本章内容介绍
l 集合的理解和好处
l 集合框架体系图
l Collection接口 特点 方法
l Collection接口的子接口:List 实现类:ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
l Collection接口的子接口:Set 实现类:HashSet、TreeSet、LinkedHashSet
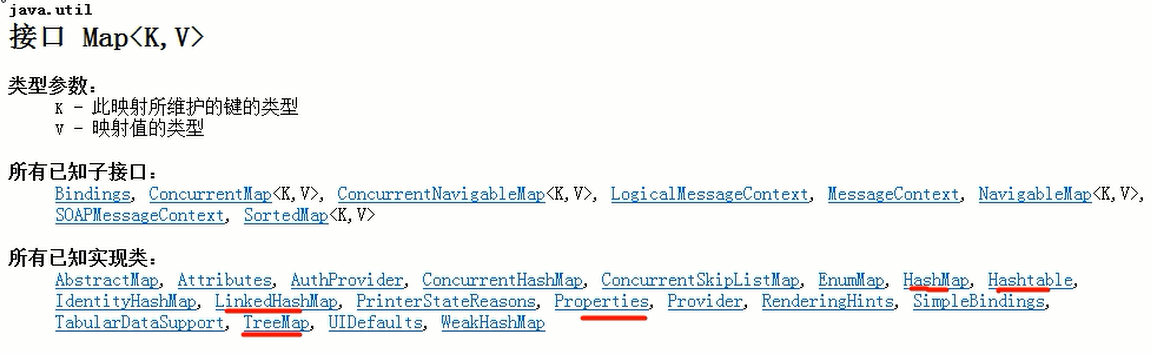
l Map接口 特点方法 遍历方式
l Map接口的实现类 :HashMap、TreeMap、Hashtable等
l Collections工具类的使用
1.集合基本介绍

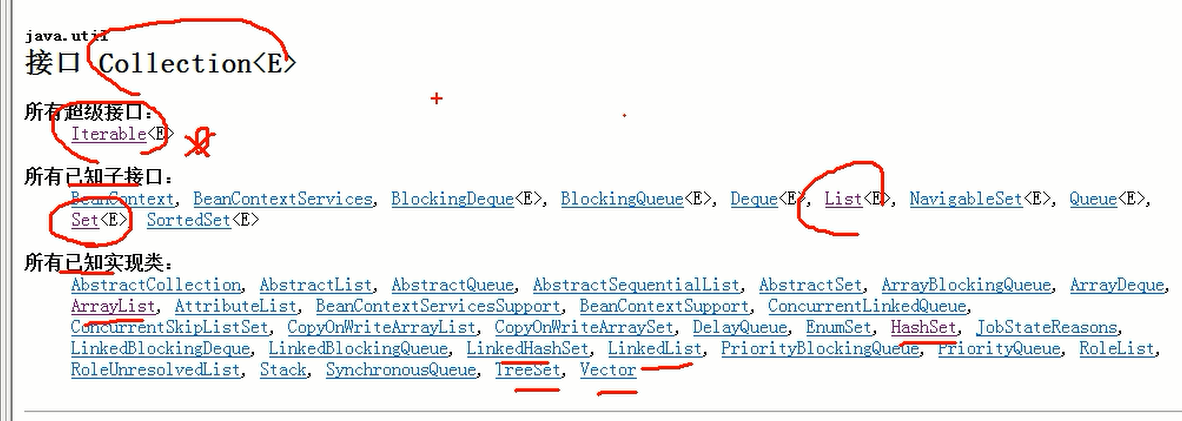
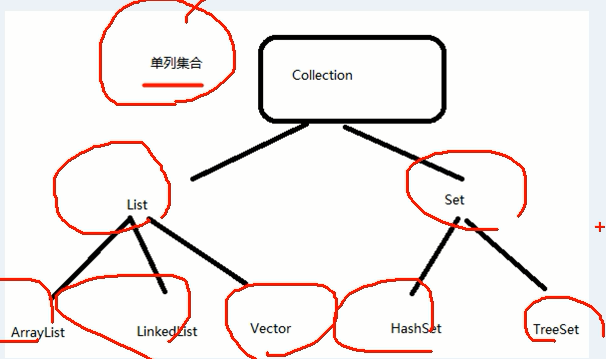
Java的集合类很多,主要分为两大类,如图:
说明
1) 单列集合,可以理解成就是直接放入一个个数据,比如前面的ArrayList
2) 单列集合的根接口是 Collection
3) Collection接口没有直接的实现子类, 而是有两个子接口List , Set
4) List 子接口的常用的实现类有 ArrayList ,LinkedList, Vector
5) Set子接口常用的实现类有 HashSet 和 TreeSet
6) 层级图
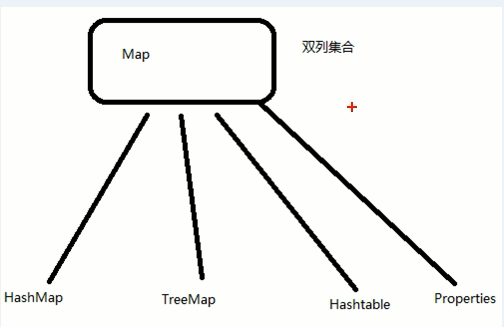
1) Map是存放双列集合的,比如 key-value
2) Map有直接的实现类,常见的有 HashMap, TreeMap, Hashtable, Propeties.

