上一篇随笔中已经介绍了解码核心工作流程,里面有个数据积累器的存在(Cumulator),其实解码中有两种Cumulator,那他们的区别是什么呢?
还是先打开ByteToMessageDecoder的channelRead();
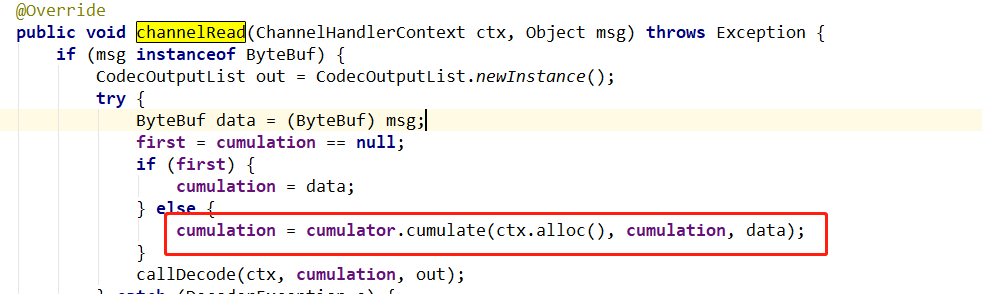
点进去查看cumulate()实现

又是一个抽象方法,看实现不难发现它有两种实现方式
两种实现分别为:MERGE_CUMULATOR(默认的):采用的是内存复制,先扩容空间,再追加数据
public static final Cumulator MERGE_CUMULATOR = new Cumulator() { @Override public ByteBuf cumulate(ByteBufAllocator alloc, ByteBuf cumulation, ByteBuf in) { try { final ByteBuf buffer; if (cumulation.writerIndex() > cumulation.maxCapacity() - in.readableBytes() || cumulation.refCnt() > 1 || cumulation.isReadOnly()) { // Expand cumulation (by replace it) when either there is not more room in the buffer // or if the refCnt is greater then 1 which may happen when the user use slice().retain() or // duplicate().retain() or if its read-only. // // See: // - https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2327 // - https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/1764 buffer = expandCumulation(alloc, cumulation, in.readableBytes()); } else { buffer = cumulation; } buffer.writeBytes(in); return buffer; } finally { // We must release in in all cases as otherwise it may produce a leak if writeBytes(...) throw // for whatever release (for example because of OutOfMemoryError) in.release(); } } };
第二种 :COMPOSITE_CUMULATOR :不是复制而是组合,先扩容,如果数据够了的话就直接把数据给组合起来,避免了内存复制
public static final Cumulator COMPOSITE_CUMULATOR = new Cumulator() { @Override public ByteBuf cumulate(ByteBufAllocator alloc, ByteBuf cumulation, ByteBuf in) { ByteBuf buffer; try { if (cumulation.refCnt() > 1) { // Expand cumulation (by replace it) when the refCnt is greater then 1 which may happen when the // user use slice().retain() or duplicate().retain(). // // See: // - https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2327 // - https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/1764 buffer = expandCumulation(alloc, cumulation, in.readableBytes()); buffer.writeBytes(in); } else { CompositeByteBuf composite; if (cumulation instanceof CompositeByteBuf) { composite = (CompositeByteBuf) cumulation; } else { composite = alloc.compositeBuffer(Integer.MAX_VALUE); composite.addComponent(true, cumulation); } composite.addComponent(true, in); in = null; buffer = composite; } return buffer; } finally { if (in != null) { // We must release if the ownership was not transferred as otherwise it may produce a leak if // writeBytes(...) throw for whatever release (for example because of OutOfMemoryError). in.release(); } } } };