一、JSP技术
1、jsp脚本和注释
jap脚本:
1)<%java代码%> ----- 内部的java代码翻译到service方法的内部,比如写在doget、dopost 内的代码
2)<%=java变量或表达式> ----- 会被翻译成service方法内部out.print()。不能写方法,只能写变量或表达式,输出值。
3)<%!java代码%> ---- 会被翻译成servlet的成员的内容。比如成员变量
jsp注释: 不同的注释可见范围是不同的,看到的人越少越安全
1)Html注释:<!--注释内容--> ---可见范围 jsp源码、翻译后的servlet、页面显示html源码
2)java注释://单行注释 /*多行注释*/ --可见范围 jsp源码 翻译后的servlet
3)jsp注释:<%--注释内容--%> ----- 可见范围 jsp源码可见
代码演示:
<%@page import="java.util.ArrayList"%> <%@page import="java.util.List"%> <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8" errorPage="/error.jsp"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <!-- 这是HTML注释 --> <body> <% int i=0; System.out.print(i); List list=new ArrayList(); session.getId(); //这是一个错误的代码,测试page指令中的errorPage属性 //int y=1/0; %> <%=i %> <%-- 这是JSP注释 --%> <%! String str="nihao China"; %> <%=str %> </body> </html>
2、JSP运行原理-------jsp本质就是servlet(面试,重要)
jsp在第一次被访问时会被Web容器翻译成servlet,再执行。
过程:
第一次访问---->helloServlet.jsp---->helloServlet_jsp.java---->编译运行
PS:被翻译后的servlet在Tomcat的work目录中可以找到
3、JSP指令(3个)
1)page指令---------属性最多的指令(实际开发中page指令为默认的)
属性最多的一个指令,根据不同的属性,指导整个页面特性
格式:<%@ page 属性名1= "属性值1" 属性名2= "属性值2" ...%>
常用属性如下:
language:jsp脚本中可以嵌入的语言种类
pageEncoding:当前jsp文件的本身编码---内部可以包含contentType。当存在时不写contentType属性也可以,但一般都会写上
contentType:response.setContentType(text/html;charset=UTF-8)
session:是否jsp在翻译时自动创建session,不写的话默认为true
import:导入java的包
errorPage:当当前页面出错后跳转到哪个页面
isErrorPage:声明一下当前页面是一个处理错误的页面
2)include指令
页面包含(静态包含)指令,可以将一个jsp页面包含到另一个jsp页面中
格式:<%@ include file="被包含的文件地址"%>
3)taglib指令
在jsp页面中引入标签库(jstl标签库、struts2标签库)
格式:<%@ taglib uri="标签库地址" prefix="前缀"%>
代码演示:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!-- 标签库 --> <%-- <%@ taglib uri="xxx.xx" prefix="c" %> --%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <%@include file="/header.jsp"%> 这是首页 </body> </html>
4、jsp内置/隐式对象(9个)---------------------重点,死记硬背
隐式对象就是不用创建对象,直接就可以引用
jsp被翻译成servlet之后,service方法中有9个对象定义并初始化完毕,我们在jsp脚本中可以直接使用这9个对象。
1.out 用于页面输出
out的类型:JspWriter jsp输出流
out作用就是向客户端输出内容----out.write()
out缓冲区默认8kb 可以设置成0 代表关闭out缓冲区 内容直接写到respons缓冲 器 buffer=”0kb”;
out也有缓冲区,叫做out缓冲区
当执行时,Tomcat会先去找response缓冲区,再去将out缓冲区刷新到response缓冲区下面,所以会先打印response内的内容再打印out缓冲区的内容。
代码演示:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> aaaaaaaaa <%out.write("bbbbbb"); response.getWriter().write("ccccccc"); %> <%="ddddddddd" %> </body> </html>
2.config 用于服务器配置,可以获得初始化参数
3.request 向服务器发送请求
4.response 服务器向客户端返回响应
5.application 项目中所有用户的共享信息
6.page 指当前页面转换后的Servlet类的实例 (相当于普通类的this)
7.pageContext JSP的页面容器,也就是jsp专用的域,可存取数据,别的servlet或class不能获取。
代码演示:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <!-- pageContext域可以存取其他域的数据 --> <% /* request.setAttribute("name", "zhangsan"); //存入到request域中,以下相同 pageContext.setAttribute("name","lisi",pageContext.REQUEST_SCOPE); */ pageContext.setAttribute("name","wangwu",pageContext.SESSION_SCOPE); pageContext.setAttribute("name","zhaoliu",pageContext.APPLICATION_SCOPE); %> <%=request.getAttribute("name")%> <%=pageContext.getAttribute("name",pageContext.SESSION_SCOPE)%> <!-- finAttribute()方法,如果域中有同名的键 会从小到大搜索,域中的name值 --> <!-- 四个域的大小顺序为:pageContext域<request域<session域<application域 --> <%=pageContext.findAttribute("name") %> </body> </html>