2.Collection集合的常用方法
- Collection接口常用方法
1) add:添加单个元素
2) remove:删除指定元素
3) contains:查找元素是否存在
4) size:获取元素个数
5) isEmpty:判断是否为空
6) clear:清空
7) addAll:添加多个元素
8) containsAll:查找多个元素是否都存在
9) removeAll:删除多个元素
以ArrayList实现类来演示.
1 import java.util.ArrayList;
2 import java.util.Collection;
3
4 public class CollectionDemo {
5
6 @SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked", "unused" })
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
9 //说明
10 //1. 创建了一个 ArrayList对象实例
11 //2. 创建了一个 ArrayList对象实例 ,赋给了Collection 应用.
12 Collection col = new ArrayList();
13 //演示Collection 添加
14 col.add("张三丰");
15 col.add(100); //100=>Integer(100)
16 col.add(true);//Boolean
17 col.add("张三丰");
18 col.add(new Integer(10));
19
20 System.out.println(col);
21
22
23 //删除元素
24 col.remove("张三丰");
25 System.out.println(col);
26 //判断集合中是否有某个元素
27
28 boolean contains = col.contains(10);
29 System.out.println("contains=" + contains);//true
30 //获取集合中有多少个元素,类似数组的length
31
32 System.out.println(col.size()); //4
33 //判断集合是否为空
34 System.out.println(col.isEmpty());//false
35
36 //清空整个集合
37 col.clear();
38 System.out.println("清空后");
39 System.out.println(col);
40
41 //可以将一个Collection 集合加入到另个一个Collection
42 Collection c = new ArrayList();
43 c.add("AA");
44 c.add("CC");
45 c.add("BB");
46 col.addAll(c);
47 System.out.println(col);//["AA","BB","CC"]
48
49 //判断Collection 集合 中是否有另外一个集合的所有元素
50 Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
51
52 c2.add("CC");
53 c2.add("AA");
54 boolean containsAll = col.containsAll(c2);//false
