1.三个法宝
①存储程序计算机工作模型,计算机系统最最基础性的逻辑结构;
②函数调用堆栈,堆栈完成了计算机的基本功能:函数的参数传递机制和局部变量存取 ;
③中断,多道程序操作系统的基点,没有中断机制程序只能从头一直运行结束才有可能开始运行其他程序。
2.堆栈的基本功能:
(1)函数调用框架、传递参数(32位)、保存返回地址(如eax保存返回值/内存地址)、提供局部变量空间
(2)与堆栈相关的寄存器:esp和ebp
与堆栈相关的操作:push(入栈时esp指针会减4)、pop(出栈时esp指针会加4)
(3)CS:eip总是指向下一条指令的地址
C代码中嵌入汇编代码
一、实验要求
完成一个简单的时间片轮转多道程序内核代码,代码见视频中或从mykernel找。
详细分析该精简内核的源代码并给出实验截图,撰写一篇署名博客,并在博客文章中注明“真实姓名(与最后申请证书的姓名务必一致) + 原创作品转载请注明出处 + 《Linux内核分析》MOOC课程http://mooc.study.163.com/course/USTC-1000029000 ”,博客内容的具体要求如下:
题目自拟,内容围绕操作系统是如何工作的进行;
博客中需要使用实验截图
博客内容中需要仔细分析进程的启动和进程的切换机制
总结部分需要阐明自己对“操作系统是如何工作的”理解。
二、实验过程
首先通过cd LinuxKernel/Linux-3.9.4,“cd”表示进入目录Linux-3.9.4,用rm -rf mykernel命令强力删除mykernel。使用命令patch -pl< ../mykernel_for_linux3.9.4sc.patch,patch命令用于为特定软件包打补丁,该命令使用diff命令对源文件进行操作。格式:patch [选项] [原始文件 [补丁文件]

在Linux系统中,专门提供了一个make命令来自动维护目标文件,与手工编译和连接相比,make命令的优点在于他只更新修改过的文件(在Linux中,一个文件被创建或更新后有一个最后修改时间,make命令就是通过这个最后修改时间来判断此文件是否被修改),(make还是不太懂)使用命令qemu -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage搭建目标环境

通过cd mykernel ,打开mykernel目录,用ls命令看到目录内容中包括 mymain.c ,myinterrupt.c,使用命令vi mymain.c以及vi myinterrupt.c可以看到代码
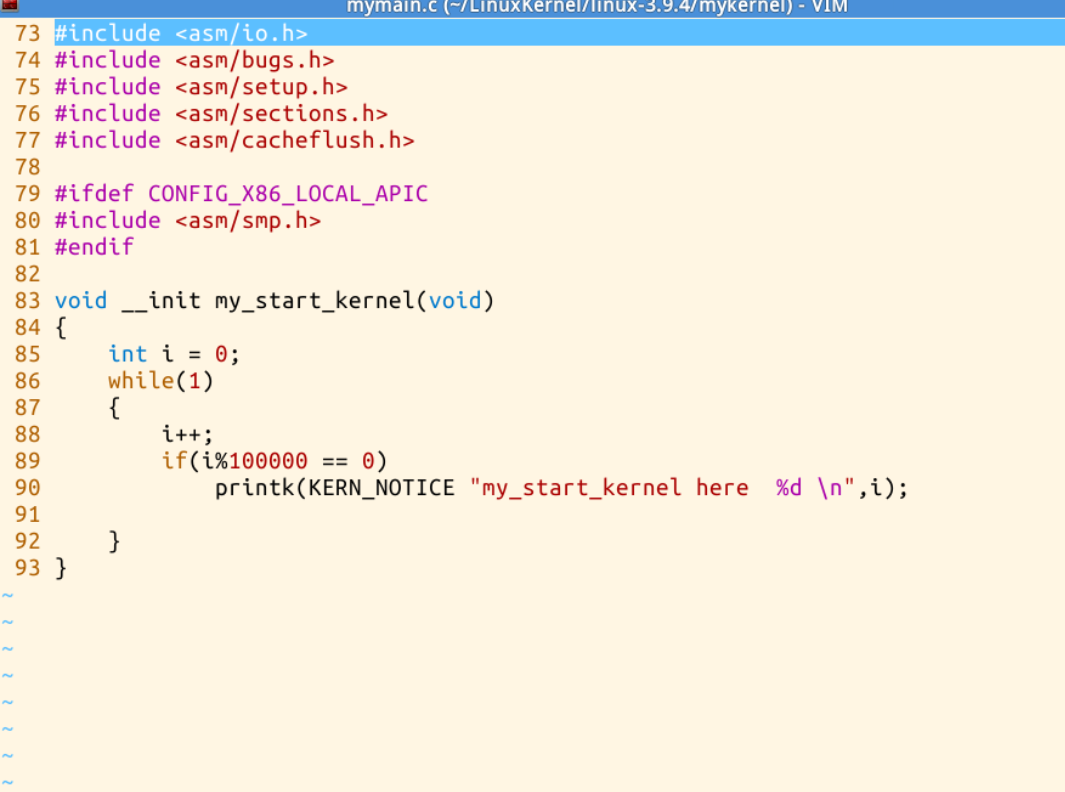
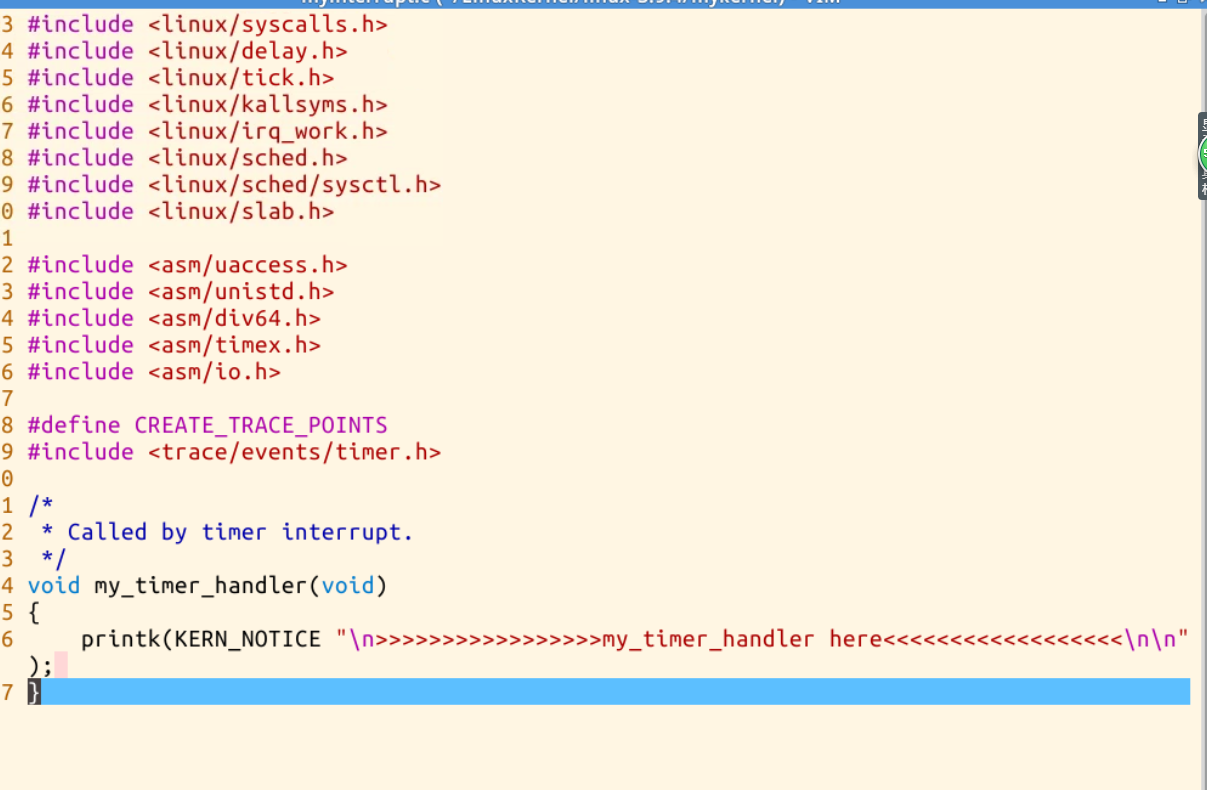
可以看到每当i增加100000会执行(printf函数输出my_ start_ kernel _ here …)时会触发一次时钟中断,在由时钟中断处理函数输出(>..>>my_timer_handler<<…<)
二 操作系统内核源代码分析
首先是mypcb.h
+#define MAX_TASK_NUM 10 // max num of task in system //进程参与内核时间片转,这个系统最多有10个进程
+#define KERNEL_STACK_SIZE 10248 //每个进程栈的大小
+#define PRIORITY_MAX 30 //priority range from 0 to 30
