生成可控的随机数据集合 使用 numpy.random 模块
numpy.random.random(size=None) 返回 [0.0, 1.0) 区间的随机 floats, 默认返回一个 float
numpy.random.randint(low, high=None, size=None, dtype='l') 按照均匀分布,返回 [low, high) 区间的随机 integers
numpy.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=1.0, size=None) 按照均匀分布,返回 [low, high) 区间的随机 floats
numpy.random.normal(loc=0.0, scale=1.0, size=None) 按照正态分布,返回随机 floats
numpy.random.triangular(left, mode, right, size=None) 按照三角分布,返回随机 floats
numpy.random.beta(a, b, size=None) 按照 beta 分布,返回随机 floats
numpy.random.exponential(scale=1.0, size=None) 按照指数分布,返回随机 floats
numpy.random.gamma(shape, scale=1.0, size=None) 按照 gamma 分布,返回随机 floats
numpy.random.lognormal(mean=0.0, sigma=1.0, size=None) 按照指数正态分布,返回随机 floats
numpy.random.pareto(a, size=None) 按照 pareto 分布,返回随机 floats
更多分布见 numpy.random 官网教程:https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/routines.random.html?highlight=random#module-numpy.random
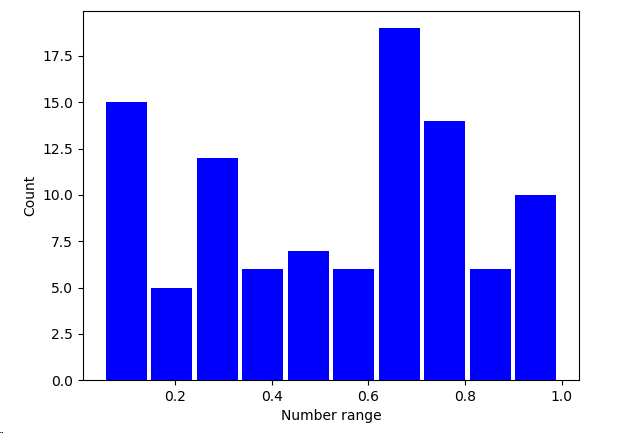
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np SAMPLE_SIZE = 100 np.random.seed() real_rand_vars = [np.random.random() for _ in range(SAMPLE_SIZE)] # 生成 100 个 [0.0, 1.0) 的随机小数 plt.figure() plt.hist(x = real_rand_vars, bins=10, rwidth=0.9, color='blue') plt.xlabel('Number range') plt.ylabel('Count') plt.show()
使用相似的方法,可以生成虚拟价格增长数据的时序图,并加上随机噪声
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np duration = 100 mean_inc = 0.2 std_dev_inc = 1.2 x = range(duration) y = [] price_today = 0 for i in x: next_delta = np.random.normal(loc=mean_inc, scale=std_dev_inc) # 按照给定的均值和方差的正态分布返回随机floats price_today += next_delta y.append(price_today) plt.figure() plt.plot(x, y, 'b.-') plt.xlabel('Time') plt.ylabel('Value') plt.show()

根据不同的需求,可以选择不同的分布
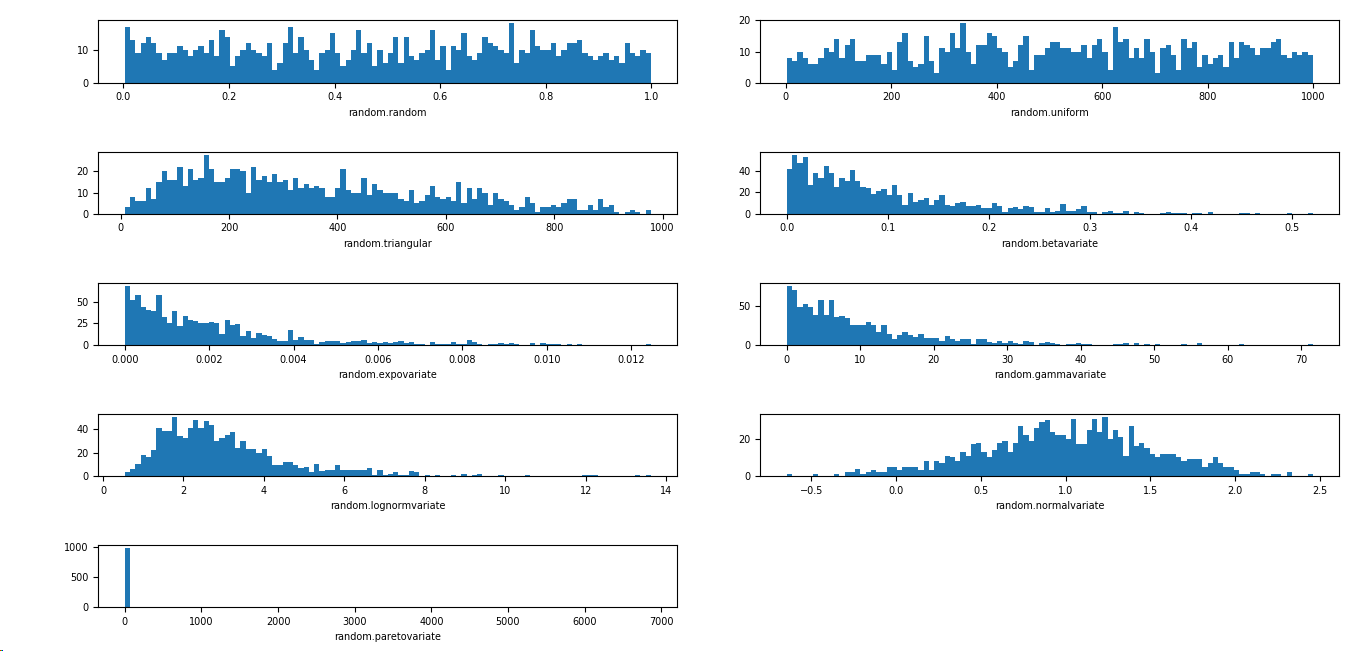