55 System.out.println("containsAll=" + containsAll);
56
57 //将一个Collection 集合 的元素一次性全部删除(删除的元素在 c2),如果没有也不报错
58 col.removeAll(c2);
59 System.out.println("col=" + col);//[BB]
60
61 }
62 }
3. Collection接口遍历元素方式1-使用Iterator(迭代器)
- 基本介绍
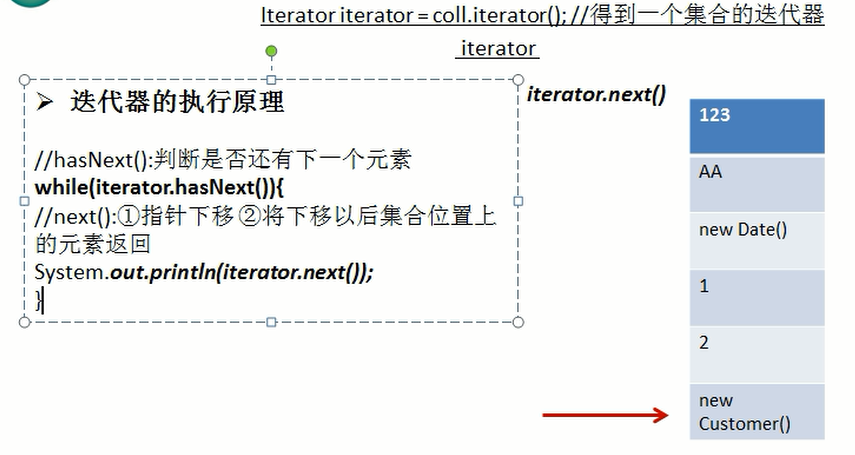
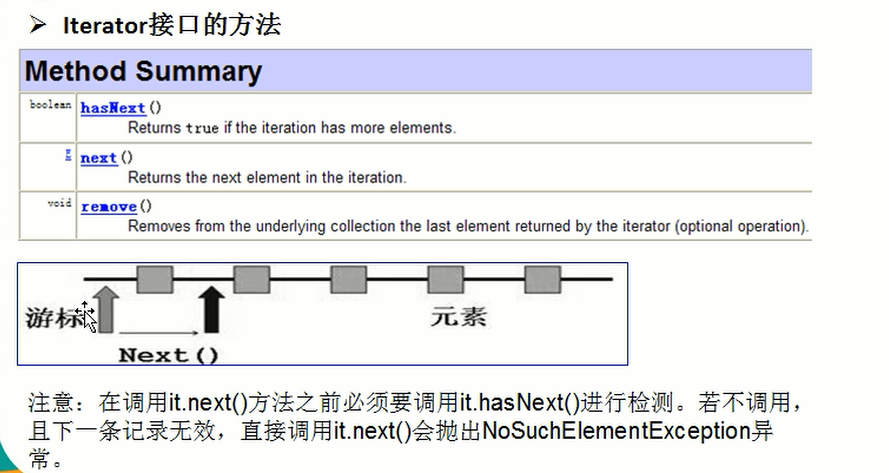
1) Iterator对象称为迭代器(设计模式的一种),主要用于遍历 Collection 集合中的元素。
2) 所有实现了Collection接口的集合类都有一个iterator()方法,用以返回一个实现了Iterator接口的对象, 即可以返回一个迭代器。
3) Iterator 的结构.[图:]
4) Iterator 仅用于遍历集合,Iterator 本身并不提供承装对象的能力。如果需要创建 Iterator 对象,则必须有一个被迭代的集合。
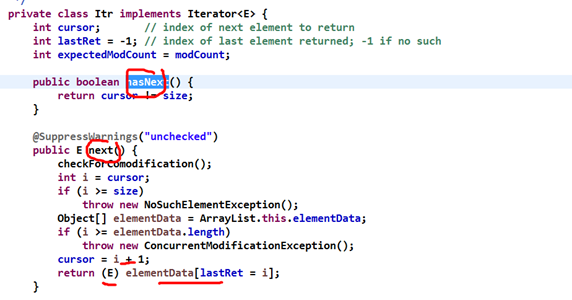
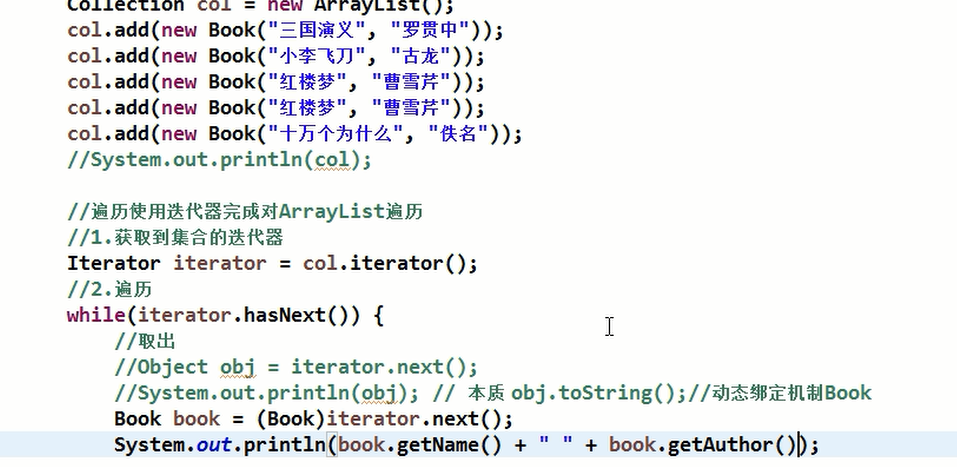

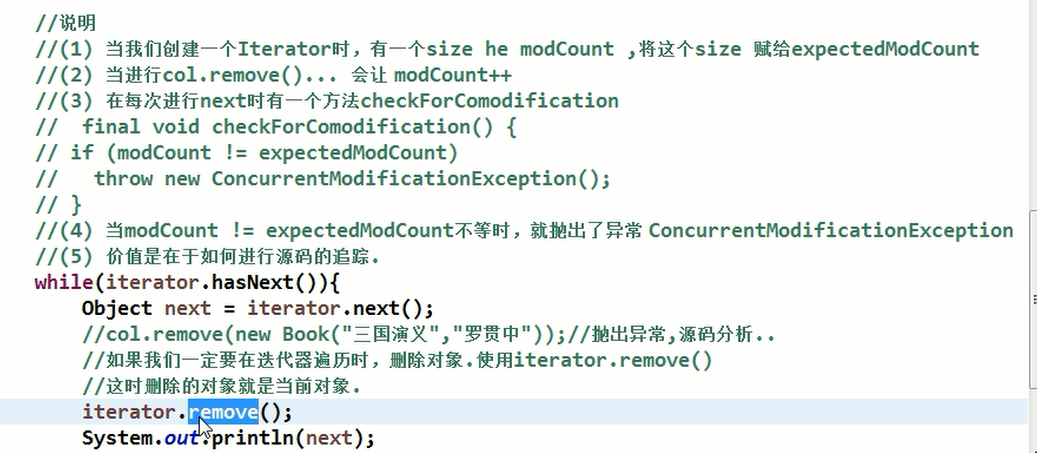
4.迭代器使用陷阱

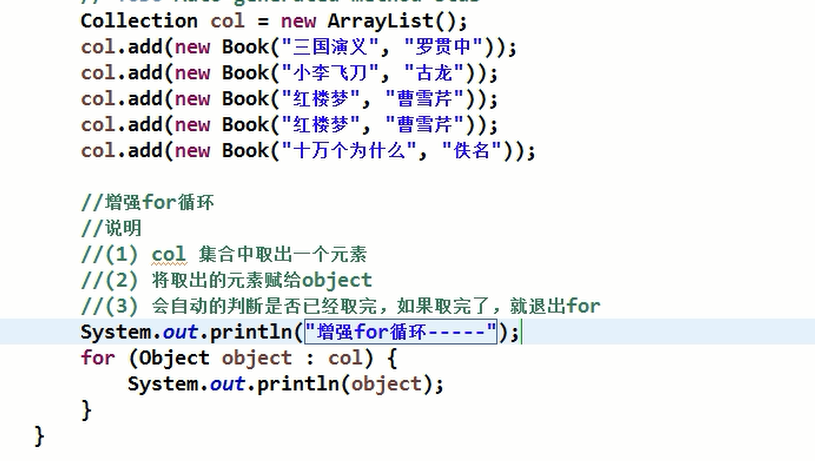
5.Collection接口遍历对象方式2-for循环增强.
