在软件开发中,发布于应用中多处的功能被称为横切关注点。通常,这些横切关注点从概念上是与应用的业务逻辑相分离的(但往往直接嵌入到应用的业务逻辑之中)。将横切关注点与业务逻辑相分离是AOP所要解决的。
一、AOP术语
1.通知(Advice):定义切面是什么以及何时使用。除了描述要完成的工作,还要解决何时执行工作。
5种类型的通知:
Before,在方法被调用之前调用通知
After,在方法完成之后调用通知,无论方法执行是否成功
After-returning,在方法成功执行之后调用通知
After-throwing,在方法抛出异常后调用通知
Around,通知包裹了被通知的方法,在被通知的方法调用之前和调用之后执行自定义的行为
2.连接点,是在应用执行过程中能够插入切面的一个点,切面可以利用这些点插入到应用的正常流程之中,并添加新的行为。
3.切点,切点的定义会匹配通知所要织入的一个或多个连接点。通常使用明确的类和方法名称来指定这些切点,或者利用正则表达式定义匹配的类和方法名称模式来指定这些切点。
4.切面,是通知和切点的结合,是什么,在何时和何处完成其功能。
5.引入,允许向现有的类添加新方法或属性,例如可以创建一个Auditable通知类,该类记录了对象最后一次修改时的状态,只需一种方法setLastModified(Date),和一个实例变量来保存这个状态。然后这个新方法和变量就可以被引入到现有的类中。从而在无需修改现有类的情况下,让它们具有新的行为和状态。
6.织入,将切面应用到目标对象来创建新的代理对象的过程,切面在指定的连接点被织入到目标对象中。在目标对象的声明周期有多个点可以进行织入。
编译期:在目标类编译时被织入,需要特殊编译器,AspectJ的织入编译器就是以这种方式织入切面的。
类加载期:在目标类加载到JVM时被织入,需要特殊的类加载器,可以在目标类被引入应用之前增强该目标类的字节码。AspectJ 5的LTW(load-time-weaving)支持以这种方式织入切面。
运行期:在应用运行的某个时刻被织入,一般情况下,在织入切面时,AOP容器会为目标对象动态地创建一个代理对象,Spring AOP以这种方式织入切面。
二、Spring对AOP的支持
提供4种各具特色的AOP支持:
1.基于代理的经典AOP
2.@AspectJ注解驱动的切面
3.纯POJO切面
4.注入式AspectJ切面(适合Spring各版本)
前3种都是Spring基于代理的AOP变体,因此,Spring对AOP的支持局限于方法拦截。如果需要构造器或属性拦截,那么应该考虑在AspectJ里实现切面,利用Spring的DI把Spring Bean注入到AspectJ切面中。
AOP框架的关键点:
1.Spring通知是Java编写的,可以使用与普通Java开发一样的IDE来开发切面,而且,定义通知所应用的切点通常在Spring配置文件里采用XML来编写。
2.Spring在运行期通知对象,通过在代理类中包裹切面,Spring在运行期将切面织入到Spring管理的Bean中。

代理类封装了目标类,并拦截被通知的方法的调用,再将调用转发给真正的目标Bean
当拦截到方法调用时,在调用目标Bean方法之前,代理会执行切面逻辑
直到应用需要被代理的Bean时,Spring才创建代理对象。如果使用ApplicationContext,在ApplicationContext从BeanFactory中加载所有Bean时,Spring创建被代理的对象。因为Spring运行时才创建代理对象,所以不需要特殊的编译器织入Spring AOP的切面。
3.Spring只支持方法连接点
二、使用切点选择连接点
切点用于准确定位应该在什么地方应用切面的通知。
在Spring AOP中,需要使用AspectJ的切点表达语言来定义切点。
Spring仅支持AspectJ切点指示器的一个子集。
| AspectJ指示器 | 描述 |
| arg() | 限制连接点匹配参数为指定类型的执行方法 |
|
@arg() |
限制连接点匹配参数由指定注解标注的执行方法 |
| execution() | 用于匹配是链接点的执行方法 |
| this() | 限制链接点匹配AOP代理的Bean引用为指定类型的类 |
| target() | 限制链接点匹配目标对象为指定类型的类 |
| @target() | 限制连接点匹配待定的执行对象,这些对象对应的类要具备指定类型的注解 |
| within() | 限制连接点匹配指定的类型 |
| @within() | 限制连接点匹配指定注解所标注的类型(当使用Spring AOP时,方法定义在由指定的注解所标注的类里) |
| @annotaion | 限制匹配带有指定注解连接点 |
1.编写切点

该切点表达式指示选择Instrument的play()方法执行时触发通知。(..)标识其诶单选择任意的play()方法,不管方法的入参是什么。
指示器之间可以混合使用,用and、or、not(&&、||、!)连接。
2.使用Spring的bean指示器
Spring 2.5引入一个新的bean()指示器,允许在切点表达式中使用Bean的ID来标识Bean。

在执行Instrument的play()方法时应用通知,但限定Bean的ID为eddie。
三、在XML中声明切面
AOP配置元素
| AOP配置元素 | 描述 |
| <aop:advisor> | 定义AOP通知器 |
| <aop:after> | 定义AOP后置通知(不管被通知的方法是否执行成功) |
| <aop:after-returning> | 定义AOP after-returning通知 |
| <aop:after-throwing> | 定义AOP after-throwing通知 |
| <aop:around> | 定义AOP环绕通知 |
| <aop:aspect> | 定义切面 |
| <aop:aspectj-autoproxy> | 启用@AspectJ注解驱动的切面 |
| <aop:before> | 定义AOP前置通知 |
| <aop:config> | 顶层的AOP配置元素,大多数的<aop:*>元素必须包含在<aop:config>元素内 |
| <aop:declare-parents> | 为被通知的对象引入额外的接口,并透明地实现 |
| <aop:pointcut> | 定义切点 |
创建一个公众类:
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; public class Audience { public void takeSeats() { System.out.println("The audience is taking their seats."); } public void turnOffPhones() { System.out.println("The audience is turning off their cellphones."); } public void applaud() { System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP CLAP CLAP..."); } public void demandRefund() { System.out.println("Boo! We want out money back!"); } }
Audience只是一个有几个方法的简单Java类。把它注册为Spring应用上下文的一个Bean
<bean id="audience" class="cn.edu.stu.springidol.Audience" />
把audience Bean变成一个切面:
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="audience">
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.edu.stu.springidol.Performer.perform(..))" id="performance"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="takeSeats"/>
<aop:before pointcut-ref="performance" method="turnOffPhones"/>
<aop:after-returning pointcut-ref="performance" method="applaud"/>
<aop:after-throwing pointcut-ref="performance" method="demandRefund"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
切点声明为当调用Performer的perform方法时,应用切面。
测试:
声明一个Instrumentalist Bean,它继承了Performer
<bean id="saxphone" class="cn.edu.stu.springidol.Saxphone" /> <bean id="kenny" class="cn.edu.stu.springidol.Instrumentalist"> <property name="song" value="Jingle Bells" /> <property name="instrument" ref="saxphone" /> </bean>
测试代码
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-idol.xml"); Performer p = (Performer) ctx.getBean("kenny"); p.perform();
结果打印出

声明环绕通知:
前面的切面使用了前置通知和后置通知,但如果不使用成员变量存储信息,那么在前置通知和后置通知之间共享信息非常麻烦。
例如,希望Audience能够知道参赛者表演了多长时间,如果使用成员变量保存开始时间,以为Audience是单例,将存在线程安全问题。
使用环绕通知,因为整个通知逻辑在一个方法内实现,所以不需要使用成员变量。
public void watchPerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint jointpoint) { try { System.out.println("The audience is taking their seats."); System.out.println("The audience is turning off their cellphone."); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); jointpoint.proceed();//执行被通知的方法 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP CLAP CLAP"); System.out.println("The performance took " + (end - start) + " milliseconds."); } catch(Throwable t) { System.out.println("Boo! We want out money back!"); } }
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="audience">
<aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.edu.stu.springidol.Performer.perform(..))" id="performance"/>
<aop:around pointcut-ref="performance" method="watchPerformance"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
测试代码一样,打印结果一样。
为通知传递参数:
有时候,通知不仅仅是对方法进行简单包装,还需要校验传递给方法的参数值,这时候为通知传递参数就非常有用了。
public interface MindReader { void interceptThoughts(String thoughts); String getThoughts(); } public class Magician implements MindReader { private String thoughts; @Override public void interceptThoughts(String thoughts) { System.out.println("Intercepting volunteer's thoughts"); this.thoughts = thoughts; } @Override public String getThoughts() { return thoughts; } } public interface Thinker { void thinkOfSomething(String thoughts); } public class Volunteer implements Thinker { private String thoughts; @Override public void thinkOfSomething(String thoughts) { this.thoughts = thoughts; } public String getThoughts() { return thoughts; } }