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import matplotlib SAMPLE_SIZE = 1000 buckets = 100 matplotlib.rcParams.update({'font.size':7}) plt.figure() # 第一个图是 [0,1) 之间分布的随机变量 plt.subplot(521) plt.xlabel('random.random') res = [np.random.random() for _ in range(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)] plt.hist(x=res, bins=buckets) # 第二个图是一个均匀分布的随机变量 plt.subplot(522) plt.xlabel('random.uniform') a = 1 b = SAMPLE_SIZE res = [np.random.uniform(a, b) for _ in range(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)] plt.hist(x=res, bins=buckets) # 第三个图是一个三角形分布 plt.subplot(523) plt.xlabel('random.triangular') low = 1 mode = 100.0 high = SAMPLE_SIZE res = [np.random.triangular(low, mode, high) for _ in range(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)] plt.hist(x=res, bins=buckets) # 第四个图是一个 beta 分布 plt.subplot(524) plt.xlabel('random.betavariate') alpha = 1 beta = 10 res = [np.random.beta(alpha, beta) for _ in range(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)] plt.hist(x=res, bins=buckets) # 第五个图是一个指数分布 plt.subplot(525) plt.xlabel('random.expovariate') lambd = 1.0 / ((SAMPLE_SIZE + 1) / 2.0) res = [np.random.exponential(lambd) for _ in range(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)] plt.hist(x=res, bins=buckets) # 第六个图是一个 gamma 分布 plt.subplot(526) plt.xlabel('random.gammavariate') alpha = 1 beta = 10 res = [np.random.gamma(alpha, beta) for _ in range(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)] plt.hist(x=res, bins=buckets) # 第七个图是一个 对数正态分布 plt.subplot(527) plt.xlabel('random.lognormvariate') mu = 1 sigma = 0.5 res = [np.random.lognormal(mu, sigma) for _ in range(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)] plt.hist(x=res, bins=buckets) # 第八个图是一个正态分布 plt.subplot(528) plt.xlabel('random.normalvariate') mu = 1 sigma = 0.5 res = [np.random.normal(mu, sigma) for _ in range(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)] plt.hist(x=res, bins=buckets) # 第九个图是一个帕累托分布 plt.subplot(529) plt.xlabel('random.paretovariate') alpha = 1 res = [np.random.pareto(alpha) for _ in range(1, SAMPLE_SIZE)] plt.hist(x=res, bins=buckets) plt.tight_layout() plt.show()