1、SpringBoot定时任务schedule讲解
定时任务应用场景:

简介:讲解什么是定时任务和常见定时任务区别
1、常见定时任务 Java自带的java.util.Timer类
timer:配置比较麻烦,时间延后问题
timertask:不推荐
2、Quartz框架
配置更简单
xml或者注解
3、SpringBoot使用注解方式开启定时任务
1)启动类里面 @EnableScheduling开启定时任务,自动扫描
2)定时任务业务类 加注解 @Component被容器扫描
3)定时执行的方法加上注解 @Scheduled(fixedRate=2000) 定期执行一次 单位:ms
代码示例:
XdclassApplication.java启动类:
1 package net.xdclass.base_project; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; 6 7 @SpringBootApplication //一个注解顶下面3个 8 @EnableScheduling //开启定时任务 9 public class XdclassApplication { 10 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 SpringApplication.run(XdclassApplication.class, args); 13 } 14 }
TestTask.java:
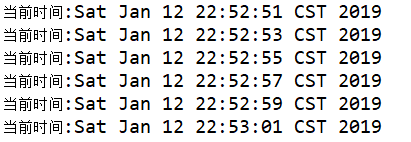
1 package net.xdclass.base_project.task; 2 3 import java.util.Date; 4 5 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; 6 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 7 8 @Component 9 public class TestTask { 10 11 12 @Scheduled(fixedRate=2000) //两秒执行一次 13 public void sum(){ 14 System.out.println("当前时间:"+new Date()); 15 } 16 17 18 }
控制台输出:
2、SpringBoot常用定时任务配置实战
简介:SpringBoot常用定时任务表达式配置和在线生成器
1、cron 定时任务表达式 @Scheduled(cron="*/1 * * * * *") 表示每秒
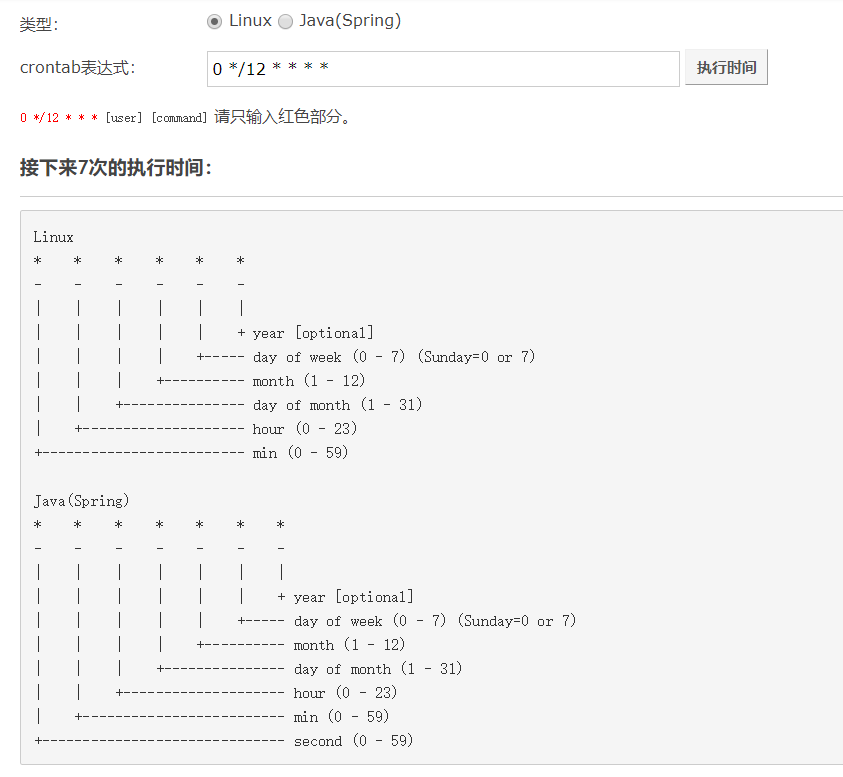
1)crontab 工具 https://tool.lu/crontab/
代码示例:(每2s执行一次)
1 @Scheduled(cron="*/2 * * * * *") 2 public void sum(){ 3 System.out.println("当前时间:"+new Date()); 4 }
2、fixedRate: 定时多久执行一次(上一次开始执行时间点后xx秒再次执行;)
3、fixedDelay: 上一次执行结束时间点后xx秒再次执行
4、fixedDelayString: 字符串形式,可以通过配置文件指定
3、SpringBoot2.x异步任务实战(核心知识)
简介:讲解什么是异步任务,和使用SpringBoot2.x开发异步任务实战
1、什么是异步任务和使用场景:适用于处理log、发送邮件、短信……等
下单接口->查库存 100
余额校验 150
风控用户100
....
2、启动类里面使用@EnableAsync注解开启功能,自动扫描
3、定义异步任务类并使用@Component标记组件被容器扫描,异步方法加上@Async
注意点:
1)要把异步任务封装到类里面,不能直接写到Controller
2)增加Future<String> 返回结果 AsyncResult<String>("task执行完成");
3)如果需要拿到结果 需要判断全部的 task.isDone()
4、通过注入方式,注入到controller里面,如果测试前后区别则改为同步则把Async注释掉
代码示例:
XdclassApplication.java:
1 package net.xdclass.base_project; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; 6 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; 7 8 @SpringBootApplication //一个注解顶下面3个 9 @EnableScheduling //开启定时任务 10 @EnableAsync //开启异步任务 11 public class XdclassApplication { 12 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 SpringApplication.run(XdclassApplication.class, args); 15 } 16 }
AsyncTask.java:
1 package net.xdclass.base_project.task; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 4 5 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; 6 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult; 7 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 8 9 @Component 10 @Async //异步方法,该方法注掉后为同步 11 public class AsyncTask { 12 13 public void task1() throws InterruptedException{ 14 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); 15 Thread.sleep(1000L); 16 