jsp页面的上下文对象,作用如下:
注意:page对象与pageContext对象不是一回事
1)pageContext是一个域对象
setAttribute(String name,Object obj)
getAttribute(String name)
removeAttrbute(String name)
pageContext可以向指定的其他域中存取数据
setAttribute(String name,Object obj,int scope) int scope代表是哪个域
getAttribute(String name,int scope)
removeAttrbute(String name,int scope)
2)可以获得其他8大隐式对象
例如: pageContext.getRequest()
pageContext.getSession()
8.session 用来保存用户的信息
9.execption 表示JSP页面所发生的异常,在错误页中才会起作用,而且必须为true才会创建
代码演示:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8" isErrorPage="true"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> 这是一个ERROR页面 </body> </html>
findAttribute(String name)
---依次从pageContext域,request域,session域,application域中获 取属性,在某个域中获取后将不在向后寻找
四大作用域的总结:
pageContext域:当前jsp页面范围
request域:一次请求
session域:一次会话
application域:整个web应用
5.jsp标签(动作)
1)页面包含(动态包含):<jsp:include page="被包含的页面"/>
代码演示:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <!-- 页面包含 --> <jsp:include page="/header.jsp"></jsp:include> 这是动态包含 <jsp:forward page="/demo05.jsp"></jsp:forward> </body> </html>
Header.jsp代码:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h1>这是导航</h1> </body> </html>
2)请求转发:<jsp:forward page="要转发的资源" />
静态包含与动态包含的区别?
动态包含是先找到本页面,当解析到<jsp:include page="被包含的页面"/>语句时,会再去找被包含的页面。
静态包含则是一执行就将被包含的页面内容找到并复制一份部署到本页面。
二、EL表达式
1.EL 表达式概述
EL(Express Lanuage)表达式可以嵌入在jsp页面内部,减少jsp脚本的编写,EL 出现的目的是要替代jsp页面中脚本的编写。(脚本是指:JAVA代码)
2.EL从域中取出数据(EL最重要的作用)
jsp脚本:<%=request.getAttribute(name)%>
EL表达式替代上面的脚本:${requestScope.name}
EL最主要的作用是获得四大域中的数据,格式${EL表达式}
EL获得pageContext域中的值:${pageScope.key}
EL获得request域中的值:${requestScope.key}
EL获得session域中的值:${sessionScope.key}
EL获得application域中的值:${applicationScope.key}
EL从四个域中获得某个值${key};
---同样是依次从pageContext域,request域,session域,application域中 获取属性,在某个域中获取后将不在向后寻找
1)获得普通字符串
2)获得User对象的值
3)获得List<User>的值
代码演示:
自定义类Student类:
package com.oracle.demo01; public class Student { private int id; private String name; private boolean face; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public boolean isFace() { return face; } public void setFace(boolean face) { this.face = face; } }
JSP代码:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <!-- EL表达式 --> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <% request.setAttribute("name", "王荣臣"); session.setAttribute("name","董斌"); application.setAttribute("name", "韩凯"); pageContext.setAttribute("name","张锐"); %> ${pageScope.name} ${requestScope.name} ${sessionScope.name} ${applicationScope.name} ${name} </body> </html>
3、EL表达式的内置对象(11个)
pageScope, requestScope, sessionScope, applicationScope---- 获取JSP中域中的数据
param, paramValues - 接收参数.
