20145327 《信息安全系统设计基础》第十周学习总结
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
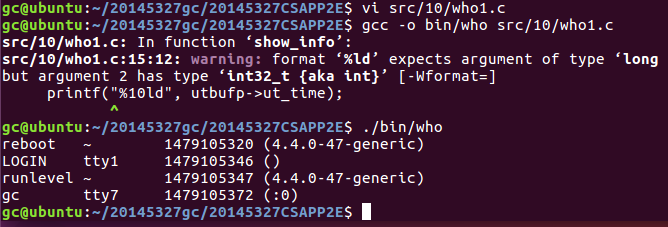
- who
这个代码的思想是,从UTMP_FILE文件中读取想要的信息到存储器中,然后再用标准输出函数打印到屏幕上,最后关闭文件。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <utmp.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define SHOWHOST
int show_info( struct utmp *utbufp )
{
printf("%-8.8s", utbufp->ut_name);
printf(" ");
printf("%-8.8s", utbufp->ut_line);
printf(" ");
printf("%10ld", utbufp->ut_time);
printf(" ");
#ifdef SHOWHOST
printf("(%s)", utbufp->ut_host);
#endif
printf("
");
return 0;
}
int main()
{
struct utmp current_record;
int utmpfd;
int reclen = sizeof(current_record);
/*打开UTMP_FILE读取信息,如果打开失败则输出失败信息。*/
if ( (utmpfd = open(UTMP_FILE, O_RDONLY)) == -1 ){
perror( UTMP_FILE );
exit(1);
}
/*读取信息到存储器中,reclen就是是读的字节数,然后再调用函数打印出来。*/
while ( read(utmpfd, ¤t_record, reclen) == reclen )
show_info(¤t_record);
close(utmpfd);
return 0;
}
- echostate
这个代码是用来检查命令行中的提示符是否显示的,如果显示,输入的命令都可见,不显示则表示输入的命令不可见,具体例子结合setecho代码一起
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <termios.h>
int main()
{
struct termios info;
int rv;
rv = tcgetattr( 0, &info ); /* read values from driver */
if ( rv == -1 ){
perror( "tcgetattr");
exit(1);
}
if ( info.c_lflag & ECHO )
printf(" echo is on , since its bit is 1
");
else
printf(" echo is OFF, since its bit is 0
");
return 0;
}
- setecho
这个与上面对应,改变echo的状态
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <termios.h>
#define oops(s,x) { perror(s); exit(x); }
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct termios info;
if ( argc == 1 )
exit(0);
if ( tcgetattr(0,&info) == -1 )
oops("tcgettattr", 1);
if ( argv[1][0] == 'y' )
info.c_lflag |= ECHO ;/*打开提示符*/
else
info.c_lflag &= ~ECHO ;/*隐藏提示符*/
if ( tcsetattr(0,TCSANOW,&info) == -1 )
oops("tcsetattr",2);
return 0;
}
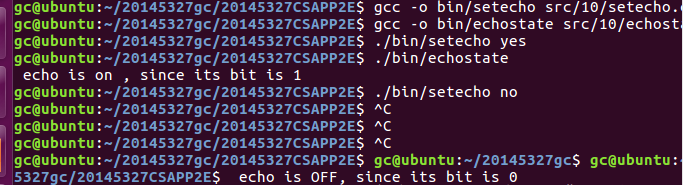
可以看出来,当echo is on的时候,输入的指令是可见的,当设置为off的时候,输入指令不可见
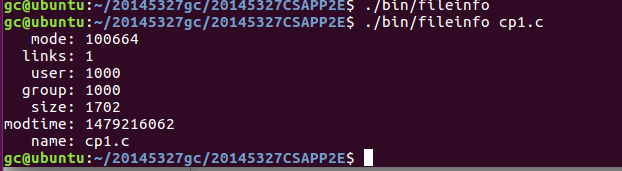
- fileinfo
用来实现显示文件信息,建立了一个stat数据结构。
先判断命令是否有操作数,有的话才能继续进行下去,如果没有报错就打印出来相关文件信息,报错就用perror将报错信息打印出来。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
void show_stat_info(char *, struct stat *);
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct stat info;
if (argc>1)
{
if( stat(argv[1], &info) != -1 ){
show_stat_info( argv[1], &info );
return 0;
}
else
perror(argv[1]);
}
return 1;
}
void show_stat_info(char *fname, struct stat *buf)
{
printf(" mode: %o
", buf->st_mode);
printf(" links: %d
", buf->st_nlink);
printf(" user: %d
", buf->st_uid);
printf(" group: %d
", buf->st_gid);
printf(" size: %d
", (int)buf->st_size);
printf("modtime: %d
", (int)buf->st_mtime);
printf(" name: %s
", fname );
}
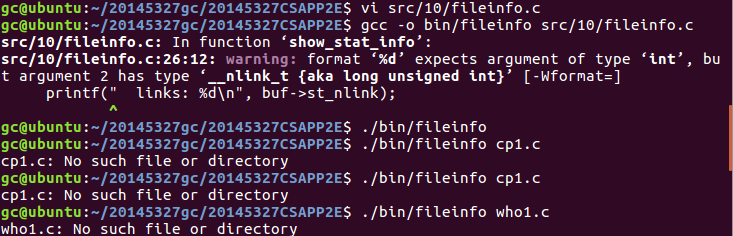
未能出结果,不知道为什么提示没有文件
路径问题后
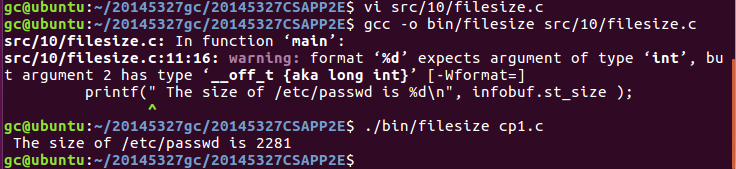