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 17 System.out.println("任务1耗时="+(end-begin)); 18 } 19 20 21 public void task2() throws InterruptedException{ 22 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); 23 Thread.sleep(2000L); 24 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 25 System.out.println("任务2耗时="+(end-begin)); 26 } 27 28 29 public void task3() throws InterruptedException{ 30 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); 31 Thread.sleep(3000L); 32 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 33 System.out.println("任务3耗时="+(end-begin)); 34 } 35 36 37 //获取异步结果 38 39 public Future<String> task4() throws InterruptedException{ 40 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); 41 Thread.sleep(2000L); 42 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 43 System.out.println("任务4耗时="+(end-begin)); 44 return new AsyncResult<String>("任务4"); 45 } 46 47 48 public Future<String> task5() throws InterruptedException{ 49 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); 50 Thread.sleep(3000L); 51 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 52 System.out.println("任务5耗时="+(end-begin)); 53 return new AsyncResult<String>("任务5"); 54 } 55 56 public Future<String> task6() throws InterruptedException{ 57 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); 58 Thread.sleep(1000L); 59 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 60 System.out.println("任务6耗时="+(end-begin)); 61 return new AsyncResult<String>("任务6"); 62 } 63 64 }
UserController.java测试:
1 package net.xdclass.base_project.controller; 2 3 import net.xdclass.base_project.domain.JsonData; 4 import net.xdclass.base_project.task.AsyncTask; 5 6 import java.util.concurrent.Future; 7 8 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; 9 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; 10 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; 11 import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; 12 13 14 @RestController 15 @RequestMapping("/api/v1") 16 public class UserController { 17 18 @Autowired 19 private AsyncTask task; 20 21 @GetMapping("async_task") 22 public JsonData exeTask() throws InterruptedException{ 23 24 long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); 25 26 // task.task1(); 27 // task.task2(); 28 // task.task3(); 29 30 Future<String> task4 = task.task4(); 31 Future<String> task5 = task.task5(); 32 Future<String> task6 = task.task6(); 33 34 //需要返回结果可以使用该方法 35 for(;;){ 36 if(task4.isDone() && task5.isDone() && task6.isDone()){ 37 break; 38 } 39 } 40 41 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); 42 long total = end - begin; 43 System.out.println("执行总耗时=" + total); 44 return JsonData.buildSuccess(total); 45 } 46 47 }
同步/异步执行时间对比:
同步:

异步:

由此可见,同步与异步,它们的执行效率是不同的,应根据需求进行选择使用。