+
+/ CPU-specific state of this task */
+struct Thread {
- unsigned long ip;//point to cpu run address //用于eip的保存
- unsigned long sp;//point to the thread stack's top address //用于esp的保存
- //todo add other attrubte of system thread
+};
+//PCB Struct
+typedef struct PCB{ //用于表示一个进程,定义了进程管理相关的数据结构 - int pid; // pcb id //进程编号
- volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
- char stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE];// each pcb stack size is 1024*8
- /* CPU-specific state of this task */
- struct Thread thread;
- unsigned long task_entry;//the task execute entry memory address ////进程第一次执行开始的地方
- struct PCB *next;//pcb is a circular linked list //用于构造进程链表
- unsigned long priority;// task priority
- //todo add other attrubte of process control block
+}tPCB;
+//void my_schedule(int pid);
+void my_schedule(void); //调用了my_schedule
接下来是mymain.c
+tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
+tPCB * my_current_task = NULL;
+volatile int my_need_sched = 0; //定义一个标志,用来判断是否需要调度
+
+void my_process(void);
+unsigned long get_rand(int );
+
+void sand_priority(void)
+{
- int i;
- for(i=0;i<MAX_TASK_NUM;i++)
-
task[i].priority=get_rand(PRIORITY_MAX);
+}
+void __init my_start_kernel(void)
+{
- int pid = 0; ////初始化一个进程0
- /* Initialize process 0*/
- task[pid].pid = pid;
- task[pid].state = 0;/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
- // set task 0 execute entry address to my_process