- filesize
用st_size成员来计算文件的字节数大小,先判断是否有错误,没有的话就调用。(老师给的代码中指定了查找/etc/passwd文件的大小,所以不管后面输入什么文件名,程序都只查找etc/passwd)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main()
{
struct stat infobuf;
if ( stat( "/etc/passwd", &infobuf) == -1 )
perror("/etc/passwd");
else
printf(" The size of /etc/passwd is %d
", infobuf.st_size );
}
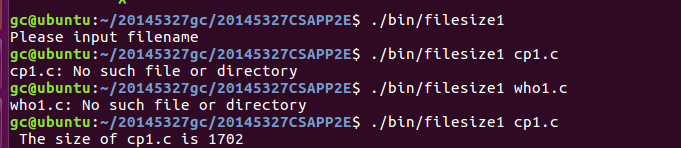
为了实现用户想查看的指定文件大小, 对代码进行如下修改:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdlib.h> //exit()
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
struct stat infobuf;
char *filename;
if (argc != 2) {
printf("Please input filename
");
exit(-1);
}
filename = argv[1];
if ( stat(filename, &infobuf) == -1 )
perror(filename);
else
printf(" The size of %s is %d
",filename, infobuf.st_size );
}
此时编译运行便能得到我们想要的结果:
- spwd
这个代码的功能是列出当前目录
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <dirent.h>
ino_t get_inode(char *);
void printpathto(ino_t);
void inum_to_name(ino_t , char *, int );
int main()
{
printpathto( get_inode( "." ) );
putchar('
');
return 0;
}
void printpathto( ino_t this_inode )
{
ino_t my_inode ;
char its_name[BUFSIZ];
if ( get_inode("..") != this_inode )
{
chdir( ".." );
inum_to_name(this_inode,its_name,BUFSIZ);
my_inode = get_inode( "." );
printpathto( my_inode );
printf("/%s", its_name );
}
}
void inum_to_name(ino_t inode_to_find , char *namebuf, int buflen)
{
DIR *dir_ptr;
struct dirent *direntp;
dir_ptr = opendir( "." );
if ( dir_ptr == NULL ){
perror( "." );
exit(1);
}
while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL )
if ( direntp->d_ino == inode_to_find )
{
strncpy( namebuf, direntp->d_name, buflen);
namebuf[buflen-1] = '�';
closedir( dir_ptr );
return;
}
fprintf(stderr, "error looking for inum %d
", (int) inode_to_find);
exit(1);
}
ino_t get_inode( char *fname )
{
struct stat info;
if ( stat( fname , &info ) == -1 ){
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot stat ");
perror(fname);
exit(1);
}
return info.st_ino;
}

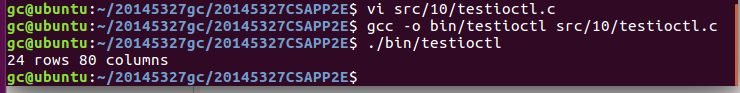
- testioctl
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
int main()
{
struct winsize size;
if( isatty(STDOUT_FILENO) == 0)
exit(1);
if (ioctl(STDOUT_FILENO, TIOCGWINSZ, &size) < 0) {
perror("ioctl TIOCGWINSZ error");
exit(1);
}
printf("%d rows %d columns
", size.ws_row, size.ws_col);
return 0;
}
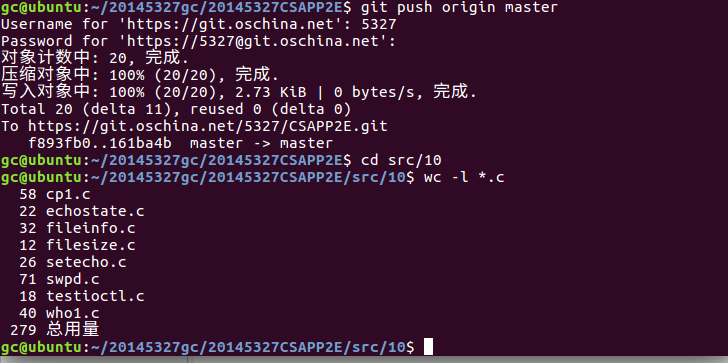
本周代码托管截图
其他(感悟、思考等,可选)
实践出真知
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 100/100 | 2/2 | 10/10 | |
| 第二周 | 100/200 | 1/3 | 20/30 | |
| 第三周 | 80/280 | 1/4 | 15/45 | |
| 第五周 | 100/380 | 1/5 | 15/60 | |
| 第六周 | 100/480 | 1/6 | 15/75 | |
| 第七周 | 20/500 | 1/7 | 15/90 | |
| 第八周 | 0/500 | 1/8 | 15/105 | |
| 第九周 | 61/561 | 1/9 | 20/125 | |
| 第十周 | 279/840 | 1/10 | 20/145 |