MindReader可以截获Thinker的想法thoughts(一个String参数)<bean id="magician" class="cn.edu.stu.springidol.Magician" />
<bean id="magician" class="cn.edu.stu.springidol.Magician" /> <bean id="volunteer" class="cn.edu.stu.springidol.Volunteer" /> <aop:config> <aop:aspect ref="magician"> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* cn.edu.stu.springidol.Thinker.thinkOfSomething(String)) and args(thoughts)" id="thinking"/> <aop:before pointcut-ref="thinking" method="interceptThoughts" arg-names="thoughts"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
切点标识了Thinker的thinkOfSomething方法,指定String参数,然后再args参数中标识了将thoughts作为参数,在<aop:before>元素引用了thoughts参数,标识该参数必须传递给Magician的interceptThoughts方法。
通过切面引入新功能:
切面只是实现了它们所包装Bean的相同接口的代理。如果代理还能发布新的接口,那么切面所通知的Bean看起来实现了新的接口,即便底层实现类并没有实现这些接口。

当引入接口的方法被调用时,代理将此调用委托给实现了新接口的某个其他对象。实际上,Bean的实现被拆分到多个类。
public interface Contestant { void receiveAward(); } public class GraciousContestant implements Contestant { @Override public void receiveAward() { System.out.println("Receive Award"); } }
XML配置
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect>
<aop:declare-parents
types-matching="cn.edu.stu.springidol.Performer+"
implement-interface="cn.edu.stu.springidol.Contestant"
default-impl="cn.edu.stu.springdiol.GraciousContestant"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
四、注解切面
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; @Aspect public class Audience { @Pointcut("execution(* cn.edu.stu.springidol.Performer.perform(..))") public void performance() { } @Before("performance()") public void takeSeats() { System.out.println("The audience is taking their seats."); } @Before("performance()") public void turnOffPhones() { System.out.println("The audience is turning off their cellphones."); } @AfterReturning("performance()") public void applaud() { System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP CLAP CLAP..."); } @AfterThrowing("performance()") public void demandRefund() { System.out.println("Boo! We want out money back!"); } }
除了注解和无操作的performance方法,Audience类在实现上没有任何改变。
让Spring将Audience应用为一个切面,需要在Spring上下文声明一个自动代理Bean,该Bean知道如何将@AspectJ注解所标注的Bean转变为代理通知。
aop提供的一个自定义的配置元素:
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
<aop:aspect>元素和@Aspect注解都是把一个POJO转变为一个切面的有效方式,但是<aop:aspect>相对@Aspect的优势是不需要实现切面功能的源码,通过@Aspect,我们必须标注类和方法,它需要源码,而<aop:aspect>可以引用任意一个Bean。
创建环绕通知:
@Around("performance()")
public void watchPerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint jointpoint) {
try {
System.out.println("The audience is taking their seats.");
System.out.println("The audience is turning off their cellphone.");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
jointpoint.proceed();//执行被通知的方法
