A Permutation Forgery standard input/output 1 s, 256 MB Submit Add to favourites x16131
输入一个p数组,然后将相邻的两个数相加生成一个新数组,需要找到一个p‘数组生成的数组 排序后 和 p数组生产的数组 排序后一样, 只需要将 原数组p 倒序输出即可
B Array Cancellation standard input/output 1 s, 256 MB Submit Add to favourites x13396
输入一个总和为0的数组,需要把所有数组元素变成0, 如果i < j ai-- aj++ 操作是free的, 否则需要花费 一个硬币 问最少需要多少个硬币, 贪心尽可能free操作 最后剩下非零元素的就是最小花费
C Balanced Bitstring standard input/output 2 s, 256 MB Submit Add to favourites x7350
输入一个长度为n字符串(由0 1 ?组成) 问是否可以通过转换?为0 或1 达到 每个k长度的子串 0 1数量相同,符合条件的字符串应该是周期k的循环串 故暴力枚举 k个位置的对应0 1 是否能一致并且k长度字符串中的已知0 1不能超过k/2 。
D Tree Tag standard input/output 1 s, 256 MB Submit Add to favourites x2888
给定一棵树,和Alice Bob的初始位置与他们能走的最大步长,问最多10100次移动后 Alice是否能抓到Bob,
首先Alice先移动 如果 da >= dist(Alice, Bob) 也就是Alice和Bob之间的距离不大于da 那么Alice第一步直接就能抓住Bob 游戏结束
否则 如果这棵树的最大距离不大于2da 那么Alice只要先移动到树中心 然后下一步就能抓住Bob 游戏结束
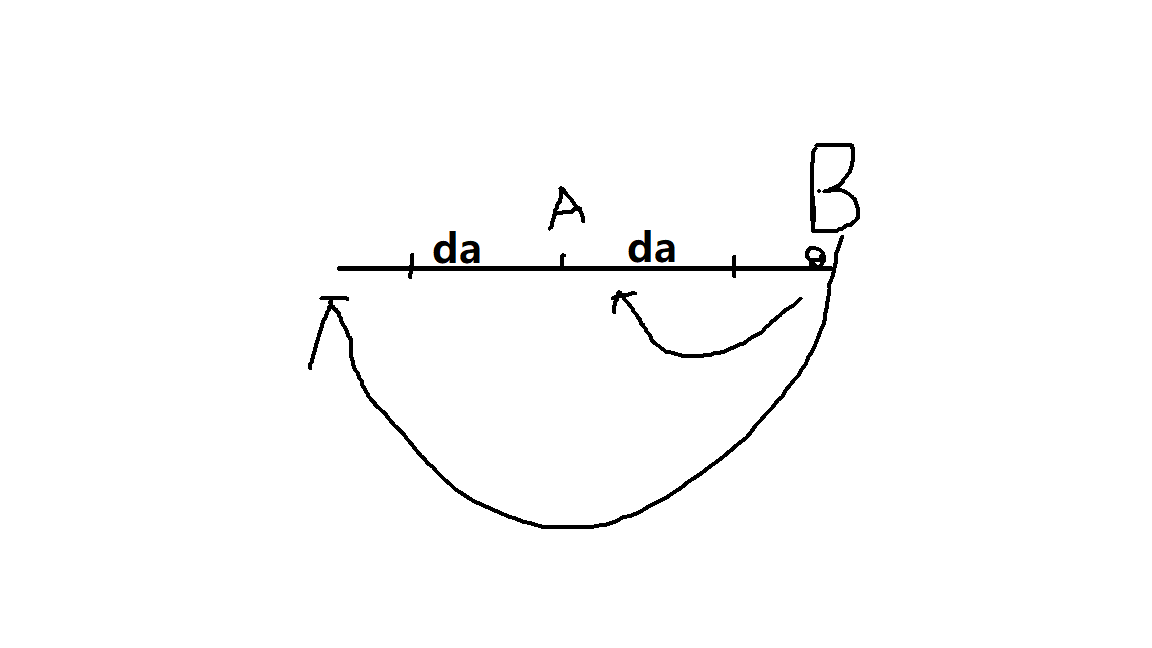
其次如果 2da>=db 则Bob 只会一步步被接近,最终被抓住, 如果db>2da 那么Bob可以一直跑两端耍Alice Alice永远不可能抓到Bob(如下图, enmmmm 有些粗糙 意会就好
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define _for(i,a,b) for(int i = (a); i < (b); i++) #define _rep(i,a,b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); i++) #define ll long long #define all(v) (v).begin(), (v).end()

void taskA() { int t; cin >> t; while(t--) { int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n); _for(i,0,n) cin >> a[n-i-1]; _for(i,0,n) cout << a[i] << " "; cout << " "; } return; }

void mis(ll& x, ll& y) { ll z = min(x, abs(y)); x -= z; y += z; } void taskB() { int t; cin >> t; while(t--) { int n; cin >> n; vector<ll> a(n); _for(i,0,n) cin >> a[i]; ll ans = 0; int f = 0; int x = 0, y = 0; _for(i,0,n) { if(a[i] > 0) ans += a[i], f = 1; else if(a[i]<0 and f and ans>0) mis(ans, a[i]); } cout << ans << " "; } return; }

void taskC() { int t; cin >> t; while(t--) { int n,k; cin >> n >> k; string s; cin >> s; int x = n/k, f = 0; _for(j,0,k) { char c = s[j]; _rep(i,1,x) { if(f) break; if(j+i*k >= n) continue; if(s[j+i*k] != '?' and c == '?') c = s[j+i*k]; if(c == s[j+i*k] or c == '?' or s[j+i*k] == '?'); else f = 1; } s[j] = c; } int a1 = 0, a2 = 0, a0 = 0; _for(i,0,k) if(s[i] == '1') a1++; else if(s[i] == '0') a0++; else a2++; //cout << " k = " << k << " , a1 = " << a1 << " , a0 = " << a0 << " "; if(a1>k/2 or a0>k/2) f = 1; cout << (f ? "NO" : "YES") << " "; } return; }

const int N = 1e5+10; int dep[N], diam; vector<int> adj[N]; int dfs(int x, int f) { int len = 0; for(int y : adj[x]) { if(y == f) continue; dep[y] = dep[x]+1; int cur = dfs(y, x) +1; diam = max(diam, cur+len); len = max(len, cur); } return len; } void taskD() { int t; cin >> t; while(t--) { int n,a,b,da,db; cin >> n >> a >> b >> da >> db; diam = 0; dep[a] = 0; _rep(i,1,n) adj[i].clear(); _for(i,1,n) { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; adj[x].push_back(y); adj[y].push_back(x); } dfs(a, 0); cout << ((da >= dep[b] or 2*da >= min(diam, db)) ? "Alice " : "Bob "); //Alice can capture Bob after first step or Alice can get closer step by step to Bob } return; }
int main() { ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr); //uva10795(); taskA(); //taskB(); //taskC(); //taskD(); return 0; }
