1.什么是AQS?
AQS的核心思想是基于volatile int state这样的volatile变量,配合Unsafe工具对其原子性的操作来实现对当前锁状态进行修改。同步器内部依赖一个FIFO的双向队列来完成资源获取线程的排队工作。
2.同步器的应用
同步器主要使用方式是继承,子类通过继承同步器并实现它的抽象方法来管理同步状态,对同步状态的修改或者访问主要通过同步器提供的3个方法:
- getState() 获取当前的同步状态
- setState(int newState) 设置当前同步状态
- compareAndSetState(int expect,int update) 使用CAS设置当前状态,该方法能够保证状态设置的原子性。
同步器可以支持独占式的获取同步状态,也可以支持共享式的获取同步状态,这样可以方便实现不同类型的同步组件。
同步器也是实现锁的关键,在锁的实现中聚合同步器,利用同步器实现锁的语义。
3.AQS同步队列
同步器AQS内部的实现是依赖同步队列(一个FIFO的双向队列,其实就是数据结构双向链表)来完成同步状态的管理。
当前线程获取同步状态失败时,同步器AQS会将当前线程和等待状态等信息构造成为一个节点(node)加入到同步队列,同时会阻塞当前线程;
当同步状态释放的时候,会把首节点中的线程唤醒,使首节点的线程再次尝试获取同步状态。AQS是独占锁和共享锁的实现的父类。
4.AQS锁的类别:分为独占锁和共享锁两种。
- 独占锁:锁在一个时间点只能被一个线程占有。根据锁的获取机制,又分为“公平锁”和“非公平锁”。等待队列中按照FIFO的原则获取锁,等待时间越长的线程越先获取到锁,这就是公平的获取锁,即公平锁。而非公平锁,线程获取的锁的时候,无视等待队列直接获取锁。ReentrantLock和ReentrantReadWriteLock.Writelock是独占锁。
- 共享锁:同一个时候能够被多个线程获取的锁,能被共享的锁。JUC包中ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock,CyclicBarrier,CountDownLatch和Semaphore都是共享锁。
JUC包中的锁的包括:Lock接口,ReadWriteLock接口;Condition条件,LockSupport阻塞原语。
AbstractOwnableSynchronizer/AbstractQueuedSynchronizer/AbstractQueuedLongSynchronizer三个抽象类,
ReentrantLock独占锁,ReentrantReadWriteLock读写锁。CountDownLatch,CyclicBarrier和Semaphore也是通过AQS来实现的。
下面是AQS和使用AQS实现的一些锁,以及通过AQS实现的一些工具类的架构图:

图 1.依赖AQS实现的锁和工具类
5.AQS同步器的结构:同步器拥有首节点(head)和尾节点(tail)。同步队列的基本结构如下:

图 1.同步队列的基本结构 compareAndSetTail(Node expect,Node update)
- 同步队列设置尾节点(未获取到锁的线程加入同步队列): 同步器AQS中包含两个节点类型的引用:一个指向头结点的引用(head),一个指向尾节点的引用(tail),当一个线程成功的获取到锁(同步状态),其他线程无法获取到锁,而是被构造成节点(包含当前线程,等待状态)加入到同步队列中等待获取到锁的线程释放锁。这个加入队列的过程,必须要保证线程安全。否则如果多个线程的环境下,可能造成添加到队列等待的节点顺序错误,或者数量不对。因此同步器提供了CAS原子的设置尾节点的方法(保证一个未获取到同步状态的线程加入到同步队列后,下一个未获取的线程才能够加入)。 如下图,设置尾节点:
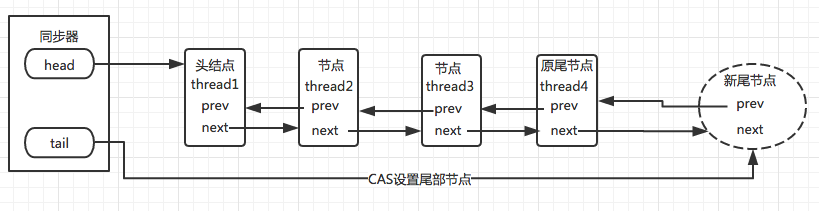 图 2.尾节点的设置 节点加入到同步队列
图 2.尾节点的设置 节点加入到同步队列
- 同步队列设置首节点(原头节点释放锁,唤醒后继节点):同步队列遵循FIFO,头节点是获取锁(同步状态)成功的节点,头节点在释放同步状态的时候,会唤醒后继节点,而后继节点将会在获取锁(同步状态)成功时候将自己设置为头节点。设置头节点是由获取锁(同步状态)成功的线程来完成的,由于只有一个线程能够获取同步状态,则设置头节点的方法不需要CAS保证,只需要将头节点设置成为原首节点的后继节点 ,并断开原头结点的next引用。如下图,设置首节点:
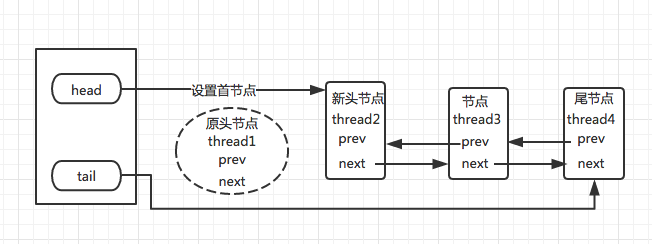
图 3.首节点的设置
6.独占式的锁的获取:调用同步器的acquire(int arg)方法可以获取同步状态,该方法对中断不敏感,即线程获取同步状态失败后进入同步队列,后续对线程进行中断操作时,线程不会从同步队列中移除。
(1) 当前线程实现通过tryAcquire()方法尝试获取锁,获取成功的话直接返回,如果尝试失败的话,进入等待队列排队等待,可以保证线程安全(CAS)的获取同步状态。
(2) 如果尝试获取锁失败的话,构造同步节点(独占式的Node.EXCLUSIVE),通过addWaiter(Node node,int args)方法,将节点加入到同步队列的队列尾部。
(3) 最后调用acquireQueued(final Node node, int args)方法,使该节点以死循环的方式获取同步状态,如果获取不到,则阻塞节点中的线程。acquireQueued方法当前线程在死循环中获取同步状态,而只有前驱节点是头节点的时候才能尝试获取锁(同步状态)( p == head && tryAcquire(arg))。
原因是:1.头结点是成功获取同步状态的节点,而头结点的线程释放锁以后,将唤醒后继节点,后继节点线程被唤醒后要检查自己的前驱节点是否为头结点。
2.维护同步队列的FIFO原则,节点进入同步队列以后,就进入了一个自旋的过程,每个节点(后者说每个线程)都在自省的观察。
下图为节点自旋检查自己的前驱节点是否为头结点:

图 4 节点自旋获取同步状态
独占式的锁的获取源码:
acquire方法源码如下
/** * Acquires in exclusive(互斥) mode, ignoring(忽视) interrupts. Implemented * by invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquire}, * returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued(排队), possibly * repeatedly(反复的) blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link * #tryAcquire} until success. This method can be used * to implement method {@link Lock#lock}. * * @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed(传达) to * {@link #tryAcquire} but is otherwise uninterpreted and * can represent anything you like. * * 独占式的获取同步状态 * */ public final void acquire(int arg) { if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) selfInterrupt(); }
尝试获取锁:tryAcquire方法:如果获取到了锁,tryAcquire返回true,反之,返回false。
//方法2: protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { // 获取当前线程 final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取“独占锁”的状态,获取父类AQS的标志位 int c = getState(); //c == 0 意思是锁(同步状态)没有被任何线程所获取 //1.当前线程是否是同步队列中头结点Node,如果是的话,则获取该锁,设置锁的状态,并设置锁的拥有者为当前线程 if (c == 0) { if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
