properties使用
什么是Properties?
Properties(Java.util.Properties),该类主要用于读取Java的配置文件,不同的编程语言有自己所支持的配置文件,配置文件中很多变量是经常改变的,为了方便用户的配置,能让用户够脱离程序本身去修改相关的变量设置。就像在Java中,其配置文件常为.properties文件,是以键值对的形式进行参数配置的。
Properties 详解
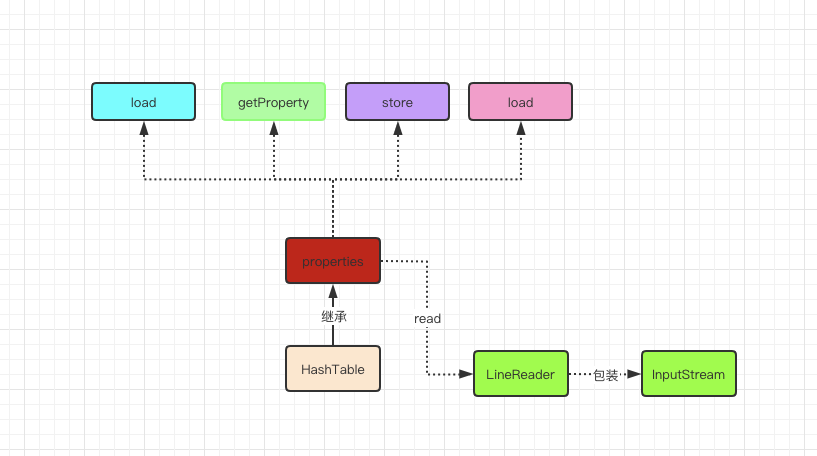 properties结构
properties结构
Api介绍
-
构造函数
| 构造函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Properties() | 创建空的Properties |
| Properties(Properties ps) | 基于已经存在的properties去创建 |
-
常用方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public synchronized void load(InputStream inStream) | 给予输入流去加载Properties |
| public synchronized void load(Reader reader) | 给予文本输入流去加载Properties |
| Object setProperty(String key, String value) | 设置属性 |
| public synchronized void load(InputStream inStream) | 给予输入流去加载Properties |
| public void store(Writer writer, String comments) | 保存文件 |
| public String getProperty(String key) | 获取properties key |
-
源码讲解
load源码分析
指定从流中加载key/value属性值,底层都是将流封装成为LineReader对象,然后通过load0方法来加载属性键值对的,加载完属性后流对象是不会关闭的。这两个方法对应的properties文件格式如下:
class LineReader {
/**
* 根据字节流创建LineReader对象
*
* @param inStream
* 属性键值对对应的字节流对象
*/
public LineReader(InputStream inStream) {
this.inStream = inStream;
inByteBuf = new byte[8192];
}
/**
* 根据字符流创建LineReader对象
*
* @param reader
* 属性键值对对应的字符流对象
*/
public LineReader(Reader reader) {
this.reader = reader;
inCharBuf = new char[8192];
}
// 字节流缓冲区, 大小为8192个字节
byte[] inByteBuf;
// 字符流缓冲区,大小为8192个字符
char[] inCharBuf;
// 当前行信息的缓冲区,大小为1024个字符
char[] lineBuf = new char[1024];
// 读取一行数据时候的实际读取大小
int inLimit = 0;
// 读取的时候指向当前字符位置
int inOff = 0;
// 字节流对象
InputStream inStream;
// 字符流对象
Reader reader;
/**
* 读取一行,将行信息保存到{@link lineBuf}对象中,并返回实际的字符个数
*
* @return 实际读取的字符个数
* @throws IOException
*/
int readLine() throws IOException {
// 总的字符长度
int len = 0;
// 当前字符
char c = 0;
boolean skipWhiteSpace = true;
boolean isCommentLine = false;
boolean isNewLine = true;
boolean appendedLineBegin = false;
boolean precedingBackslash = false;
boolean skipLF = false;
while (true) {
if (inOff >= inLimit) {
// 读取一行数据,并返回这一行的实际读取大小
inLimit = (inStream == null) ? reader.read(inCharBuf) : inStream.read(inByteBuf);
inOff = 0;
// 如果没有读取到数据,那么就直接结束读取操作
if (inLimit <= 0) {
// 如果当前长度为0或者是改行是注释,那么就返回-1。否则返回len的值。
if (len == 0 || isCommentLine) {
return -1;
}
return len;
}
}
// 判断是根据字符流还是字节流读取当前字符
if (inStream != null) {
// The line below is equivalent to calling a ISO8859-1 decoder.
