题目链接:http://codeforces.com/gym/101987
题目描述
ICPC manager plans a new project which is to be carried out for n days. In this project, m persons numbered from 1 to m are supposed to work. Each day j (1 ≤ j ≤ n) requires dj persons, and each person i (1 ≤ i ≤ m) wants to work wi days.
To increase the efficiency in performing the project, the following two conditions should be satisfied:
1.each person works for only consecutive w days when he/she works, and
2.each person can work again after he/she has a rest for at least h days.
ICPC manager wants to find a working plan to assign the working days for all persons such that the number of working days of each person i (1 ≤ i ≤ m) is equal to wi and the number of persons who work for each day j (1 ≤ j ≤ n) is equal to dj, and above two conditions are also satisfied.
For example, assume the project is carried out for n = 9 days, and m = 4 persons participate in the project. Let w = 2 and h = 1. Also, assume (w1, w2, w3, w4) = (4, 4, 6, 2) and (d1, d2, d3, d4, d5, d6, d7, d8, d9) = (1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1, 1, 3, 2). The table below shows a feasible solution where the i-th row corresponds to person i, and the j-th column corresponds to day j. If person i works or has a rest in day j, the value of the table element with row i and column j is 1 or 0, respectively.
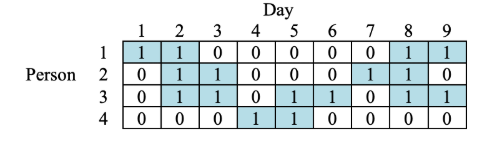
Given m, n, w, h, wi (1 ≤ i ≤ m) which is a multiple of w, and dj (1 ≤ j ≤ n), write a program to find a feasible solution as a working plan.
输入
Your program is to read from standard input. The input starts with a line containing four integers, m, n, w, h (1 ≤ m ≤ 2,000, 1 ≤ n ≤ 2,000, 1 ≤ w, h ≤ n). The following line contains m integers where the i-th (1 ≤ i ≤ m) integer represents wi (1 ≤ wi ≤ n) which is a multiple of w. The next line contains n integers where the j-th (1 ≤ j ≤ n) integer represents dj (0 ≤ dj ≤ m).
输出
Your program is to write to standard output. If there is a feasible working plan, print 1 in the first line followed by m lines, each i-th (1 ≤ i ≤ m) line should contain wi/w integers. These integers form an increasing sequence of first days that person i works in the feasible plan. If there is no feasible working plan, print only -1 in the first line. The first sample below corresponds to the example given in the table above.
样例输入
样例数据
4 9 2 1
4 4 6 2
1 3 2 1 2 1 1 3 2
样例输出
1
1 8
2 7
2 5 8
4
题意:有m个工人,要工作n天,每个工人可以连续工作w天,之后就要休息h天,给定每个工人的工作天数b[i],和每天需要的工人数a[i],问工人的数量能否满足每天的工作安排,若可以,输出1,并输出每个工人每次开始工作的日期(每个工人的工作次数为b[i]/w),若不能,直接输出-1.
题解:建立两个优先队列,工作队列Q和休息队列T,Q的优先级是工作次数,工作次数越多的越先进入工作队列,T的优先级是休息之后可以开始工作的时间,工作时间越早越先进入队列。工作队列的每个工人工作w天之后进入休息队列,休息队列里记录休息h天之后可以开始工作的日期,若这个日期小于当天日期,就可以进入工作队列
因为每个工人可以连续工作,在用一个vis数组记录每天需要新加入的工人数量
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<queue> #include<vector> using namespace std; int n, m, w, h; int a[2005], b[2005], vis[2005];//vis记录每天需要新加入几个工人 vector<int>v[2005]; typedef struct node { int num;//编号 int cnt;//工作次数 int time;//休息之后可以开始工作的日期 }node; typedef struct cmp1//对队列T,可以开始工作的日期越早越先入队列 { bool operator () (const node &x, const node &y) { return x.time > y.time; } }cmp1; typedef struct cmp2//对队列Q,工作次数越多的越先进入队列 { bool operator () (const node &x, const node &y) { return x.cnt < y.cnt; } }cmp2; priority_queue<node, vector<node>, cmp2>Q;//工作队列 priority_queue<node, vector<node>, cmp1>T;//休息队列 int main() { node p[2005]; cin >> m >> n >> w >> h; for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { cin >> b[i]; p[i].num = i; p[i].cnt = b[i] / w; p[i].time = 0; Q.push(p[i]); } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i]; int flag = 1; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if(a[i]!=0) { int temp = a[i]; vis[i] = a[i]; for (int j = i; j <= i + w - 1; j++)//因为每个人都是连续工作的,之后的w天都要减去a[i]得到需要新加入的人数 a[j] = a[j] - temp; } } node temp; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { while (!T.empty()) { temp = T.top(); if (temp.time <= i)//如果可以开始工作的日期小于当前日期 { Q.push(temp); T.pop(); } else break; } while (!Q.empty() && vis[i]) { temp = Q.top(); Q.pop(); vis[i]--; temp.time = i + w + h; temp.cnt--; v[temp.num].push_back(i);//记录每次开始工作的日期 if (temp.cnt != 0) T.push(temp); } if (vis[i] != 0)//人数不够 { flag = 0; break; } } if (flag == 0) cout << -1 << endl; else { cout << 1 << endl; for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < v[i].size(); j++) { cout << v[i][j]; if (j != v[i].size()) cout << ' '; } cout << endl; } } return 0; }