// 修改下状态为,这里的acquires的值是1,是写死的调用子类的lock的方法的时候传进来的,如果c == 0,compareAndSetState操作会更新成功为1. compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
// 上面CAS操作更新成功为1,表示当前线程获取到了锁,因为将当前线程设置为AQS的一个变量中,代表这个线程拿走了锁。 setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } //2.如果c不为0,即状态不为0,表示锁已经被拿走。
//因为ReetrantLock是可重入锁,是可以重复lock和unlock的,所以这里还要判断一次,获取锁的线程是否为当前请求锁的线程。 else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
//如果是,state继续加1,这里nextc的结果就会 > 1,这个判断表示获取到的锁的线程,还可以再获取锁,这里就是说的可重入的意思 int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); setState(nextc); return true; } return false; }
addWaiter方法的源码:回到aquire方法,如果尝试获取同步状态(锁)失败的话,则构造同步节点(独占式的Node.EXCLUSIVE),
通过addWaiter(Node node,int args)方法
将该节点加入到同步队列的队尾。
/** * Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode. * * @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared * @return the new node * * * 如果尝试获取同步状态失败的话,则构造同步节点(独占式的Node.EXCLUSIVE),通过addWaiter(Node node,int args)方法将该节点加入到同步队列的队尾。 * */ private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 用当前线程够着一个Node对象,mode是一个表示Node类型的字段,或者说是这个节点是独占的还是共享的,或者说AQS的这个队列中,哪些节点是独占的,哪些节点是共享的。 Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); // Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure Node pred = tail;
//队列不为空的时候 if (pred != null) { node.prev = pred; // 确保节点能够被线程安全的添加,使用CAS方法
// 尝试修改为节点为最新的节点,如果修改失败,意味着有并发,这个时候进入enq中的死循环,进行“自旋”的方式修改 if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { pred.next = node; return node; } }
//进入自旋 enq(node); return node; }
enq方法的源码:同步器通过死循环的方式来保证节点的正确添加,在“死循环” 中通过CAS将节点设置成为尾节点之后,当前线程才能从该方法中返回,否则
当前线程不断的尝试设置。
enq方法将并发添加节点的请求通过CAS变得“串行化”了。
/** * Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary. See picture above. * @param node the node to insert * @return node's predecessor * * 同步器通过死循环的方式来保证节点的正确添加,在“死循环” 中通过CAS将节点设置成为尾节点之后,当前线程才能从该方法中返回,否则当前线程不断的尝试设置。 * enq方法将并发添加节点的请求通过CAS变得“串行化”了。 * */ private Node enq(final Node node) { for (;;) { Node t = tail; if (t == null) { // Must initialize if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) tail = head; } else { node.prev = t; if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { t.next = node; return t; } } } }
acquireQueued方法:在队列中的线程获取锁的过程:
/** * Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in * queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire. * * @param node the node * @param arg the acquire argument * @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting * * acquireQueued方法当前线程在死循环中获取同步状态,而只有前驱节点是头节点才能尝试获取同步状态(锁)( p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) * 原因是:1.头结点是成功获取同步状态(锁)的节点,而头节点的线程释放了同步状态以后,将会唤醒其后继节点,后继节点的线程被唤醒后要检查自己的前驱节点是否为头结点。 * 2.维护同步队列的FIFO原则,节点进入同步队列之后,就进入了一个自旋的过程,每个节点(或者说是每个线程)都在自省的观察。 * */ final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true; try { boolean interrupted = false;
//死循环检查(自旋检查)当前节点的前驱节点是否为头结点,才能获取锁 for (;;) {
// 获取节点的前驱节点 final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {//节点中的线程循环的检查,自己的前驱节点是否为头节点
//将当前节点设置为头结点,移除之前的头节点 setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return interrupted; }
// 否则检查前一个节点的状态,看当前获取锁失败的线程是否要挂起 if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
//如果需要挂起,借助JUC包下面的LockSupport类的静态方法park挂起当前线程,直到被唤醒
parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true; } } finally {
//如果有异常 if (failed)
//取消请求,将当前节点从队列中移除 cancelAcquire(node); } }
独占式的获取同步状态的流程如下:

图5 独占式的获取同步状态的流程
7.独占锁的释放:下面直接看源码:
/*
1. unlock():unlock()是解锁函数,它是通过AQS的release()函数来实现的。 * 在这里,“1”的含义和“获取锁的函数acquire(1)的含义”一样,它是设置“释放锁的状态”的参数。 * 由于“公平锁”是可重入的,所以对于同一个线程,每释放锁一次,锁的状态-1。 unlock()在ReentrantLock.java中实现的,源码如下: */ public void unlock() { sync.release(1); }
release()会调用tryRelease方法尝试释放当前线程持有的锁(同步状态),成功的话唤醒后继线程,并返回true,否则直接返回false
