Python 图像库(Python Image Library,PIL)为 Python 提供了图像处理能力。
PIL 官网:http://www.pythonware.com/products/pil/
PIL 在线手册:http://www.pythonware.com/library/pil/handbook/index.htm
pillow 是 PIL 的一个派生分支,更加活跃。
pillow 的 github 主页:https://github.com/python-pillow/Pillow
pillow 的文档:https://pillow.readthedocs.io/en/latest/handbook/index.html
安装 pillow
pip install pillow
使用 pillow
from PIL import Image im = Image.open("hopper.ppm")
PIL 坐标系统假定坐标(0,0)位于左上角。
一个对图片进行过滤的例子
import os from PIL import Image, ImageFilter class DemoPIL(object): def __init__(self, image_file=None): # 构造器 self.fixed_filters = [ff for ff in dir(ImageFilter) if ff.isupper()] # dir(ImageFilter)返回ImageFilter类的属性。 isupper()是str的方法,当所有字母大写返回True assert image_file is not None assert os.path.isfile(image_file) is True # 断言文件是否存在 self.image_file = image_file self.image = Image.open(self.image_file) # 返回一个 Image 对象实例 def _make_temp_dir(self): from tempfile import mkdtemp self.ff_tempdir = mkdtemp(prefix="ff_demo_", dir="C:\Users\mail.simcere.com\Desktop") # 创建临时路径 def _get_temp_name(self, filter_name): name, ext = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(self.image_file)) newimage_file = name + "-" + filter_name + ext path = os.path.join(self.ff_tempdir, newimage_file) return path def _get_filter(self, filter_name): real_filter = eval("ImageFilter." + filter_name) return real_filter def apply_filter(self, filter_name): print('Applying filter:' + filter_name) filter_callable = self._get_filter(filter_name) if filter_name in self.fixed_filters: temp_img = self.image.filter(filter_callable) else: print("Can't apply non-fixed filter now.") return temp_img def run_fixed_filters_demo(self): self._make_temp_dir() for ffilter in self.fixed_filters: temp_img = self.apply_filter(ffilter) temp_img.save(self._get_temp_name(ffilter)) # 保存图像 print("Images are in: {0}".format((self.ff_tempdir),)) if __name__ == '__main__': # assert len(sys.argv) == 2 demo_image = "sunset.jpg" demo = DemoPIL(demo_image) # 获取 DemoPIL 实例对象 demo.run_fixed_filters_demo()


处理某一特定文件夹下的所有图像文件
指定一个目标路径,用程序读取目标路径下的所有图像,并按给定比例调整他们的大小,然后把每一个文件存储到另一个指令文件夹下。
import os import sys from PIL import Image class Thumbnailer(object): def __init__(self, src_folder=None): self.src_folder = src_folder self.ratio = 0.3 self.thumbnail_folder = "thumbnails" def _create_thumbnails_folder(self): thumb_path = os.path.join(self.src_folder, self.thumbnail_folder) if not os.path.isdir(thumb_path): os.makedirs(thumb_path) def _build_thumb_path(self, image_path): root = os.path.dirname(image_path) name, ext = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(image_path)) suffix = ".thumbnail" return os.path.join(root, self.thumbnail_folder, name + suffix + ext) def _load_files(self): files = set() for each in os.listdir(self.src_folder): each = os.path.abspath(self.src_folder + '/' + each) if