输入数据
使用键盘输入数据
只能处理小样本,很少使用
在创建 data.txt 字符串之后,用函数 read.table() 创建数据框 data.1。这种方法可以让我们把数据嵌入到R代码中,此处切记,read.table() 使我们最为常用的读取外部数据的函数。
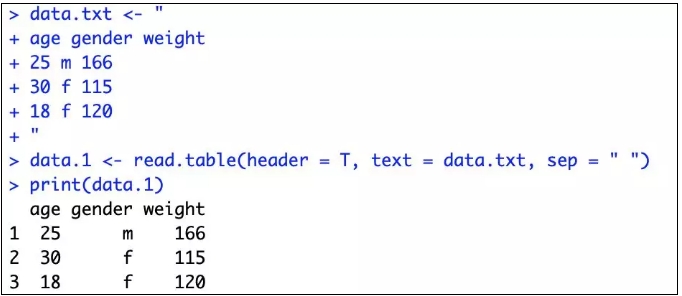
下面的方法是用函数 fix() 创建了一个和data.1一样的数据框 data.2,函数 edit() 也有同样的效果。


从文本文件导入数据 read.table()
函数 read.table() 更加常用的是从带有分隔符的文本文件中国读入数据并创建数据框。类似的函数有 read.csv(),read.csv2()
例子
data.3 <- read.table(file="example.txt", header = T, quote = """, sep = ",") # header = T 表示第一行是变量名不做事数据一部分 header = F 表示第一行也作为数据的一部分
data.4 <- read.table(file="example.txt", header = T, skip = 7, sep = ",", quote = """, row.names = "Study")
从 xlsx 文件中读入数据
需要使用R包 openxlsx 或者 readxl
输出数据
输出函数:cat() print() write() sink() writeLines() write.table()
在R里,输出到屏幕不要用print() 而是用cat()。因为 print() 输出的字符都是只能显示在控制台,而控制台只能显示文本,所以回车符 制表符都会员样输出
cat() 函数既能输出到屏幕也能输出到文件 需要手动添加换行符
cat(..., file = " ", sep = " ", fill = FALSE, labels = NULL, append = FALSE)
有file时,输出到file;无file时,输出到屏幕
append 参数:布尔值。TRUE 输出内容追加到文件尾部,FALSE 输出的内容覆盖文件的原始内容。
print() 函数 原封不动的输出对象 比对列表
print(x, ...)
## S3 method for class 'factor'
print(x, quote = FALSE, max.levels = NULL, width = getOption("width"), ...)
## S3 method for class 'table'
print(x, digits = getOption("digits"), quote = FALSE, na.print = "", zero.print = "0", right = is.numeric(x) || is.complex(x), justify = "none", ...)
## S3 method for class 'function'
print(x, useSource = TRUE, ...)

write()用于输出到文件,也可以输出到标准输出,无需手动添加换行符
write(x, file = "data", ncolumns = if(is.character(x)) 1 else 5, append = FALSE, sep = " ")
当 file = "" 时 输出到标准输出
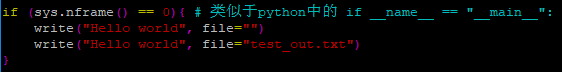
sink() 函数将输出结果重定向到文件
sink(file = NULL, append =FALSE, type = c("output", "message"), split = FALSE)
append参数:布尔值。TRUE时 输出内容追加到文件尾部,FALSE时 覆盖文件的原始内容。

writeLines() 函数将字符串向量输出到文件中 也可以输出到标准输出 会覆盖原始内容
writeLines(text, con = stdout(), sep = " ", useBytes = FALSE)
text:字符串向量
con:输出文件, 默认输出到标准输出
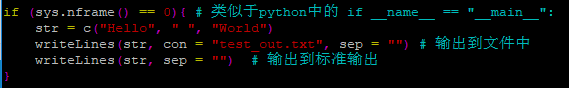
write.table()函数将 data.frame 的内容输出到文件或者标准输出
write.table(x file = "", append = FALSE, quote = TRUE, sep = " ", eol = " ", na = "NA", dec = ",", row.names = TRUE, col.names = TRUE, qmethod = c("escape", "double"), fileEncoding = "")

