Description
有一个森林最初由 (n) 个互不相连的点构成
你需要处理以下 (m) 次操作:
link A B:添加从顶点A到B的边,使 (A) 成为 (B) 的子节点,其中保证 (A) 是一个根顶点,(A) 和 (B) 在不同的树中。
cut A:切断点 (A) 到其父节点的边,保证 (A) 是一个非根节点。
lca A B:输出 (A) 和 (B) 的最近共同祖先,保证 (A) 和 (B) 在同一棵树中。
Hint
(1le n, mle 10^5)
Solution
看到加边和删边,不难想到用 ( exttt{Link-Cut Tree})。
但难点在于求 LCA。
假设我们有这样一颗树,以 1 为根,并要求 lca 6 9:
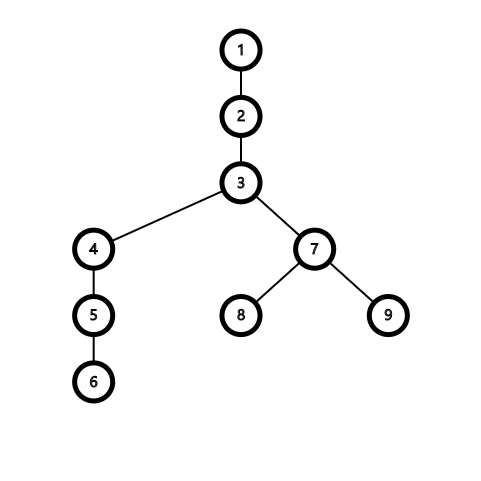
先打通 6 到 根 的实链(红色边为实边),access(6):
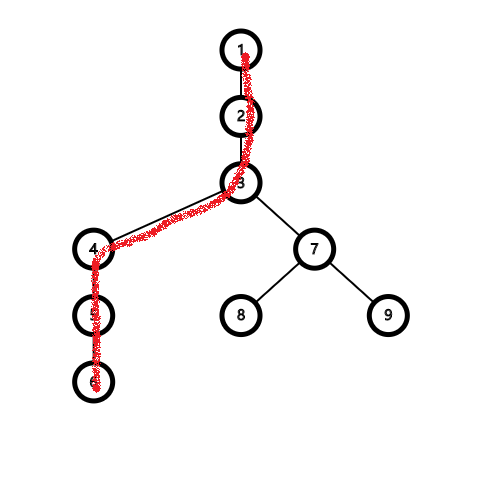
如果我们再 access(9),那么:
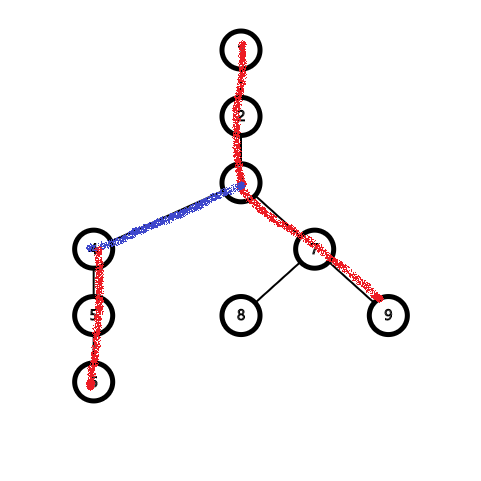
可以发现,原来有一条实边变虚(蓝色边)了,而这条虚边的父结点正是所求的最近公共祖先。
结论,access(x) 后,再 access(y) 的过程中实变虚的最后一条边就是 LCA(x, y)。
具体做法,可以在 access 函数中加入返回值会好做一些。
inline int access(int x) {
register int y = 0;
for (; x; x = fa[y = x]) splay(x), rc = y;
return y;
}
inline int LCA(int x, int y) {
return access(x), access(y);
}
注意,cut 操作不能 makrRoot,因为 LCA 这个东西是会受根结点的位置影响的,不可随意换根。而 link 由于 (x) 本来就是根,makeRoot 没有关系。
Code
/*
* Author : _Wallace_
* Source : https://www.cnblogs.com/-Wallace-/
* Problem : SPOJ DYNALCA Dynamic LCA
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int ch[N][2], fa[N];
bool rev[N];
#define lc ch[x][0]
#define rc ch[x][1]
inline bool isRoot(int x) {
return x != ch[fa[x]][0] && x != ch[fa[x]][1];
}
inline int getc(int x) {
return x == ch[fa[x]][1];
}
inline void setRev(int x) {
swap(lc, rc), rev[x] ^= 1;
}
inline void pushdown(int x) {
if (rev[x]) {
if (lc) setRev(lc);
if (rc) setRev(rc);
rev[x] = 0;
}
}
inline void pushdownAll(int x) {
if (!isRoot(x)) pushdownAll(fa[x]);
pushdown(x);
}
inline void rotate(int x) {
int y = fa[x], z = fa[y];
int k = getc(x), w = ch[x][!k];
if (!isRoot(y)) ch[z][getc(y)] = x;
ch[x][!k] = y, ch[y][k] = w;
if (w) fa[w] = y;
fa[y] = x, fa[x] = z;
}
inline void splay(int x) {
pushdownAll(x);
for (register int y = fa[x]; !isRoot(x); rotate(x), y = fa[x])
if (!isRoot(y)) rotate(getc(x) != getc(y) ? x : y);
}
inline int access(int x) {
register int y = 0;
for (; x; x = fa[y = x]) splay(x), rc = y;
return y;
}
inline void makeRoot(int x) {
access(x), splay(x), setRev(x);
}
inline void link(int c, int f) {
makeRoot(c), fa[c] = f;
}
inline void cut(int x) {
access(x), splay(x), fa[lc] = 0, lc = 0;
}
inline int LCA(int x, int y) {
return access(x), access(y);
}
signed main() {
int n, q;
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> q;
for (; q; --q) {
string cmd; int x, y;
cin >> cmd;
if (cmd == "lca")
cin >> x >> y, cout << LCA(x, y) << endl;
if (cmd == "link")
cin >> x >> y, link(x, y);
if (cmd == "cut")
cin >> x, cut(x);
}
return 0;
}