第八章实验报告
实验项目:
1.指针基础及指针运算
2.数据交换
3.字符串反转及字符串连接
4.数组元素奇偶排列
姓名:魏志远 实验地点:第一教学楼514 实验时间:6月12
一、实验目的与要求
1.指针基础及指针运算
加强学生对指针数据类型的理解,熟悉指针的定义,通过指针间接访问变量。
2.数据交换
加强学生对指针类型作为参数传递的理解。
3.字符串反转及字符串连接
加强学生对字符指针以及将指针作为函数的返回类型的理解。
4.数组元素奇偶排列
加强学生对使用指针对数组进行操作的理解。
二、实验内容
8.3.1 指针基础及指针运算
1.问题描述:
(1)定义一个整型指针变量p,使它指向一个整型变量a,定义一个浮点型指针q,使它指向一个浮点型变量b,同时定义另外一个整型变量c并赋初值3
(2)使用指针变量,调动scanf函数分别输入a和b的值。
(3)通过指针间接访问并输出a和b的值。
(4)按十六进制方式输出p、q的值以及a、b的地址。
(5)将p指向c,通过p间接访问c的值并输出
(6)输出p的值及c的地址,并与上面的结果进行比较。
2.实验代码:
#include<stdio.h> int main() { int *p,a,c=3; float *q,b; p=&a; q=&b; printf("please input the value of a,b:"); scanf("%d%f",&*p,&*q); printf("result: "); printf(" %d %f ",a,b); printf(" %d %f ",*p,*q); printf("the address of a,b:%p %p ",&a,&b); printf("the address of a,b:%p %P ",p,q); p=&c; printf("c=%d ",*p); printf("the address of c:%x %x ",p,&c); return 0; }
运行结果:
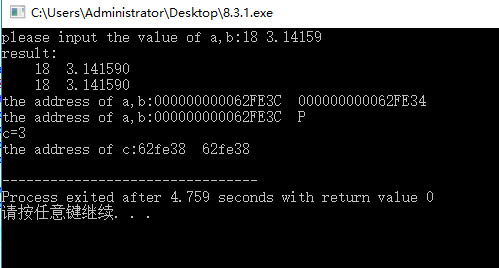
3.问题分析:
scanf要用&*p,&*q,这里的&表示scanf里的输入,不是指针的意思。
还有问题就是为什么运行结果里有个P,对比其他同学代码发现是一样的,结果不同,求解。
8.3.2 数据交换
1.问题描述:
(1)定义两个函数,分别为void swap1(int a,int b)和void swap2(int*a,int *b),用于交换a,b的值。
(2)从主函数中分别输入两个整形变量a、b。
(3)从主函数中分别调用上述两个交换函数,并打印输出交换后a、b的结果。
2.实验代码:
#include<stdio.h> void swap1(int x,int y); void swap2(int *x,int *y); int main() { int a,b; printf("please input a="); scanf("%d",&a); printf(" b="); scanf("%d",&b); swap1(a,b); printf(" after call swap1:a=%d,b=%d ",a,b); swap2(&a,&b); printf(" after call swap2 :a=%d,b=%d ",a,b); return 0; } void swap1(int x,int y) { int temp; temp=x;x=y;y=temp; } void swap2(int *x,int *y) { int temp; temp=*x;*x=*y;*y=temp; }
运行结果:
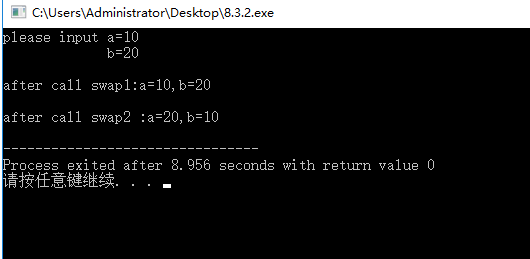
3.问题分析:无
8.3.3 字符串反转及字符串连接
1.问题描述
(1)定义两个字符指针,通过gets()函数输入两个字符。
(2)定义一个函数char*reverse(char*str),通过指针移动方式将字符串反转。
(3)定义一个函数char*link(char*str1,char*str2),通过指针移动方式将两个字符串连接起来
(4)从主函数中分别调用上述函数,输入字符串并打印输出结果。
2.实验代码
#include<stdio.h>
char *reverse(char *str);
char *link(char *str1,char *str2);
int main()
{
char str[30],str1[30],*str2;
printf("input reverse character string:");
gets(str);
str2=reverse(str);
printf("
output reverse character string:");
puts(str2);
printf("input string1:");
gets(str);
printf("
input string2:");
gets(str);
str2=link(str,str1);
printf("
link string1 and string2: ");
puts(str2);
return 0;
}
char *reverse(char *str)
{
char *p,*q,temp;
p=str,q=str;
while(*p!='�')
p++;
p--;
while(q<p)
{
temp=*q;*q=*p;*p=temp;
++q;--p;
}
return str;
}
char *link(char *str1,char *str2)
{
char *p=str1,*q=str2;
while(*p!='�')
p++;
while(*q!='�')
{
*p=*q;
p++;
q++;
}
str2=NULL;return str1;
}
运行结果:
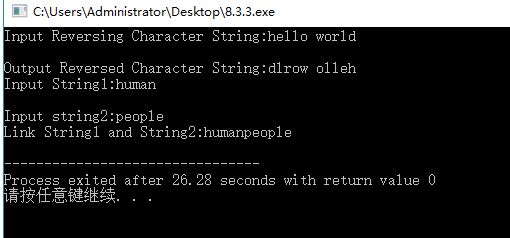
3.问题分析:指针做相向移动不知道怎么做。以及怎么样令结束字符为空字符不会做,后来发现先要知道指针的意义和空字符即为'�'。
8.3.4 数组元素奇偶排列
1.问题描述:
(1)定义一个整型一维数组,任意输入数组的元素,其中包含奇数和偶数。
(2)定义一个函数,实现将数组元素奇数在左,偶数在右的排列。
(3)在上述定义的函数中,不允许再增加新的数组。
(4)从主函数中分别调用上述函数,打印输出结果。
2.实验代码:
#include <stdio.h> # define N 10 void arrsort(int a[],int n); int main() { int a[N],i; for(i=0;i<N;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); arrsort(a,N); for(i=0;i<N;i++) printf("%d ",a[i]); } void arrsort(int a[],int n) { int *p,*q,temp; p=a;q=a+n-1;/*p为第一个,q为最后一个,两者比较*/ while(p<q) { while(*p%2==1) p++; while(*q%2==0) q--; if(p>q) break; temp=*p; *p=*q; *q=temp; p++; q--; } }
运行结果:

3.问题分析:
开始没有理解void arrsort函数里面pq的含义,导致不知道运算是怎么样进行的。
还有就是指针前移与后移的指针表示,后移用++,前移用--。
三、实验小结
收获:对于指针的理解有了一定的加深,并且了解到了如何使指针进行交换和相向移动,以及指针向前移动与向后移动的差别。
同时,对于形参的变化不影响实参了解更加深刻。
不足:对于指针还是有许多地方不了解,希望学习到更多。