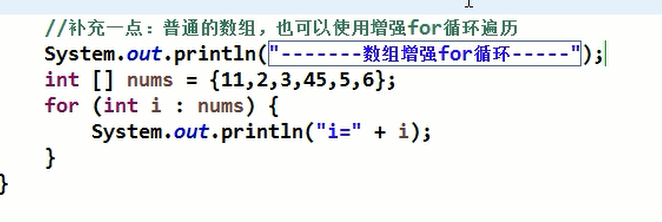
说明:jdk5.0出现了增强for循环,可以代替iterator迭代器,特点:增强for就是简化版的iterator,本质一样。只能用于遍历集合或数组。
- 基本语法
for(元素类型 元素名 : 集合名或数组名) {
访问元素
}
6.List


1.1.1 List接口的常用方法
List 集合里添加了一些根据索引来操作集合元素的方法
1) void add(int index, Object ele):在index位置插入ele元素
2) boolean addAll(int index, Collection eles):从index位置开始将eles中的所有元素添加进来
3) Object get(int index):获取指定index位置的元素
4) int indexOf(Object obj):返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置
5) int lastIndexOf(Object obj):返回obj在当前集合中末次出现的位置
6) Object remove(int index):移除指定index位置的元素,并返回此元素
7) Object set(int index, Object ele):设置指定index位置的元素为ele
8) List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex):返回从fromIndex到toIndex位置的子集合
1 import java.util.List; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 4 public class ListCommonMethod { 5 6 @SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" }) 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 List list = new ArrayList(); 10 list.add(100); //自动装箱 11 list.add(3); //自动装箱 12 13 //说明: 14 //(1)void add(int index, E element); 15 //(2)int index : 表示将数据加入到list集合哪个位置(插入) 16 //(3)element: 添加元素 17 list.add(1, 4); // 18 19 for (Object object : list) { 20 System.out.println(object); 21 } 22 23 24 //List的remove 25 //(1) E remove(int index); 26 //(2) 指定删除list第几个元素 27 list.remove(1); 28 //说明: 可以指定内容删除 29 list.remove(new Integer(100)); 30 31 System.out.println("删除后"); 32 for (Object object : list) { 33 System.out.println(object); 34 } 35 36 //修改 37 //说明 38 //(1) Object java.util.List.set(int index, Object element) 39 //(2) int index: 指定修改哪个索引对应值 40 //(3) Object element : 修改成什么 41 list.set(0, "张无忌"); 42 43 System.out.println("修改后"); 44 for (Object object : list) { 45 System.out.println(object); 46 } 47 48 49 // //查询 50 //说明 int java.util.List.indexOf(Object o) 51 //(1) Object o 传入的是list集合中的对象 52 //(2) 如果找到了则返回对应的索引,如果没有返回-1 53 //(3) 方法原型 54 // public int indexOf(Object o) { 55 // if (o == null) { 56 // for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 57 // if (elementData[i]==null) 58 // return i; 59 // } else { 60 // for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) 61 // if (o.equals(elementData[i])) 62 // return i; 63 // } 64 // return -1; 65 // } 66 int index = list.indexOf("张无忌"); 67 System.out.println(index); 68 69 70 //测试indexOf 71 Dog dog = new Dog("小黄"); 72 Dog dog2 = new Dog("小黄"); 73 74 list.add(dog); 75 System.out.println("测试indexOf"); 76 for (Object object : list) { 77 System.out.println(object); 78 } 79 80 int index2 = list.indexOf(dog2);//equals 81 System.out.println("index2=" + index2);//1 82 83 84 } 85 86 } 87 88 class Dog { 89 private String name; 90 91 public Dog(String name) { 92 super(); 93 this.name = name; 94 } 95 96 @Override 97 public String toString() { 98 return "Dog [name=" + name + "]"; 99 } 100 101 102 @Override 103 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 104 if(obj == this) { 105 return true; 106 } 107 if(!(obj instanceof Dog)){ 108 return false; 109 } 110 Dog dog = (Dog)obj; 111 return name.equals(dog.name); 112 } 113 114 115 }
7.List接口三种遍历方式

