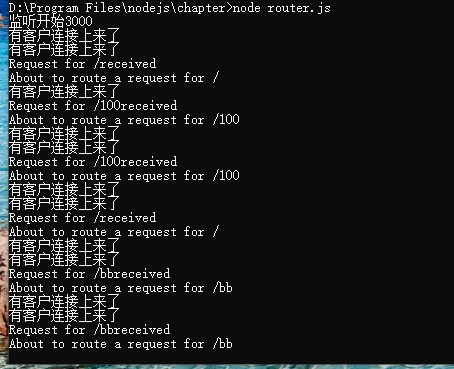
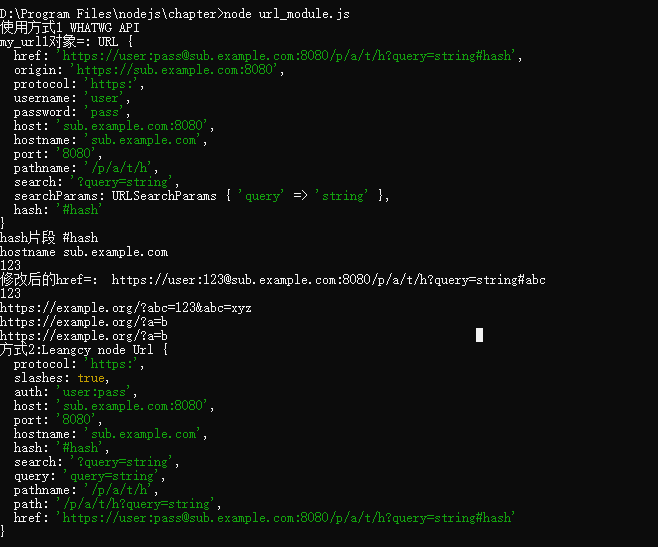
/* 1:url模块:url模块提供了对URl字符串的解析, (1):每一个url字符串由多个有特定的意义的组件构成. 例如href:'http://user:pass@sub.example.com:8080/p/a/t/h?query=string#hash' 由protocol,auth,,host,path,hash所构成 ┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │ href │ ├──────────┬──┬─────────────────────┬────────────────────────┬───────────────────────────┬───────┤ │ protocol │ │ auth │ host │ path │ hash │ │ │ │ ├─────────────────┬──────┼──────────┬────────────────┤ │ │ │ │ │ hostname │ port │ pathname │ search │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ ├─┬──────────────┤ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ query │ │ " https: // user : pass @ sub.example.com : 8080 /p/a/t/h ? query=string #hash " │ │ │ │ │ hostname │ port │ │ │ │ │ │ │ │ ├─────────────────┴──────┤ │ │ │ │ protocol │ │ username │ password │ host │ │ │ │ ├──────────┴──┼──────────┴──────────┼────────────────────────┤ │ │ │ │ origin │ │ origin │ pathname │ search │ hash │ ├─────────────┴─────────────────────┴────────────────────────┴──────────┴────────────────┴───────┤ │ href │ └────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ */ const url = require('url'); //导入url模块 //解析url有两种方式: console.log("使用方式1","WHATWG API"); //方式1:使用WHATWG API const my_url1 = new URL('https://user:pass@sub.example.com:8080/p/a/t/h?query=string#hash'); //获取href片段的内容 console.log("my_url1对象=:",my_url1); console.log("hash片段",my_url1.hash); console.log("hostname",my_url1.hostname); my_url1.password = "123"; console.log(my_url1.password); //修改片段 my_url1.hash = 'abc'; console.log("修改后的href=:",my_url1.href); console.log("方法toString",my_url1.toString); console.log(my_url1); /* class:URLSearchParams:提供了对url的读与查,写。该类的实例为全局对象。 */ const myURL = new URL('https://example.org/?abc=123'); console.log(myURL.searchParams.get('abc')); // Prints 123 myURL.searchParams.append('abc', 'xyz'); console.log(myURL.href); // Prints https://example.org/?abc=123&abc=xyz myURL.searchParams.delete('abc'); myURL.searchParams.set('a', 'b'); console.log(myURL.href); // Prints https://example.org/?a=b const newSearchParams = new URLSearchParams(myURL.searchParams); // The above is equivalent to // const newSearchParams = new URLSearchParams(myURL.search); newSearchParams.append('a', 'c'); console.log(myURL.href); // Prints https://example.org/?a=b //方式2: const my_url2 = url.parse('https://user:pass@sub.example.com:8080/p/a/t/h?query=string#hash'); console.log("方式2:Leangcy node",my_url2)
二:node.js路由:
server.js
var http = require("http"); var url = require("url"); /* var server = http.createServer(); server.on('request',(res,req)=>{ }); */ function open(route) { /*server.listen(3000,function(){ console.log('server is listening at port 3000'); });*/ function Request(res,rep) { var pathname = url.parse(res.url).pathname; console.log("Request for "+pathname+"received"); route(pathname); //路由 rep.writeHead(200,{"Conten-Type":"text/plain"}); rep.write("Hello World"); rep.end(); } server = http.createServer(Request).listen(3000) server.on('listening',function(){ console.log("监听开始3000"); }); server.on('connection',function() { console.log('有客户连接上来了'); }); server.on('error',function(e) { rep.write('Not Get 3000'); rep.end(); console.log(e); }); } exports.open = open; /*对外开放*/
router.js
var server = require("./server_url"); server.open(function (pathname) { console.log("About to route a request for " + pathname); if(pathname.port===3000) { rep.write("端口为3000"); rep.end(); } })