os.path.isfile(each): files.add(each) return files def _thumb_size(self, size): return (int(size[0]*self.ratio), int(size[1]*self.ratio)) def create_thumbnails(self): self._create_thumbnails_folder() files = self._load_files() for each in files: print("Processing: " + each) try: img = Image.open(each) # 返回 Image对象实例 thumb_size = self._thumb_size(img.size) resized = img.resize(thumb_size, Image.ANTIALIAS) # 重新设置大小 savepath = self._build_thumb_path(each) resized.save(savepath) except IOError as ex: print("Error: " + str(ex)) if __name__ == "__main__": # assert len(sys.argv) == 2 src_folder = "images" # 这里提供相对路径 if not os.path.isdir(src_folder): print("Error: Path '{0}' does not exists.".format((src_folder))) sys.exit(-1) thumbs = Thumbnailer(src_folder) # 得到 Thumbnailer的实例对象 thumbs.thumbnail_folder = "THUMBS" # 直接修改了对象的属性,破坏了数据封装的原则 thumbs.ratio =0.1 thumbs.create_thumbnails()

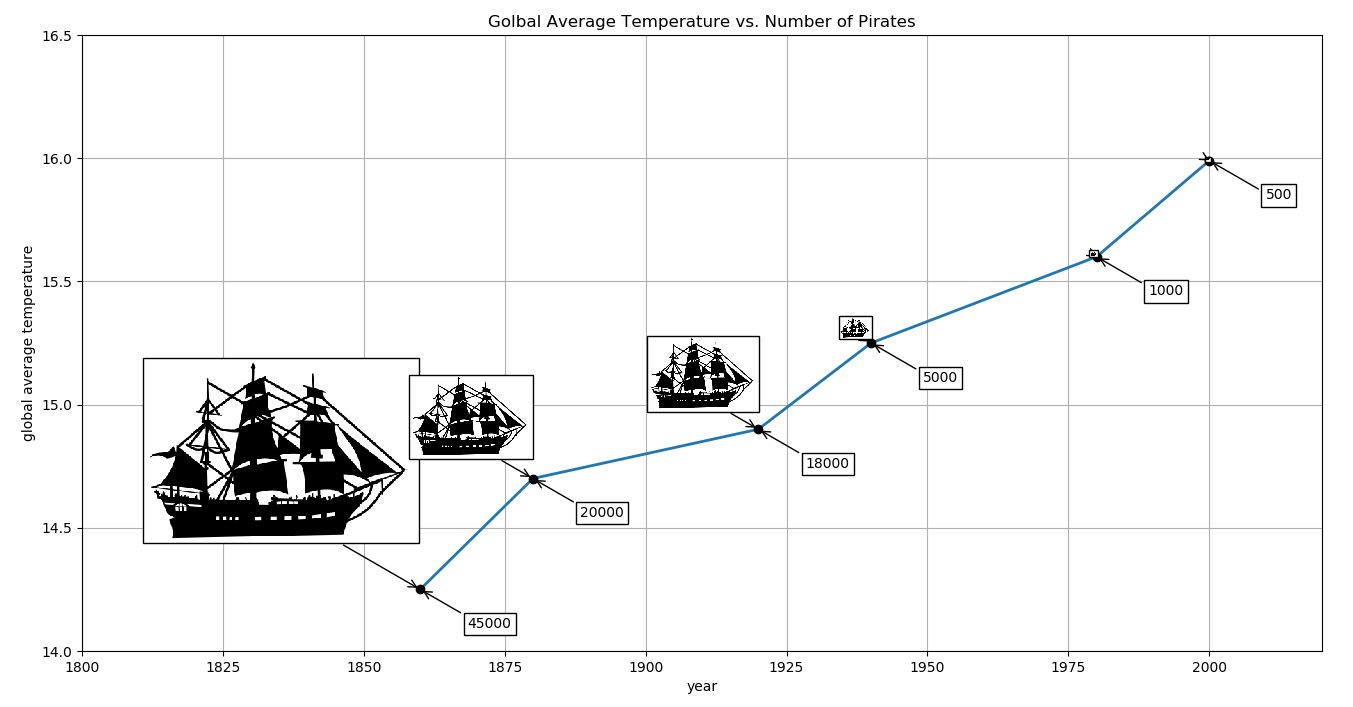
绘制带图像的图表
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib._png import read_png from matplotlib.offsetbox import TextArea, OffsetImage, AnnotationBbox def load_data(): import csv with open('pirates_temperature.csv', 'r') as f: reader = csv.reader(f) header = next(reader) datarows = [] for row in reader: datarows.append(row) return header, datarows def format_data(datarows): years, temps, pirates = [], [], [] for each in datarows: years.append(each[0]) temps.append(each[1]) pirates.append(each[2]) return years, temps, pirates if __name__ == '__main__': fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 8)) ax = plt.subplot(111) header, datarows = load_data() xlabel, ylabel, _ = header # 将列表中的元素赋值到三个变量中 years, temperature, pirates = format_data(datarows) title = 'Golbal Average Temperature vs. Number of Pirates' plt.plot([int(i) for i in years], [float(i) for i in temperature], lw=2) plt.xlabel(xlabel) plt.ylabel(ylabel) for x in range(len(years)): xy = int(years[x]), float(temperature[x]) ax.plot(int(xy[0]), float(xy[1]), "ok") pirate = read_png('tall-ship.png') zoomc = int(pirates[x])*(1/90000.0) imagebox = OffsetImage(pirate, zoom=zoomc) # ab = AnnotationBbox(imagebox, xy, xybox=(-200.0*zoomc, 200.0*zoomc), xycoords='data', boxcoords="offset points", pad=0.1, arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="angle, angleA=0, angleB=-30, rad=3")) ax.add_artist(ab) no_pirates = TextArea(pirates[x], minimumdescent=False) ab = AnnotationBbox(no_pirates, xy, xybox=(50.0, -25.0), xycoords = 'data', boxcoords='offset points', pad=0.3, arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="angle, angleA=0, angleB=-30, rad=3")) ax.add_artist(ab) plt.grid() plt.xlim(1800, 2020) plt.ylim(14, 16.5) plt.title(title) plt.show()
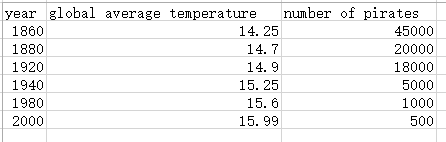
pirates_temperature.csv 中的内容
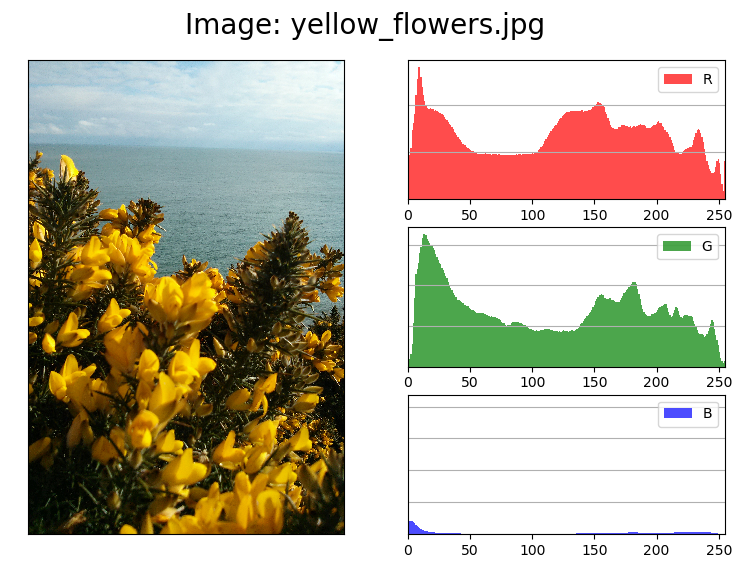
在有其它图形的图表中显示图像
操作步骤:
1. 加载图像