相当于request.getParameter() request.getParameterValues()
获取表单数据
header, headerValues - 获取请求头信息
相当于request.getHeader(name)
initParam - 获取全局初始化参数
相当于this.getServletContext().getInitParameter(name)
cookie - WEB开发中cookie
相当于request.getCookies()---cookie.getName()---cookie.getValue()
pageContext - WEB开发中的pageContext.
pageContext获得其他八大对象
${pageContext.request.contextPath}
4、EL执行表达式
例如:
${1+1}
${empty user} //判断域对象
${user==null?true:false}
代码演示:
<%@page import="java.util.ArrayList"%> <%@page import="com.oracle.demo01.Student"%> <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ page import="com.oracle.demo01.Student" %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <% //往域中存字符串 request.setAttribute("name","王荣臣"); //往域中存对象 Student s1=new Student(); s1.setId(1); s1.setFace(true); s1.setName("王荣臣"); session.setAttribute("Student1",s1); //往域中存集合 Student s2=new Student(); s2.setId(2); s2.setName("韩凯"); s2.setFace(true); Student s3=new Student(); s3.setId(3); s3.setName("董斌"); s3.setFace(false); ArrayList<Student> studentList=new ArrayList<Student>(); studentList.add(s2); studentList.add(s3); application.setAttribute("StudentList",studentList); %> <!-- 获取键值 --> ${name } <!-- 对象的属性 --> ${Student1.name} <!-- 获取集合中对象的属性值 --> ${StudentList.get(1).face} </body> </html>
获取表格内容与请求头:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <% request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8"); %> <!-- 获取表格内容 --> ${param.username } ....${param.pwd } <!-- 获取请求头 --> ${header['User-Agent'] } </body> </html>
获取Cookie内容:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <% Cookie cookie=new Cookie("name","aaa"); response.addCookie(cookie); %> ${cookie.name.value } </body> </html>
EL执行表达式:
<%@page import="com.oracle.demo01.Student"%> <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <% Student s1=new Student(); s1.setName("小猪佩奇 "); session.setAttribute("s1",s1); %> <!-- EL执行表达式 --> ${1+2 } <!-- empty判断的是域中是否有该对象,如果有则返回fasle 如果没有,则返回true --> ${empty s1 } ${si==null?true:false} </body> </html>
三、JSTL技术
1.JSTL概述
JSTL(JSP Standard Tag Library),JSP标准标签库,可以嵌入在jsp页面中使用标签的形式完成业务逻辑等功能。jstl出现的目的同el一样也是要代替jsp页面中的脚本代码。JSTL标准标准标签库有5个子库,但随着发展,目前常使用的是他的核心库Core。
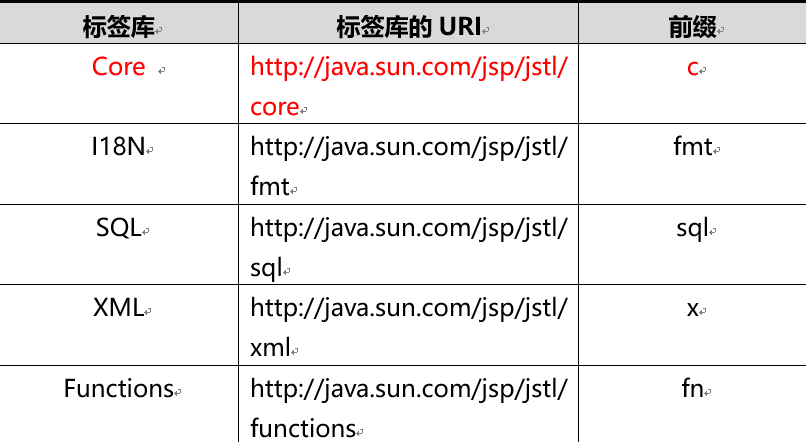
2、JSTL下载与导入

3、JSTL常用标签:
(1)<c:if test=" "> test返回的是boolean的条件,用来判定
(2)<c:forEach> 相当于for循环
四、JavaEE的开发模式
1、什么是开发模式
模式在开发过程中总结出的“套路”,总结出的一套约定俗成的设计模式。
2、模式:
MVC开发模式:由模型、视图、控制器组成,是WEB开发的设计模式,不只是java模式。
3、JavaEE的三层架构
开发时,分为WEB层、service层、dao层。
MVC模式在javaEE三层架构中会体现但不是一定会体现。
总结:
EL表达式
从域中取出数据 ${域中存储的数据的name}
${pageContext.request.contextPath}
JSTL标签(核心库)
<%@ taglib uri=”” prefix=”c”%>
<c:if test=””>
<c:forEach items=”数组或集合” var=”数组或集合中的每一个元素”
javaEE三层架构+MVC
web层:收集页面数据,封装数据,传递数据,指定响应jsp页面
service层:逻辑业务代码的编写
dao层:数据库的访问代码的编写