/** * Releases in exclusive mode. Implemented by unblocking one or * more threads if {@link #tryRelease} returns true. * This method can be used to implement method {@link Lock#unlock}. * * @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to * {@link #tryRelease} but is otherwise uninterpreted and * can represent anything you like. * @return the value returned from {@link #tryRelease} * * * */ public final boolean release(int arg) { if (tryRelease(arg)) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) unparkSuccessor(h); return true; } return false; }
// tryRelease() 尝试释放当前线程的同步状态(锁) protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) { //c为释放后的同步状态 int c = getState() - releases; //判断当前释放锁的线程是否为获取到锁(同步状态)的线程,不是抛出异常(非法监视器状态异常) if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException(); boolean free = false; //如果锁(同步状态)已经被当前线程彻底释放,则设置锁的持有者为null,同步状态(锁)变的可获取 if (c == 0) { free = true; setExclusiveOwnerThread(null); } setState(c); return free; }
释放锁成功后,找到AQS的头结点,并唤醒它即可:
// 4. 唤醒头结点的后继节点 private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) { //获取头结点(线程)的状态 int ws = node.waitStatus; //如果状态<0,设置当前线程对应的锁的状态为0 if (ws < 0) compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0); Node s = node.next; //解释:Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally just the next node. //But if cancelled or apparently(显然) null, traverse backwards(向后遍历) from tail to find the actual(实际的) non-cancelled successor(前继节点). //从队列尾部开始往前去找最前面的一个waitStatus小于0的节点。 if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) { s = null; for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev) if (t.waitStatus <= 0) s = t; } //唤醒后继节点对应的线程 if (s != null) LockSupport.unpark(s.thread); }
上面说的是ReentrantLock的公平锁获取和释放的AQS的源码,唯独还剩下一个非公平锁NonfairSync没说,其实,它和公平锁的唯一区别就是获取锁的方式不同,公平锁是按前后顺序一次获取锁,非公平锁是抢占式的获取锁,那ReentrantLock中的非公平锁NonfairSync是怎么实现的呢?
/** * Sync object for non-fair locks */ static final class NonfairSync extends Sync { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L; /** * Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal * acquire on failure. */ final void lock() { if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); else acquire(1); } protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires); } }
非公平锁的lock的时候多了上面加粗的代码:在lock的时候先直接用cas判断state变量是否为0(尝试获取锁),成功的话更新成1,表示当前线程获取到了锁,不需要在排队,从而直接抢占的目的。而对于公平锁的lock方法是一开始就走AQS的双向队列排队获取锁。更详细的关于ReentrantLock的实现请看后面写的一篇文章:http://www.cnblogs.com/200911/p/6035765.html
总结:在获取同步状态的时候,同步器维护一个同步队列,获取失败的线程会被加入到队列中并在队列中自旋;移除队列(或停止自旋)的条件是前驱节点为头结点并且获取到了同步状态。在释放同步状态时,同步器调用tryRelease(int args)方法释放同步状态,然后唤醒头结点的后继节点。AQS的实现思路其实并不复杂,用一句话准确的描述的话,其实就是使用标志状态位status(volatile int state)和 一个双向队列的入队和出队来实现。AQS维护一个线程何时访问的状态,它只是对状态负责,而这个状态的含义,子类可以自己去定义。
自己注释的AQS的源码:如下:

public class AbstractQueuedSynchronizerTest { /** * * (AQS节点的定义,同步队列的节点定义) * * <p> * 修改历史: <br> * 修改日期 修改人员 版本 修改内容<br> * -------------------------------------------------<br> * 2016年7月4日 上午10:26:38 user 1.0 初始化创建<br> * </p> * * @author Peng.Li * @version 1.0 * @since JDK1.7 */ static final class Node { /** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in shared mode */ static final Node SHARED = new Node(); /** Marker to indicate a node is waiting in exclusive mode * * */ static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null; /** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled * 在同步队列中等待的线程等待超时或者被中断,需要从同步队列中取消等待 * */ static final int CANCELLED = 1; /** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking(唤醒) * 后继节点的线程处于等待状态,而当前的节点如果释放了同步状态或者被取消,将会通知后继节点,使后继节点的线程得以运行。 **/ static final int SIGNAL = -1; /** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition * 节点在等待队列中,节点的线程等待在Condition上,当其他线程对Condition调用了signal()方法后,该节点会从等待队列中转移到同步队列中,加入到同步状态的获取中 **/ static final int CONDITION = -2; /** * waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should * unconditionally(无条件的) propagate(传播) * * 表示下一次共享式同步状态获取将会被无条件地传播下去 */ static final int PROPAGATE = -3; /** * Status field, taking on only the values: * SIGNAL: The successor of this node is (or will soon be) * blocked (via park), so the current node must * unpark its successor when it releases or * cancels. To avoid races, acquire methods must * first indicate they need a signal, * then retry the atomic acquire, and then, * on failure, block. * CANCELLED: This node is cancelled due to timeout or interrupt. * Nodes never leave this state. In particular, * a thread with cancelled node never again blocks. * CONDITION: This node is currently on a condition queue. * It will not be used as a sync queue node * until transferred, at which time the status * will be set to 0. (Use of this value here has * nothing to do with the other uses of the * field, but simplifies mechanics.) * PROPAGATE: A releaseShared should be propagated(传播) to other * nodes. This is set (for head node only) in * doReleaseShared to ensure propagation * continues, even if other operations have * since intervened(干涉). * 0: None of the above * * The values are arranged numerically to simplify use. * Non-negative values mean that a node doesn't need to * signal. So, most code doesn't need to check for particular * values, just for sign. * * The field is initialized to 0 for normal sync nodes, and * CONDITION for condition nodes. It is modified using CAS * (or when possible, unconditional volatile writes). * * 使用CAS更改状态,volatile保证线程可见性,即被一个线程修改后,状态会立马让其他线程可见。 * */ volatile int waitStatus; /** * Link to predecessor node that current node/thread relies on * for checking waitStatus. Assigned during enqueing(入队), and nulled * out (for sake of GC) only upon dequeuing. Also, upon * cancellation of a predecessor, we short-circuit while * finding a non-cancelled one, which will always exist * because the head node is never cancelled: A node becomes * head only as a result of successful acquire. A * cancelled thread never succeeds in acquiring, and a thread only * cancels itself, not any other node. * * 前驱节点,当前节点加入到同步队列中被设置 */ volatile Node prev; /** * Link to the successor node that the current node/thread * unparks upon release. Assigned during enqueuing, adjusted * when bypassing cancelled predecessors, and nulled out (for * sake of GC) when dequeued. The enq operation does not * assign next field of a predecessor until after attachment, * so seeing a null next field does not necessarily mean that * node is at end of queue. However, if a next field appears * to be null, we can scan prev's from the tail to * double-check. The next field of cancelled nodes is set to * point to the node itself instead of null, to make life * easier for isOnSyncQueue. * * 后继节点 */ volatile Node next; /** * The thread that enqueued this node. Initialized on * construction and nulled out after use. * * 获取同步状态的线程 */ volatile Thread thread; /** * Link to next node waiting on condition, or the special * value SHARED. Because condition queues are accessed only * when holding in exclusive(独有的) mode, we just need a simple * linked queue to hold nodes while they are waiting on * conditions. They are then transferred(移动到) to the queue(同步队列) to * re-acquire. And because conditions can only be exclusive, * we save a field by using special value to indicate shared * mode. * * 等待队列中的后继节点,如果当前节点是共享的,那么这个字段是一个SHARED常量, * 也就是说节点类型(独占和共享)和等待队列中的后继节点共用同一个字段。 */ Node nextWaiter; /** * Returns true if node is waiting in shared mode */ final boolean isShared() { return nextWaiter == SHARED; } /** * Returns previous node, or throws NullPointerException if null. * Use when predecessor cannot be null. The null check could * be elided, but is present to help the VM. * * @return the predecessor of this node */ final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException { Node p = prev; if (p == null) throw new NullPointerException(); else return p; } Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker } Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter this.nextWaiter = mode; this.thread = thread; } Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition this.waitStatus = waitStatus; this.thread = thread; } } /** * Head of the wait queue, lazily initialized. Except for (除...以外) * initialization(初始化), it is modified only via method setHead. Note: * If head exists, its waitStatus is guaranteed not to be * CANCELLED.(如果head引用已经存在,等待状态保证不会被取消) */ private transient volatile Node head; /** * Tail of the wait queue(等待队列), lazily initialized. Modified only via * method enq to add new wait node. */ private transient volatile Node tail; /** * The synchronization state. * 同步状态,线程可见的,共享内存里面保存 * */ private volatile int state; /** * Returns the current value of synchronization state. * This operation has memory semantics of a <tt>volatile</tt> read. * @return current state value * * 得到同步状态的值 * */ protected final int getState() { return state; } /** * Sets the value of synchronization state. * This operation has memory semantics of a <tt>volatile</tt> write. * @param newState the new state value */ protected final void setState(int newState) { state = newState; } /** * Acquires in exclusive(互斥) mode, ignoring(忽视) interrupts. Implemented * by invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquire}, * returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued(排队), possibly * repeatedly(反复的) blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link * #tryAcquire} until success. This method can be used * to implement method {@link Lock#lock}. * * @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed(传达) to * {@link #tryAcquire} but is otherwise uninterpreted and * can represent anything you like. * * 独占式的获取同步状态 * */ public final void acquire(int arg) { if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) selfInterrupt(); } protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } /** * Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode. * * @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared * @return the new node * * * 如果尝试获取同步状态失败的话,则构造同步节点(独占式的Node.EXCLUSIVE),通过 addWaiter(Node node,int args)方法将该节点加入到同步队列的队尾。 * */ private Node addWaiter(Node mode) { Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); // Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure Node pred = tail; if (pred != null) { node.prev = pred; // 确保节点能够被安全的添加 if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { pred.next = node; return node; } } enq(node); return node; } /** * Convenience method to interrupt current thread. * 分析:如果在acquireQueued()中,当前线程被中断过,则执行selfInterrupt();否则不会执行。 * 线程在阻塞状态被“中断唤醒”而获取CPU的执行权;但是该线程前面还有其他等待锁的线程,根据公平性原则,该线程仍然无法获取到锁,他会再次阻塞。 * 直到该线程被他前面等待锁的线程唤醒;线程才会获取锁。该线程“成功获取锁并真正执行起来之前”,他的中断会被忽略并且中断标记会被清除,因为在parkAndCheckInterrupt()中, * 我们线程的中断状态时调用了Thread.interrupted(),这个函数在返回中断状态之后,还会清除中断状态,正因为清除了中断状态,所以在selfInterrupt重新产生一个中断。 * * * 当前线程自己产生一个中断 */ private static void selfInterrupt() { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } /** * Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in * queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire. * * @param node the node * @param arg the acquire argument * @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting * * acquireQueued方法当前线程在死循环中获取同步状态,而只有前驱节点是头节点才能尝试获取同步状态( p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) * 原因是:1.头结点是成功获取同步状态的节点,而头节点的线程释放了同步状态以后,将会唤醒其后继节点,后继节点的线程被唤醒后要检查自己的前驱节点是否为头结点。 * 2.维护同步队列的FIFO原则,节点进入同步队列之后,就进入了一个自旋的过程,每个节点(或者说是每个线程)都在自省的观察。 * */ final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true; try { boolean interrupted = false; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return interrupted; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true; } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } } /** * Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary. See picture above. * @param node the node to insert * @return node's predecessor * * 同步器通过死循环的方式来保证节点的正确添加,在“死循环” 中通过CAS将节点设置成为尾节点之后,当前线程才能从该方法中返回,否则当前线程不断的尝试设置。 * enq方法将并发添加节点的请求通过CAS变得“串行化”了。 * */ private Node enq(final Node node) { for (;;) { Node t = tail; if (t == null) { // Must initialize if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) tail = head; } else { node.prev = t; if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { t.next = node; return t; } } } } /** * Convenience method to park and then check if interrupted * * @return {@code true} if interrupted * * 阻塞当前线程 * */ private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() { // 阻塞当前线程 LockSupport.park(this); // 线程被唤醒之后的中断状态 return Thread.interrupted(); } /** * Releases in exclusive mode. Implemented by unblocking one or * more threads if {@link #tryRelease} returns true. * This method can be used to implement method {@link Lock#unlock}. * * @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to * {@link #tryRelease} but is otherwise uninterpreted and * can represent anything you like. * @return the value returned from {@link #tryRelease} * * 释放公平锁 * */ public final boolean release(int arg) { if (tryRelease(arg)) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) unparkSuccessor(h); return true; } return false; } /** * Attempts to set the state to reflect a release in exclusive * mode. * * <p>This method is always invoked by the thread performing release. * * <p>The default implementation throws * {@link UnsupportedOperationException}. * * @param arg the release argument. This value is always the one * passed to a release method, or the current state value upon * entry to a condition wait. The value is otherwise * uninterpreted and can represent anything you like. * @return {@code true} if this object is now in a fully released * state, so that any waiting threads may attempt to acquire; * and {@code false} otherwise. * @throws IllegalMonitorStateException if releasing would place this * synchronizer in an illegal state. This exception must be * thrown in a consistent fashion for synchronization to work * correctly. * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if exclusive mode is not supported */ protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } /** * Checks and updates status for a node that failed to acquire. * Returns true if thread should block. This is the main signal * control in all acquire loops. Requires that pred == node.prev * * @param pred node's predecessor holding status * @param node the node * @return {@code true} if thread should block * 返回当前线程是否应该阻塞 * * 说明: (01) 关于waitStatus请参考下表(中扩号内为waitStatus的值),更多关于waitStatus的内容,可以参考前面的Node类的介绍。 CANCELLED[1] -- 当前线程已被取消 SIGNAL[-1] -- “当前线程的后继线程需要被unpark(唤醒)”。一般发生情况是:当前线程的后继线程处于阻塞状态,而当前线程被release或cancel掉,因此需要唤醒当前线程的后继线程。 CONDITION[-2] -- 当前线程(处在Condition休眠状态)在等待Condition唤醒 PROPAGATE[-3] -- (共享锁)其它线程获取到“共享锁” [0] -- 当前线程不属于上面的任何一种状态。 (02) shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire()通过以下规则,判断“当前线程”是否需要被阻塞。 规则1:如果前继节点状态为SIGNAL,表明当前节点需要被unpark(唤醒),此时则返回true。 规则2:如果前继节点状态为CANCELLED(ws>0),说明前继节点已经被取消,则通过先前回溯找到一个有效(非CANCELLED状态)的节点,并返回false。 规则3:如果前继节点状态为非SIGNAL、非CANCELLED,则设置前继的状态为SIGNAL,并返回false。 * */ private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) { // 前驱节点的状态 int ws = pred.waitStatus; // 如果前驱节点是SIGNAL状态,则意味着当前线程需要unpark唤醒,此时返回true if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) /* * This node has already set status asking a release to signal it, so it can safely park. */ return true; // 如果前继节点是取消的状态,则设置当前节点的“当前前继节点为”原节点的前继节点 if (ws > 0) { /* * Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and indicate retry. */ do { node.prev = pred = pred.prev; } while (pred.waitStatus > 0); pred.next = node; } else { /* * waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to retry to make sure * it cannot acquire before parking. */ compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL); } return false; } /** * Cancels an ongoing attempt to acquire. * * @param node the node */ private void cancelAcquire(Node node) { // Ignore if node doesn't exist if (node == null) return; node.thread = null; // Skip cancelled predecessors Node pred = node.prev; while (pred.waitStatus > 0) node.prev = pred = pred.prev; // predNext is the apparent node to unsplice. CASes below will // fail if not, in which case, we lost race vs another cancel // or signal, so no further action is necessary. Node predNext = pred.next; // Can use unconditional write instead of CAS here. // After this atomic step, other Nodes can skip past us. // Before, we are free of interference from other threads. node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED; // If we are the tail, remove ourselves. if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) { compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null); } else { // If successor needs signal, try to set pred's next-link // so it will get one. Otherwise wake it up to propagate. int ws; if (pred != head && ((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL || (ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) && pred.thread != null) { Node next = node.next; if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0) compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next); } else { unparkSuccessor(node); } node.next = node; // help GC } } /** * Wakes up node's successor, if one exists. * * @param node the node */ private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) { /* * If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this fails or if * status is changed by waiting thread. */ int ws = node.waitStatus; if (ws < 0) compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0); /* * Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null, traverse * backwards from tail to find the actual non-cancelled successor. */ Node s = node.next; if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) { s = null; for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev) if (t.waitStatus <= 0) s = t; } if (s != null) LockSupport.unpark(s.thread); } /** * Sets head of queue to be node, thus dequeuing. Called only by * acquire methods. Also nulls out unused fields for sake of GC * and to suppress unnecessary signals and traversals. * * @param node the node */ private void setHead(Node node) { head = node; node.thread = null; node.prev = null; } /** * Atomically sets synchronization state to the given updated * value if the current state value equals the expected value. * This operation has memory semantics of a <tt>volatile</tt> read * and write. * * @param expect the expected value * @param update the new value * @return true if successful. False return indicates that the actual * value was not equal to the expected value. */ protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) { // See below for intrinsics setup to support this return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update); } /** * CAS waitStatus field of a node. */ private static final boolean compareAndSetWaitStatus(Node node, int expect, int update) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(node, waitStatusOffset, expect, update); } /** * CAS next field of a node. */ private static final boolean compareAndSetNext(Node node, Node expect, Node update) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(node, nextOffset, expect, update); } /** * CAS tail field. Used only by enq. */ private final boolean compareAndSetTail(Node expect, Node update) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, tailOffset, expect, update); } /** * CAS head field. Used only by enq. */ private final boolean compareAndSetHead(Node update) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, headOffset, null, update); } /** * Setup to support compareAndSet. We need to natively implement * this here: For the sake of permitting future enhancements, we * cannot explicitly subclass AtomicInteger, which would be * efficient and useful otherwise. So, as the lesser of evils, we * natively implement using hotspot intrinsics(编译器内部函数) API. And while we * are at it, we do the same for other CASable fields (which could * otherwise be done with atomic field updaters). */ private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe(); private static final long stateOffset; private static final long headOffset; private static final long tailOffset; private static final long waitStatusOffset; private static final long nextOffset; static { try { stateOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("state")); headOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("head")); tailOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("tail")); waitStatusOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(Node.class.getDeclaredField("waitStatus")); nextOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(Node.class.getDeclaredField("next")); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); } } }
AbstractOwnableSynchronizer的源码如下:

package concurrentMy.aqs; /** * * (设置和获取锁的持有者线程) * * <p> * 修改历史: <br> * 修改日期 修改人员 版本 修改内容<br> * -------------------------------------------------<br> * 2016年7月5日 下午3:42:37 user 1.0 初始化创建<br> * </p> * * @author Peng.Li * @version 1.0 * @since JDK1.7 */ public abstract class AbstractOwnableSynchronizerTest implements java.io.Serializable { /** Use serial ID even though all fields transient. */ private static final long serialVersionUID = 3737899427754241961L; /** * Empty constructor for use by subclasses. */ protected AbstractOwnableSynchronizerTest() { } /** * The current owner of exclusive mode synchronization. * * 加 transient 表示exclusiveOwnerThread不能被串行化,不会被作为序列化的一部分 * * 锁的持有线程 */ private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread; /** * Sets the thread that currently owns exclusive access. A * <tt>null</tt> argument indicates that no thread owns access. * This method does not otherwise impose any synchronization or * <tt>volatile</tt> field accesses. * * protected final来修饰,表示子类可以使用这个方法,但是不能重载这个方法,也就是不能修改这个方法 */ protected final void setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread t) { exclusiveOwnerThread = t; } /** * Returns the thread last set by * <tt>setExclusiveOwnerThread</tt>, or <tt>null</tt> if never * set. This method does not otherwise impose any synchronization * or <tt>volatile</tt> field accesses. * @return the owner thread */ protected final Thread getExclusiveOwnerThread() { return exclusiveOwnerThread; } }
参考文章:
1.Doug Lea的论文: http://gee.cs.oswego.edu/dl/papers/aqs.pdf
2. 深度解析Java 8:JDK1.8 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的实现分析(上): http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/jdk1.8-abstractqueuedsynchronizer
3. 深度解析Java 8:AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的实现分析(下): http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/java8-abstractqueuedsynchronizer
4. 深入浅出 Java Concurrency (7): 锁机制 part 2 AQS: http://www.blogjava.net/xylz/archive/2010/07/06/325390.html
5 AQS:http://www.cnblogs.com/leesf456/p/5350186.html
6.参考:https://tech.meituan.com/Java_Lock.html
