Petya loves computer games. Finally a game that he's been waiting for so long came out!
The main character of this game has n different skills, each of which is characterized by an integer ai from 0 to 100. The higher the numberai is, the higher is the i-th skill of the character. The total rating of the character is calculated as the sum of the values of 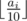 for all i from 1 to n. The expression ⌊ x⌋ denotes the result of rounding the number x down to the nearest integer.
for all i from 1 to n. The expression ⌊ x⌋ denotes the result of rounding the number x down to the nearest integer.
At the beginning of the game Petya got k improvement units as a bonus that he can use to increase the skills of his character and his total rating. One improvement unit can increase any skill of Petya's character by exactly one. For example, if a4 = 46, after using one imporvement unit to this skill, it becomes equal to 47. A hero's skill cannot rise higher more than 100. Thus, it is permissible that some of the units will remain unused.
Your task is to determine the optimal way of using the improvement units so as to maximize the overall rating of the character. It is not necessary to use all the improvement units.
The first line of the input contains two positive integers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 0 ≤ k ≤ 107) — the number of skills of the character and the number of units of improvements at Petya's disposal.
The second line of the input contains a sequence of n integers ai (0 ≤ ai ≤ 100), where ai characterizes the level of the i-th skill of the character.
The first line of the output should contain a single non-negative integer — the maximum total rating of the character that Petya can get using k or less improvement units.
2 4
7 9
2
3 8
17 15 19
5
2 2
99 100
20
In the first test case the optimal strategy is as follows. Petya has to improve the first skill to 10 by spending 3 improvement units, and the second skill to 10, by spending one improvement unit. Thus, Petya spends all his improvement units and the total rating of the character becomes equal to lfloor frac{100}{10} rfloor + lfloor frac{100}{10} rfloor = 10 + 10 = 20.
In the second test the optimal strategy for Petya is to improve the first skill to 20 (by spending 3 improvement units) and to improve the third skill to 20 (in this case by spending 1 improvement units). Thus, Petya is left with 4 improvement units and he will be able to increase the second skill to 19 (which does not change the overall rating, so Petya does not necessarily have to do it). Therefore, the highest possible total rating in this example is 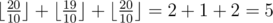 .
.
In the third test case the optimal strategy for Petya is to increase the first skill to 100 by spending 1 improvement unit. Thereafter, both skills of the character will be equal to 100, so Petya will not be able to spend the remaining improvement unit. So the answer is equal to 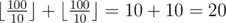 .
.
不能超过100没看到...
贡献若干次wa...蠢哭了.
然后写蠢了...
最后觉得这样写比较好:
开一个结构体数组... a,b
a用来记录原始值,b用来记录mod10的余数与10的差..
整个填充过程分两步骤
第一步是把余数不为0的填充到10..
这部分要先填充...显然比先填充余数为0的更优.而且先填充余数大的..也就是b小的...
以b为关键字...从小到达排序..
然后填充的时候记得更新 a的值到整十
同时用一个sum累加更新后的a[i] 到100的距离...
sum/10是一个限制条件
而k/10是第二个限制条件
所以答案最后加上 min(k,sum)/10;

1 /************************************************************************* 2 > File Name: code/cf/#322/C.cpp 3 > Author: 111qqz 4 > Email: rkz2013@126.com 5 > Created Time: 2015年09月29日 星期二 00时40分26秒 6 ************************************************************************/ 7 8 #include<iostream> 9 #include<iomanip> 10 #include<cstdio> 11 #include<algorithm> 12 #include<cmath> 13 #include<cstring> 14 #include<string> 15 #include<map> 16 #include<set> 17 #include<queue> 18 #include<vector> 19 #include<stack> 20 #include<cctype> 21 #define y1 hust111qqz 22 #define yn hez111qqz 23 #define j1 cute111qqz 24 #define ms(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a)) 25 #define lr dying111qqz 26 using namespace std; 27 #define For(i, n) for (int i=0;i<int(n);++i) 28 typedef long long LL; 29 typedef double DB; 30 const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; 31 const int N=1E5+7; 32 int n; 33 int k,ans; 34 35 struct Q 36 { 37 int a,b; 38 }q[N]; 39 40 bool cmp(Q x, Q y) 41 { 42 if (x.b<y.b) return true; 43 return false; 44 } 45 int main() 46 { 47 #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE 48 // freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); 49 #endif 50 51 ans = 0 ; 52 scanf("%d %d",&n,&k); 53 for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) 54 { 55 scanf("%d",&q[i].a); 56 ans = ans + q[i].a / 10; 57 q[i].b = q[i].a % 10 ; 58 q[i].b = 10 - q[i].b; 59 } 60 sort(q,q+n,cmp); 61 int sum = 0 ; 62 int i = 0; 63 for ( int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) 64 { 65 // if (q[i].b==10) break; 66 if (k-q[i].b>=0) 67 { 68 k = k - q[i].b; 69 q[i].a = 100-(q[i].a/10+1)*10; 70 sum = sum + q[i].a; 71 ans++; 72 } 73 if (k<=0) break; 74 } 75 ans = ans + min(k,sum)/10 ; 76 77 // cout<<"ans:"<<ans<<endl; 78 79 printf("%d",ans); 80 81 82 #ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE 83 fclose(stdin); 84 #endif 85 return 0; 86 }