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("CLAP CLAP CLAP CLAP CLAP");
System.out.println("The performance took " + (end - start) + " milliseconds.");
} catch(Throwable t) {
System.out.println("Boo! We want out money back!");
}
}
传递参数给所标注的通知:
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; @Aspect public class Magician implements MindReader { private String thoughts; @Pointcut("execution(* cn.edu.stu.springidol.Thinker.thinkOfSomething(String)) && args(thoughts)") public void thinking(String thoughts) { } @Override @Before("thinking(thoughts)") public void interceptThoughts(String thoughts) { System.out.println("Intercepting volunteer's thoughts : " + thoughts); this.thoughts = thoughts; } @Override public String getThoughts() { return thoughts; } }
标注引入:
@Aspect public class ContestantIntroducer { @DeclareParents(value = "cn.edu.stu.springidol.Performer+", defaultImpl = GraciousContestant.class) public static Contestant contestant; }
ContestantIntroducer是一个切面,它为Performer Bean引入Contestant接口,单没有delegate-ref的对应物,所以单靠@DeclareParents还不行,必须借助<aop:declare-parents>
五、注入AspectJ切面
AspectJ提供比Spring AOP更细粒度的通知,例如拦截对象字段的修改,支持构造器链接点。
创建一个新切面(这是一个aspect):
public aspect JudgeAspect { public JudgeAspect() { } pointcut performance() : execution(* perform(..)); after() returning() : performance() { System.out.println(criticismEngine.getCriticism()); } private CriticismEngine criticismEngine; public void setCriticismEngine(CriticismEngine criticismEngine) { this.criticismEngine = criticismEngine; } }
JudgeAspect的职责是在表演结束后为表演发表评论,performance()切点匹配perform()方法,当它与after() returning()通知一起配合使用时,可以让该切面在表演结束时起作用。
并不是JudgeAspect本身发表评论,它与一个CriticismEngine对象相协作,调用该对象的getCriticism()方法发表一个评论,为了避免JudgeAspect和CriticismEngine产生耦合,通过setter依赖注入为JudgeAspect赋予CriticismEngine。
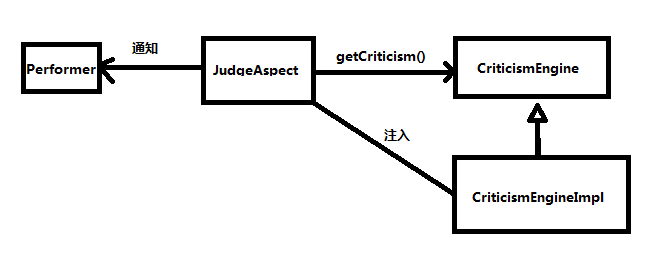
public interface CriticismEngine { String getCriticism(); } public class CriticismEngineImpl implements CriticismEngine { @Override public String getCriticism() { int i = (int) (Math.random() * criticismPool.length); return criticismPool[i]; } private String[] criticismPool; public void setCriticismPool(String[] criticismPool) { this.criticismPool = criticismPool; } }
<bean id="criticismEngine" class="cn.edu.stu.springidol.CriticismEngineImpl"> <property name="criticisms"> <list> <value>I'm not being rude, but that was appalling.</value> <value>You may be the least talented person in this show.</value> <value>Do every a favor and keep your day job.</value> </list> </property> </bean> <bean class="cn.edu.stu.springidol.JudgeAspect" factory-method="aspectOf"> <property name="criticismEngine" ref="criticismEngine" /> </bean>
通常情况下,Spring Bean由Spring容器初始化,但是AspectJ切面是由AspectJ在运行期创建的。因为Spring无法负责创建JudgeAspect,就不能简单地将JudgeAspect声明为一个Bean,相反,需要一种方式为所有的AspectJ切面提供一个静态的aspectOf()方法,该方法返回切面的一个单例。必须使用factory-method来调用aspectOf()方法来代替调用JudgeAspect的构造器方法。