注释:使用re之前,要导入re库文件。
(1). :匹配任意字符,换行符 除外;每个 . 表示一个占位符。
例子:
a = 'xy123'
b = re.findall('x..',a)
print b
输出结果:

(2)*:匹配前一个字符的0次或无限次。
例子:
a = 'xxyxy123'
b = re.findall('x*',a)
print b
输出结果为:

(3)? :匹配前一个字符0次或1次。
例子:
a = 'xxyxy123'
b = re.findall('xy?',a)
print b
输出结果:
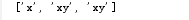
(4).* :贪心算法,尽可能的匹配多的字符。
例子:
secret_code = 'hadkfalifexxIxxfasdjifja134xxlovexx23345sdfxxyouxx8dfse'
b = re.findall('xx.*xx',secret_code)
print b
输出结果如下:

(5).*? :非贪心算法。
例子:
secret_code = 'hadkfalifexxIxxfasdjifja134xxlovexx23345sdfxxyouxx8dfse'
c = re.findall('xx.*?xx',secret_code)
print c
输出结果如下:
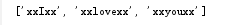
(6)() :括号内的数据作为结果返回。
例子:
secret_code = 'hadkfalifexxIxxfasdjifja134xxlovexx23345sdfxxyouxx8dfse'
d = re.findall('xx(.*?)xx',secret_code)
print d
输出结果:
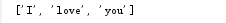
(7) re.S的使用举例。在Python的正则表达式中,有一个参数为re.S。它表示“.”(不包含外侧双引号,下同)的作用扩展到整个字符串,包括“ ”。看如下代码:
import re
a = '''asdfsafhellopass:
234455
worldafdsf
'''
b = re.findall('hello(.*?)world',a)
c = re.findall('hello(.*?)world',a,re.S)
print 'b is ' , b
print 'c is ' , c
输出结果如下:

正则表达式中,“.”的作用是匹配除“ ”以外的任何字符,也就是说,它是在一行中进行匹配。这里的“行”是以“ ”进行区分的。a字符串有每行的末尾有一个“ ”,不过它不可见。
如果不使用re.S参数,则只在每一行内进行匹配,如果一行没有,就换下一行重新开始,不会跨行。而使用re.S参数以后,正则表达式会将这个字符串作为一个整体,将“ ”当做一个普通的字符加入到这个字符串中,在整体中进行匹配。
(8)
re.findall(pattern, string[, flags]):搜索string,以列表形式返回全部能匹配的子串。
例子1:
pattern = re.compile(r'd+')
print re.findall(pattern,'one1two2three3four4')
输出结果为:
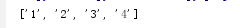
例子2:
s2 = 'asdfxxIxx123xxlovexxdfd'
f2 = re.findall('xx(.*?)xx123xx(.*?)xx',s2)
print f2
print f2[0]
输出结果为:

(9) search的使用举例
例子:
s2 = 'asdfxxIxx123xxlovexxdfd'
f = re.search('xx(.*?)xx123xx(.*?)xx',s2)
print f.group()
print f.group(0)
print f.group(1)
print f.group(2)
print f.group(1,2)
print f.groups()
输出结果为:

group([group1, …]):
获得一个或多个分组截获的字符串;指定多个参数时将以元组形式返回。group1可以使用编号也可以使用别名;编号0代表整个匹配的子串;不填写参数时,返回group(0);没有截获字符串的组返回None;截获了多次的组返回最后一次截获的子串。
groups([default]):
以元组形式返回全部分组截获的字符串。相当于调用group(1,2,…last)。default表示没有截获字符串的组以这个值替代,默认为None。
(10) d 的使用举例,d用于匹配数字;d+ 可以匹配数字字符串。
例子:
a = 'asdfasf1234567fasd555fas'
b = re.findall('(d+)',a)
print b
输出结果:

(11)sub()方法