Tutorial样例实战
实验一:SIGCOMM_2015/Sourse_Routing
实验环境:
实验准备:
- 认真阅读readme文件,按照提示做下去!
- 修改环境变量脚本env.sh,该脚本记录了bmv2和p4c-bm的位置。
- 我的脚本信息如下:
THIS_DIR=$( cd "$( dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" && pwd )
# ---------------- EDIT THIS ------------------
BMV2_PATH=/home/liuhy/behavioral-model
# e.g. BMV2_PATH=$THIS_DIR/../bmv2
P4C_BM_PATH=/home/liuhy/p4c-bm
# e.g P4C_BM_PATH=$THIS_DIR/../p4c-bm
# ---------------- END ------------------
- 其实就是注明bmv2的路径和p4c-bm的路径,为了保险起见我选择了绝对路径。
实验描述
- 本次实验是为了实现一个名为Sourse_Routing的协议,其协议格式如下:
preamble (8 bytes) | num_valid (4 bytes) | port_1 (1 byte) | port_2 (1 byte) | ... | port_n (1 byte) | payload
- 其中各字段含义为:
- preamble:8bytes,恒为0,用于区分Sourse_Routing协议的数据包,为parser的编码提供了思路。
- num_valid:4bytes,可用端口数,这各字段的值代表头部中端口字段的数目,假定一个Sourse_Routing数据包要通过三个switch,把它的num_valid字段设置为3,意味着端口列表长度为3bytes。每经过一个switch,该字段值减1并移除第一个端口字段,第一个端口字段表明该数据包的出端口。为action提供了编码思路。
- payload:该字段代表我们要发送的信息,目前不用管。
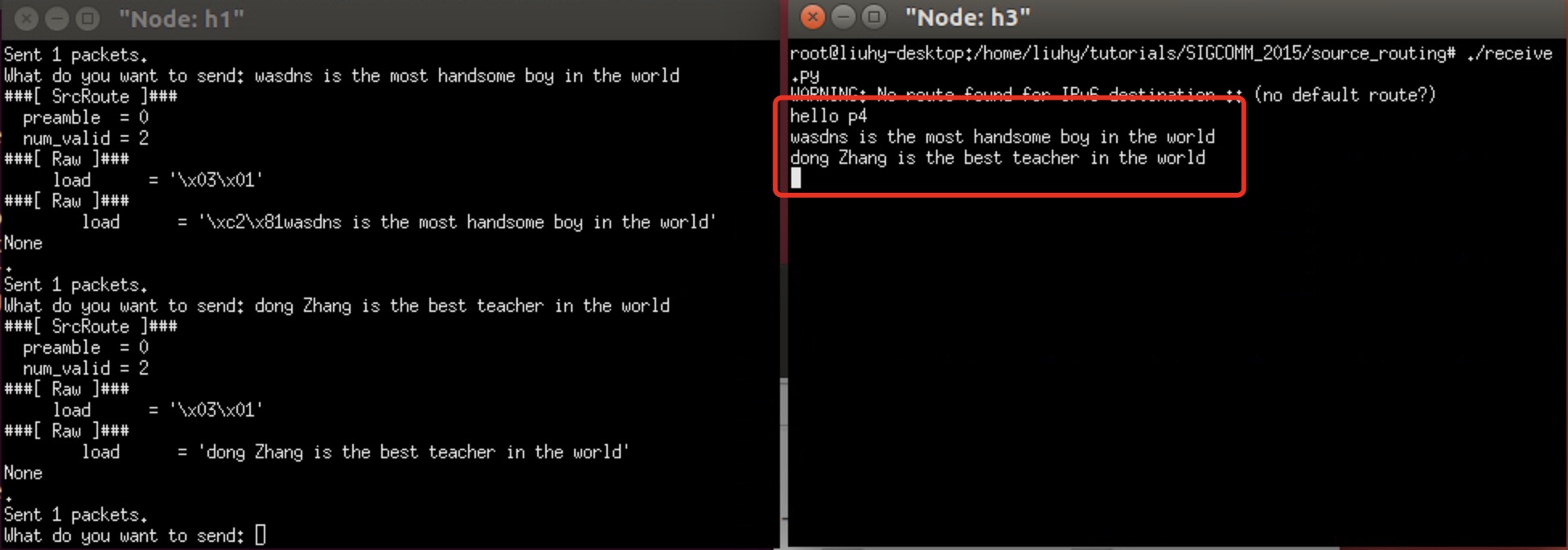
- 举个例子,如果想利用Sourse_Routing协议从h1主机发送hello p4到主机h3,根据本次实验拓扑,可以设置数据包格式为:
00000000 00000000 | 00000002 | 03 | 01 | Hello
00000000 00000000 | 00000001 | 01 | Hello
00000000 00000000 | 00000000 | Hello
- 注意:最后一个交换机不能移除Easyroute头部,因为这会导致主机无法解析数据包。而其他交换机可以,因为它会把数据包给交换机而不是主机,交换机会自动丢弃该数据包。
实验要求
- 非Easyroute数据包直接丢弃,无Easyroute头部或者其他协议数据包。
- num_vaild字段值为0的数据包直接丢弃。
Tips
- in the start parse state, you can use
current() to check if the packet is
an EasyRoute packet. A call to current(0, 64) will examine the first 64 bits
of the packet, without shifting the packet pointer.
- do not forget that a table can match on the validity of a header. Furthermore
if a header is not valid, our software switch will set all its fields to 0.
- a table can "match" on an empty key, which means the default action will
always be executed - if configured correctly by the runtime. Just omit the
"reads" attribute to achieve this.
- you can remove a header with a call to
remove_header()
- when parsing the EasyRoute header, you do not have to parse the whole port
list. Actually P4 is currently missing language constructs needed to parse a
general Type-Length-Value style header1, and hence
you’ll need to simply extract the first port of the list and ignore the rest
(including the payload). Also preamble, num_valid and the port number don't have
to all be placed in the same header type.
- finally, we advise you to put all your logic in the ingress control flow and
leave the egress empty. You will not need more than 1 or 2 tables to implement
EasyRoute.
填充流表
- readme中给出了必要的两个bmv2命令:
table_set_default <table_name> <action_name> [action_data]: this is used to
set the default action of a given tabletable_add <table_name> <action_name> <match_fields> => [action_data]: this
is used to add an entry to a table
Run!