- 说明:使用LinkedList完成
1 import java.util.List; 2 import java.util.Iterator; 3 import java.util.LinkedList; 4 5 public class LinkedListForDemo { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 //使用LinkedList演示List实现子类的三种遍历方式 10 //1. 有序,可以有重复数据,可以有null 11 List list = new LinkedList(); 12 list.add("jack"); 13 list.add("tom"); 14 list.add("smith"); 15 list.add("mary"); 16 list.add("jack"); 17 list.add(null); 18 //遍历方式1 -迭代器 [推荐使用] 19 Iterator iterator = list.iterator(); 20 while(iterator.hasNext()) { 21 Object object = iterator.next(); 22 System.out.println(object); 23 } 24 25 System.out.println("遍历方式2- 增强for"); 26 //遍历方式2- 增强for [推荐使用] 27 for (Object object : list) { 28 System.out.println(object); 29 30 } 31 32 System.out.println("遍历方式3-传统的遍历方式【使用索引】"); 33 //遍历方式3-传统的遍历方式【使用索引】 34 for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 35 Object object = list.get(i); 36 System.out.println(object); 37 } 38 } 39 40 }
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.LinkedList; 3 import java.util.List; 4 import java.util.Vector; 5 6 public class ListSortExercise { 7 8 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 11 // 使用List的实现类添加三本图书,并遍历,打印如下效果 12 // 13 // 名称:xx 价格:xx 作者:xx 14 // 名称:xx 价格:xx 作者:xx 15 // 要求 16 // 按价格排序,从低到高(使用冒泡法) 17 // 要求使用ArrayList、LinkedList 和 Vector 三种集合实现 18 // 结论:主要说明,只要实现了List接口,那么List的实现类都可以使用List接口中的方法 5min 19 20 //List list = new ArrayList(); // shift+ctrl+o 21 //List list = new LinkedList(); 22 List list = new Vector(); 23 list.add(new Book2("西游记", 123.4, "吴承恩")); 24 list.add(new Book2("三国演义", 12.4, "罗贯中")); 25 list.add(new Book2("水浒传", 112.4, "施耐庵")); 26 list.add(new Book2("红楼梦", 42.44, "曹雪芹")); 27 list.add(new Book2("java从入门到跑路", 2.44, "韩老师")); 28 29 for (Object object : list) { 30 System.out.println(object); 31 } 32 33 // 使用冒泡法 34 for (int i = 0; i < list.size() - 1; i++) {// 外层大循环 35 for (int j = 0; j < list.size() - 1 - i; j++) {// 内存循环 36 //取出相邻的两个元素[Book2类型] 37 Book2 book1 = (Book2)list.get(j); 38 Book2 book2 = (Book2)list.get(j+1); 39 if(book1.getPrice() > book2.getPrice()) {//成立 40 //定时临时变量 41 list.set(j, book2); 42 list.set(j+1, book1); 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 //遍历 47 System.out.println("排序后"); 48 for (Object object : list) { 49 System.out.println(object); 50 } 51 52 } 53 54 } 55 56 class Book2 { 57 private String name; 58 private double price; 59 private String author; 60 61 public Book2(String name, double price, String author) { 62 super(); 63 this.name = name; 64 this.price = price; 65 this.author = author; 66 } 67 68 public String getName() { 69 return name; 70 } 71 72 public void setName(String name) { 73 this.name = name; 74 } 75 76 public double getPrice() { 77 return price; 78 } 79 80 public void setPrice(double price) { 81 this.price = price; 82 } 83 84 public String getAuthor() { 85 return author; 86 } 87 88 public void setAuthor(String author) { 89 this.author = author; 90 } 91 92 @Override 93 public String toString() { 94 return "Book2 [name=" + name + ", price=" + price + ", author=" + author + "]"; 95 } 96 97 }