- task[pid].task_entry = task[pid].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process;
- task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];
- task[pid].next = &task[pid];
- /*fork more process */
- for(pid=1;pid<MAX_TASK_NUM;pid++)
- {
-
memcpy(&task[pid],&task[0],sizeof(tPCB)); -
task[pid].pid = pid; -
task[pid].state = -1; -
task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1]; - task[pid].priority=get_rand(PRIORITY_MAX);//each time all tasks get a random priority //每个进程都有自己的堆栈,把创建好的新进程放到进程列表的尾部
- }
- task[MAX_TASK_NUM-1].next=&task[0];
- printk(KERN_NOTICE " system begin :>>>process 0 running!!!<<< ");
- /* start process 0 by task[0] */
- pid = 0;
- my_current_task = &task[pid];
+asm volatile( -
"movl %1,%%esp " /* set task[pid].thread.sp to esp */ -
"pushl %1 " /* push ebp */ -
"pushl %0 " /* push task[pid].thread.ip */ -
"ret " /* pop task[pid].thread.ip to eip */ -
"popl %%ebp " -
: -
: "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp) /* input c or d mean %ecx/%edx*/
+);
+}
+void my_process(void) //定义所有进程的工作,if语句表示循环1000万次才有机会判断是否需要调度。
+{
- int i = 0;
- while(1)
- {
-
i++; -
if(i%10000000 == 0) -
{ -
if(my_need_sched == 1) -
{ -
my_need_sched = 0; -
sand_priority(); -
my_schedule(); -
} -
} - }
+}//end of my_process
+//produce a random priority to a task
+unsigned long get_rand(max)
+{
- unsigned long a;
- unsigned long umax;
- umax=(unsigned long)max;
- get_random_bytes(&a, sizeof(unsigned long ));
- a=(a+umax)%umax;
- return a;
+}