2. 从图像矩阵中分离出RGB通道
3. 配置图表和坐标轴(自区)
4. 绘制通道直方图
5. 绘制图像
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib.image as mplimage import matplotlib as mpl import os class ImageViewer(object): def __init__(self, imfile): self._load_image(imfile) self._configure() self.figure = plt.gcf() t = "Image: {0}".format(os.path.basename(imfile)) self.figure.suptitle(t, fontsize=20) self.shape=(3, 2) def _load_image(self, imfile): self.im = mplimage.imread(imfile) # 读取图像 read an image from a file into an array def _configure(self): mpl.rcParams['font.size'] = 10 mpl.rcParams['figure.autolayout'] = False mpl.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (9, 6) mpl.rcParams['figure.subplot.top'] = 0.9 @staticmethod def _get_chno(ch): chmap = {'R': 0, 'G': 1, 'B':2} return chmap.get(ch, -1) def show_channel(self, ch): bins = 256 ec = 'none' chno = self._get_chno(ch) loc = (chno, 1) ax = plt.subplot2grid(self.shape, loc) ax.hist(self.im[:, :, chno].flatten(), bins, color=ch, ec=ec, label=ch, alpha=0.7) ax.set_xlim(0, 255) plt.setp(ax.get_xticklabels(), visible=True) plt.setp(ax.get_yticklabels(), visible=False) plt.setp(ax.get_xticklines(), visible=True) plt.setp(ax.get_yticklines(), visible=False) plt.legend() plt.grid(True, axis='y') return ax def show(self): loc = (0, 0) axim = plt.subplot2grid(self.shape, loc, rowspan=3) axim.imshow(self.im) plt.setp(axim.get_xticklabels(), visible=False) plt.setp(axim.get_yticklabels(), visible=False) plt.setp(axim.get_xticklines(), visible=False) plt.setp(axim.get_yticklines(), visible=False) axr = self.show_channel('R') axg = self.show_channel('G') axg = self.show_channel('B') plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__': im = 'yellow_flowers.jpg' try: iv = ImageViewer(im) iv.show() except Exception as ex: print(ex)
使用 Basemap 在地图上绘制数据
Basemap 本身不进行任何绘图工作,它只是把给定的地理坐标转换到地图投影,并把数据传给 matplotlib 进行绘图。
basemap文档:https://matplotlib.org/basemap/api/basemap_api.html
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np map = Basemap(projection='merc', resolution='h',area_thresh=0.1, llcrnrlon=-126.619875, llcrnrlat=31.354158, urcrnrlon=-59.647219, urcrnrlat=47.517613) map.drawcoastlines() map.drawcountries() map.fillcontinents(color='coral', lake_color='aqua') map.drawmapboundary(fill_color='aqua') map.drawmeridians(np.arange(0, 360, 30)) map.drawparallels(np.arange(-90, 90, 30)) plt.show()

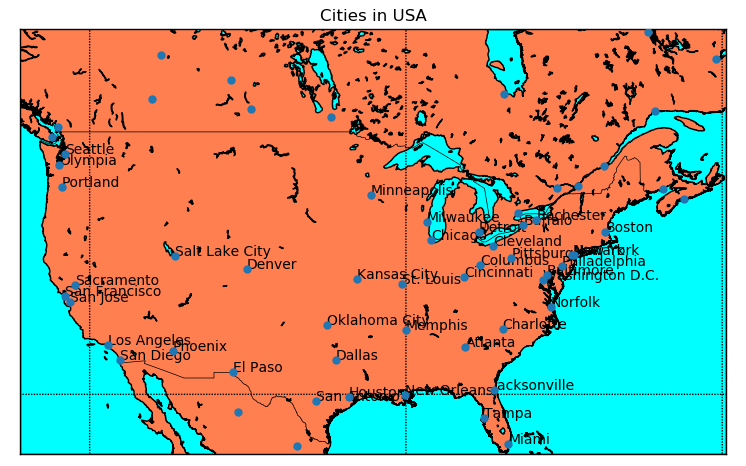
from mpl_toolkits.basemap import Basemap import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np map = Basemap(projection='merc', resolution='h', area_thresh=100, llcrnrlon=-126.619875, llcrnrlat=25, urcrnrlon=-59.647219, urcrnrlat=55) shapeinfo = map.readshapefile('cities', 'cities') x, y = zip(*map.cities) city_names = [] for each in map.cities_info: if each['COUNTRY'] != 'US': city_names.append("") else: city_names.append(each['NAME']) map.drawcoastlines() map.drawcountries() map.fillcontinents(color='coral', lake_color='aqua') map.drawmapboundary(fill_color='aqua') map.drawmeridians(np.arange(0, 360, 30)) map.drawparallels(np.arange(-90, 90, 30)) map.scatter(x, y, 25, marker='o', zorder=10) for city_label, city_x, city_y, in zip(city_names, x, y): plt.text(city_x, city_y, city_label) plt.title('Cities in USA') plt.show()
