluate(test_x, test_y) print('Test score:', score[0]) print('Test accuracy:', score[1])