读取命令行参数
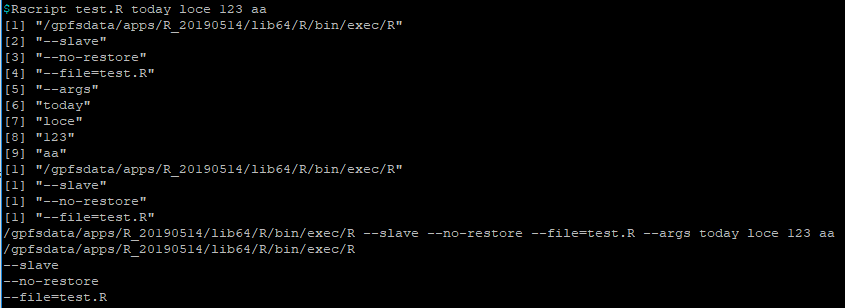
commandArgs() 是R自带的参数传递,属于位置参数
args = commandArgs(trailingOnly = FALSE) # R程序自带参数,从第6个开始才是命令行输入的参数
args = commandArgs(trailingOnly = TRUE) # 此时 输入的第一个参数就是程序的第一个参数
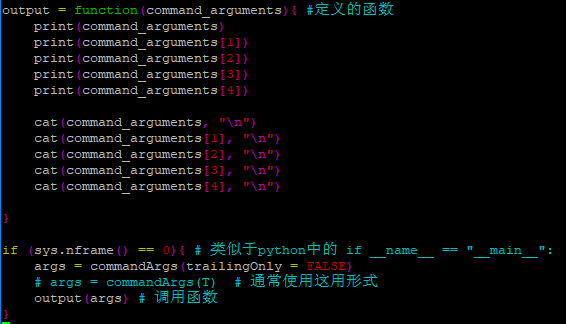
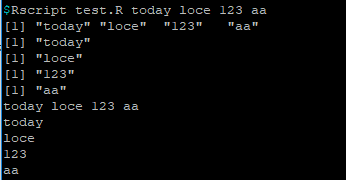
如果改为 args = commandArgs(trailingOnly = FALSE) 输出结果如下:
getopt 包中的 getopt() 函数也可以接受从终端传递的参数,并且功能更加丰富
getopt(spec = NULL, opt = commandArgs(TRUE), command = get_Rscript_filename(), usage = FALSE, debug = FALSE)
其中 spec 是一个4列或者5列的矩阵,里面包括了参数信息,前四列是必须的,第五列是可选的
第一列:指定参数的 longname ,多个字符
第二列:指定参数的 shortname,一个字符
第三列:指定参数是必须的还是可选的,数字,0 不接受参数 1 必须有参数 2 参数可选
第四列:指定参数的类型 logical integer double complex character numeric
第五列:注释信息 可选
usage:默认为FALSE 这是参数无实际意义,而是以用法的形式输出。
library(getopt) spec = matrix(c( 'verbose', 'v', 2, "integer", 'help' , 'h', 0, "logical", 'count' , 'c', 1, "integer", 'mean' , 'm', 1, "double", ), byrow=TRUE, ncol=4) opt = getopt(spec) print(opt$count) print(opt$mean)

如何制作脚本的帮助
command=matrix(c("bam","b",1,"character", "bed","d",1,"character", "png","p",1,"character", "help","h",0,"logical"),byrow=T,ncol=4) args=getopt(command) if (!is.null(args$help) || is.null(args$bam) || is.null(args$png) || is.null(args$bed)) { cat(paste(getopt(command, usage = T), " ")) q() }