生成验证码图像
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont import random import string class SimpleCaptchaException(Exception): pass class SimpleCaptcha(object): def __init__(self, length=5, size=(200, 100), fontsize=36, random_text=None, random_bgcolor=None): self.size = size self.text = 'CAPTCHA' self.fontsize = fontsize self.bgcolor = 255 self.length = length self.image = None if random_text: self.text = self._random_text() if not self.text: raise SimpleCaptchaException("field text must not be empty.") if not self.size: raise SimpleCaptchaException('Size must not be empty.') if not self.fontsize: raise SimpleCaptchaException('Font size must be defined.') if random_bgcolor: self.bgcolor = self._random_color() def _center_coords(self, draw, font): width, height = draw.textsize(self.text, font) xy = (self.size[0] - width)/2.0, (self.size[1] - height)/2.0 return xy def _add_noise_dots(self, draw): size = self.image.size for _ in range(int(size[0]*size[1]*0.1)): draw.point((random.randint(0, size[0]), random.randint(0, size[1])), fill='white') return draw def _add_noise_lines(self, draw): size = self.image.size for _ in range(8): width = random.randint(1, 2) start = (0, random.randint(0, size[1]-1)) end = (size[0], random.randint(0, size[1]-1)) draw.line([start, end], fill="white", width=width) for _ in range(8): start = (-50, 50) end = (size[0] + 10, random.randint(0, size[1] + 10)) draw.arc(start + end, 0, 360, fill='white') return draw def _random_text(self): letters = string.ascii_lowercase + string.ascii_uppercase random_text = "" for _ in range(self.length): random_text += random.choice(letters) return random_text def _random_color(self): r = random.randint(0, 255) g = random.randint(0, 255) b = random.randint(0, 255) return (r, g, b) def get_captcha(self, size=None, text=None, bgcolor=None): if text is not None: self.text = text if size is not None: self.size = size if bgcolor is not None: self.bgcolor = bgcolor self.image = Image.new('RGB', self.size, self.bgcolor) # font = ImageFont.truetype('fonts/Vera.ttf', self.fontsize) draw = ImageDraw.Draw(self.image) xy = self._center_coords(draw, font) draw.text(xy=xy, text=self.text, font=font) draw = self._add_noise_dots(draw) draw = self._add_noise_lines(draw) self.image.show() return self.image, self.text if __name__ == "__main__": sc = SimpleCaptcha(length=7, fontsize=36, random_text=True, random_bgcolor=True) sc.get_captcha()
