使用C语言的数据结构模拟进程的调度
一、 实验目的
通过模拟进程的调度,进一步了解进程的调度的具体过程。
二、 实验内容和要求
1.进程PCB的结构体定义
2.定义队列
3.输入进程序列
4.排序(按到位时间)
5.输出进程运行的结果
三、 实验方法、步骤及结果测试
- 1. 源程序:
#include<stdio.h> #include<malloc.h> #include<time.h> /*定义一个Course类型的结构体*/ typedef struct queue{ int number; int intime; int runningtime; int alltime; int waitingtime; struct node *next; }Course; /*定义一个PCB类型来表示队列*/ typedef struct node2{ Course *front; Course *rear; }PCB; /*初始化队列*/ PCB initqueue(){ PCB q; q.front=(Course *)malloc(sizeof(Course)); q.front->next=NULL; q.rear=q.front; return(q); } /*进入队列*/ PCB inserq(PCB q,int x,int j,int y,int k){ Course *p; p=(Course *)malloc(sizeof(Course)); //申请结点p p->number=x;//x.j.y.k储存到新结点p中 p->intime=j; p->runningtime=y; p->waitingtime=k; p->alltime=y+k; p->next=NULL;//p的指针域置空 q.rear->next=p;//指针域指向p,p成为新的队尾 q.rear=p; //对尾指针域指向p,保证rear指向新的队尾 return (q); } /* 打印进程调度的结果*/ void display(PCB q) { Course *p; printf(" 队列: "); p=q.front->next; while(p!=NULL) { printf("进程进入的顺序:%d ",p->intime);printf(" "); printf("进程的编号:%d ",p->number); printf("进程运行的时间:%d ",p->runningtime); printf("进程等待的时间:%d ",p->waitingtime); printf("进程所用的总时间:%d ",p->alltime); printf(" "); p=p->next; } } main(){ int x,y,z,i=0,k,j=1/*用来记录进程进入的顺序*/; PCB q; q=initqueue(); for(i=0;i<5;i++ ){ printf("请输入进程的编号:"); scanf("%d",&x); printf("请输入进程的运行的时间:"); scanf("%d",&y); k=rand()%10;//随机产生0-9的数,代表进程要等待的时间。 q=inserq(q,x,j,y,k); j++; } display(q); }
- 2. 原理分析及流程图
主要总体设计问题。
存储结构:链式存储
主要算法:结构体的定义;队列的实现。
关键函数:
initqueue()//初始化队列
inserq()//进入队列
display()//打印队列
- 3. 主要程序段及其解释:
/*主函数,实现对结构体类型变量的定义以及对队列的使用*/
main(){ int x,y,z,i=0,k,j=1/*用来记录进程进入的顺序*/; PCB q; q=initqueue(); for(i=0;i<5;i++ ){ printf("请输入进程的编号:"); scanf("%d",&x); printf("请输入进程的运行的时间:"); scanf("%d",&y); k=rand()%10;//随机产生0-9的数,代表进程要等待的时间。 q=inserq(q,x,j,y,k); j++; } display(q);
}
/*定义一个Course类型的结构体*/
typedef struct queue{
int number;
int intime;
int runningtime;
int alltime;
int waitingtime;
struct node *next;
}Course;
/*初始化队列*/
PCB initqueue(){
PCB q;
q.front=(Course *)malloc(sizeof(Course));
q.front->next=NULL;
q.rear=q.front;
return(q);
}
/*进入队列*/
PCB inserq(PCB q,int x,int j,int y,int k){
Course *p;
p=(Course *)malloc(sizeof(Course)); //申请结点p
p->number=x;//x.j.y.k储存到新结点p中
p->intime=j;
p->runningtime=y;
p->waitingtime=k;
p->alltime=y+k;
p->next=NULL;//p的指针域置空
q.rear->next=p;//指针域指向p,p成为新的队尾
q.rear=p; //对尾指针域指向p,保证rear指向新的队尾
return (q);
}
/* 打印进程调度的结果*/
void display(PCB q)
{
Course *p;
printf("
队列:
");
p=q.front->next;
while(p!=NULL)
{
printf("进程进入的顺序:%d ",p->intime);printf("
");
printf("进程的编号:%d ",p->number);
printf("进程运行的时间:%d ",p->runningtime);
printf("进程等待的时间:%d ",p->waitingtime);
printf("进程所用的总时间:%d ",p->alltime);
printf("
");
p=p->next;
}
}
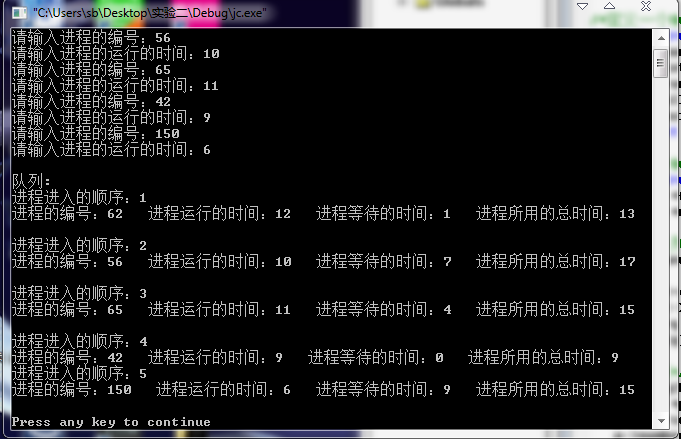
- 4. 运行结果及分析
运行结果的截图: