Bogdan has a birthday today and mom gave him a tree consisting of n vertecies. For every edge of the tree i, some number xi was written on it. In case you forget, a tree is a connected non-directed graph without cycles. After the present was granted, m guests consecutively come to Bogdan's party. When the i-th guest comes, he performs exactly one of the two possible operations:
- Chooses some number yi, and two vertecies ai and bi. After that, he moves along the edges of the tree from vertex ai to vertex biusing the shortest path (of course, such a path is unique in the tree). Every time he moves along some edge j, he replaces his current number yi by
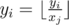 , that is, by the result of integer division yi div xj.
, that is, by the result of integer division yi div xj. - Chooses some edge pi and replaces the value written in it xpi by some positive integer ci < xpi.
As Bogdan cares about his guests, he decided to ease the process. Write a program that performs all the operations requested by guests and outputs the resulting value yi for each i of the first type.
The first line of the input contains integers, n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 200 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 200 000) — the number of vertecies in the tree granted to Bogdan by his mom and the number of guests that came to the party respectively.
Next n - 1 lines contain the description of the edges. The i-th of these lines contains three integers ui, vi and xi (1 ≤ ui, vi ≤ n, ui ≠ vi,1 ≤ xi ≤ 1018), denoting an edge that connects vertecies ui and vi, with the number xi initially written on it.
The following m lines describe operations, requested by Bogdan's guests. Each description contains three or four integers and has one of the two possible forms:
- 1 ai bi yi corresponds to a guest, who chooses the operation of the first type.
- 2 pi ci corresponds to a guests, who chooses the operation of the second type.
For each guest who chooses the operation of the first type, print the result of processing the value yi through the path from ai to bi.
6 6
1 2 1
1 3 7
1 4 4
2 5 5
2 6 2
1 4 6 17
2 3 2
1 4 6 17
1 5 5 20
2 4 1
1 5 1 3
2
4
20
3
5 4
1 2 7
1 3 3
3 4 2
3 5 5
1 4 2 100
1 5 4 1
2 2 2
1 1 3 4
2
0
2
由于a/b/c=a/(b*c),所以直接维护乘积即可,注意爆longlong。
这里由于溢出可以溢回正数,所以不能用判断是否负数来判溢出,直接在中间过程设一个double型的tmp判断是否大于limit就可以了。。

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define REP(i,a,b) for(int i=a;i<=b;i++) #define MS0(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a)) #define PB push_back #define lson l,m,rt<<1 #define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1 using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int maxn=1000100; const ll INF=(1LL<<60); struct Tree { int u,v; ll w; };Tree tree[maxn]; int fa[maxn],dep[maxn],top[maxn],son[maxn],siz[maxn]; int id[maxn],num; int n,m; vector<int> G[maxn]; ll val[maxn]; int op,u,v;ll y; int p;ll c; ll w; struct SegTree { int l,r; ll val; void debug() { printf("%2d %2d %2d ",l,r,val); } };SegTree T[maxn<<2]; const ll limit=1e18+28; void dfs(int u,int f,int d) { fa[u]=f; dep[u]=d; siz[u]=1; son[u]=0; for(int i=0;i<G[u].size();i++){ int v=G[u][i]; if(v==f) continue; dfs(v,u,d+1); siz[u]+=siz[v]; if(siz[v]>siz[son[u]]) son[u]=v; } } void dfs1(int u,int tp) { top[u]=tp; id[u]=++num; if(son[u]) dfs1(son[u],tp); for(int i=0;i<G[u].size();i++){ int v=G[u][i]; if(v==son[u]||v==fa[u]) continue; dfs1(v,v); } } void push_up(int rt) { double tmp=T[rt<<1].val*1.0*T[rt<<1|1].val; if(tmp>limit) T[rt].val=limit+1; else T[rt].val=T[rt<<1].val*T[rt<<1|1].val; } void build(int l,int r,int rt) { T[rt].l=l;T[rt].r=r; if(l==r){ T[rt].val=val[l]; return; } int m=(l+r)>>1; build(lson); build(rson); push_up(rt); } ll query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt) { if(L<=l&&r<=R) return T[rt].val; ll res=1; int m=(l+r)>>1; if(L<=m){ ll a=res,b=query(L,R,lson); double tmp=a*1.0*b; if(tmp>limit) res=limit+1; else res=a*b; } if(R>m){ ll a=res,b=query(L,R,rson); double tmp=a*1.0*b; if(tmp>limit) res=limit+1; else res=a*b; } return res; } void update(int p,ll c,int l,int r,int rt) { if(l==r){ T[rt].val=c; return; } int m=(l+r)>>1; if(p<=m) update(p,c,lson); else update(p,c,rson); push_up(rt); } ll cha(int u,int v) { ll res=1; while(top[u]!=top[v]){ if(dep[top[u]]<dep[top[v]]) swap(u,v); if(top[u]!=u){ ll a=res,b=query(id[top[u]]+1,id[u],1,num,1); double tmp=a*1.0*b; if(tmp>limit) res=limit+1; else res=a*b; } ll a=res,b=query(id[top[u]],id[top[u]],1,num,1); double tmp=a*1.0*b; if(tmp>limit) res=limit+1; else res=a*b; u=fa[top[u]]; } if(dep[u]>dep[v]) swap(u,v); if(u!=v){ ll a=res,b=query(id[u]+1,id[v],1,num,1); double tmp=a*1.0*b; if(tmp>limit) res=limit+1; else res=a*b; } return res; } ll change(int u,ll c) { update(id[u],c,1,num,1); } int main() { freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); while(cin>>n>>m){ REP(i,0,n) G[i].clear(); MS0(son); REP(i,1,n-1){ scanf("%d%d%I64d",&u,&v,&w); tree[i]={u,v,w}; G[u].PB(v);G[v].PB(u); } num=0; dfs(1,0,1); dfs1(1,1); val[1]=1; REP(i,1,n-1){ if(dep[tree[i].v]<dep[tree[i].u]) swap(tree[i].u,tree[i].v); val[id[tree[i].v]]=tree[i].w; } build(1,num,1); while(m--){ scanf("%d",&op); if(op==1){ scanf("%d%d%I64d",&u,&v,&y); printf("%I64d ",y/cha(u,v)); } else{ scanf("%d%I64d",&p,&c); change(tree[p].v,c); } } } return 0; }