// 字节流是根据ISO8859-1进行编码的,所以在这里进行解码操作。
c = (char) (0xff & inByteBuf[inOff++]);
} else {
c = inCharBuf[inOff++];
}
// 如果前一个字符是换行符号,那么判断当前字符是否也是换行符号
if (skipLF) {
skipLF = false;
if (c == '
') {
continue;
}
}
// 如果前一个字符是空格,那么判断当前字符是不是空格类字符
if (skipWhiteSpace) {
if (c == ' ' || c == ' ' || c == 'f') {
continue;
}
if (!appendedLineBegin && (c == '
' || c == '
')) {
continue;
}
skipWhiteSpace = false;
appendedLineBegin = false;
}
// 如果当前新的一行,那么进入该if判断中
if (isNewLine) {
isNewLine = false;
// 如果当前字符是#或者是!,那么表示该行是一个注释行
if (c == '#' || c == '!') {
isCommentLine = true;
continue;
}
}
// 根据当前字符是不是换行符号进行判断操作
if (c != '
' && c != '
') {
// 当前字符不是换行符号
lineBuf[len++] = c;// 将当前字符写入到行信息缓冲区中,并将len自增加1.
// 如果len的长度大于行信息缓冲区的大小,那么对lineBuf进行扩容,扩容大小为原来的两倍,最大为Integer.MAX_VALUE
if (len == lineBuf.length) {
int newLength = lineBuf.length * 2;
if (newLength < 0) {
newLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
char[] buf = new char[newLength];
System.arraycopy(lineBuf, 0, buf, 0, lineBuf.length);
lineBuf = buf;
}
// 是否是转义字符
// flip the preceding backslash flag
if (c == '\') {
precedingBackslash = !precedingBackslash;
} else {
precedingBackslash = false;
}
} else {
// reached EOL
if (isCommentLine || len == 0) {
// 如果这一行是注释行,或者是当前长度为0,那么进行clean操作。
isCommentLine = false;
isNewLine = true;
skipWhiteSpace = true;
len = 0;
continue;
}
// 如果已经没有数据了,就重新读取
if (inOff >= inLimit) {
inLimit = (inStream == null) ? reader.read(inCharBuf) : inStream.read(inByteBuf);
inOff = 0;
if (inLimit <= 0) {
return len;
}
}
// 查看是否是转义字符
if (precedingBackslash) {
// 如果是,那么表示是另起一行,进行属性的定义,len要自减少1.
len -= 1;
// skip the leading whitespace characters in following line
skipWhiteSpace = true;
appendedLineBegin = true;
precedingBackslash = false;
if (c == '
') {
skipLF = true;
}
} else {
return len;
}
}
}
}
}
store源码分析
private void store0(BufferedWriter bw, String comments, boolean escUnicode) throws IOException {
2 if (comments != null) {
3 // 写出注释, 如果是中文注释,那么转化成为8859-1的字符
4 writeComments(bw, comments);
5 }
6 // 写出时间注释
7 bw.write("#" + new Date().toString());
8 // 新起一行
9 bw.newLine();
10 // 进行线程间同步的并发控制
11 synchronized (this) {
12 for (Enumeration e = keys(); e.hasMoreElements();) {
13 String key = (String) e.nextElement();
14 String val = (String) get(key);
15 // 针对空格进行转义,并根据是否需要进行8859-1编码
16 key = saveConvert(key, true, escUnicode);
17 /*
18 * No need to escape embedded and trailing spaces for value,
19 * hence pass false to flag.
20 */
21 // value不对空格进行转义
22 val = saveConvert(val, false, escUnicode);
23 // 写出key/value键值对
24 bw.write(key + "=" + val);
25 bw.newLine();
26 }
27 }
28 bw.flush();
29 }
properties实战
实现读取ex1.properties文件写入另外一个文件ex2.properties
- 准备文件test.properties
#bbaba
#Mon Jun 07 11:38:21 CST 2021
hah=ceshi
- 开始拷贝
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(new FileReader(new File("test.properties")));
System.out.println(properties.get("hah"));
properties.store(new FileWriter(new File("test2.properties")),"ceshi2");
- 控制台输出
ceshi
Process finished with exit code 0
此时classpath下可以查看到新建的test2.properties文件。
结束
识别下方二维码!回复:
入群,扫码加入我们交流群!
 点赞是认可,在看是支持
点赞是认可,在看是支持
