上篇文章(http://www.cnblogs.com/zzqcn/p/3508442.html)里提到的BF和KMP算法都是单模式串匹配算法,也就是说,模式串只有一个。当需要在字符串中搜索多个关键字(模式)时,则需要用到多模式串匹配算法。
简介
AC(Aho-Corasick)算法是一个经典的多模式串匹配算法,它借鉴了KMP算法的思想,可以由有限状态机(Finite State Automata:FSA)来表示。AC算法的基本原理是:
先根据多模式串建立一个有限状态自动机FSA,在进行模式匹配时,设当前状态为Scur,输入串中的当前符号为C,运行FSA,试图得到下一状态Snext。如果Snext无效,即发生失配,则根据规则,将当前状态回退到一个适合的状态Sfail,然后重复上一过程,直到Snext有效或Scur为0。在匹配的过程中,如果当前状态正好匹配了某个模式P,则输出它。
由AC算法的原理,我们可以知道,用于匹配的FSA与输入串无关,而只与模式串有关;匹配过程中如果发生失配,则FSA应回退到某一状态,而输入串指针无需回退。这两点都与KMP算法的思想吻合。
要实现基本的AC算法,即实现FSA逻辑,需要构建3样东西:
- 状态跳转表goto :决定对于当前状态S和条件C,如何得到下一状态S‘
- 失配跳转表fail : 决定goto表得到的下一状态无效时,应该回退到哪一个状态
- 匹配结果输出表output : 决定在哪个状态时输出哪个恰好匹配的模式
构造示例
原理比较抽象,下面以一个简单而且经典的例子(来自于AC算法创始人的论文)来演示一下AC算法的原理及goto、fail、output这3个表的构建。设多模式为 {“he”, “she”, “his”, “hers”}。下面来一步一步构建FSA。
首先规定一个初始状态0,接着依次处理多个模式串,首先是he:
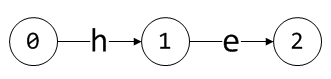
每个圆圈代表一个状态(State),圆圈中的数字表示状态的编号;有向箭头代表状态的转换,它由当前状态指向下一状态,箭头上的字符表示此次状态转换的条件。
接下来是she,注意每处理一个模式串时,都要先回到起始状态0:
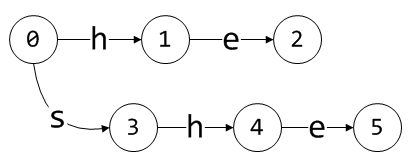
注意,如果给定条件C,从当前状态出发能转换到一个有效状态,那么只进行状态转换,而不创建新状态,这一点在处理后面两个模式串时可以看到。接着是his:
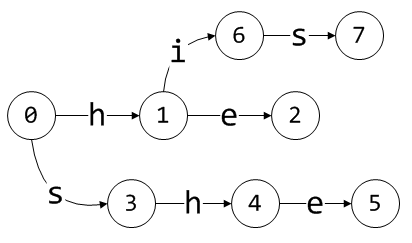
最后是hers,而且AC规定,当当前状态为初始状态(0)时,对于任意条件C来,都能转换到有效状态(这也避免了回退的死循环),因此,除了条件h和s外,对其他任意条件,状态0还应转换至状态0:

其实,最后的FSA图就表示了goto表,因为上面画的状态及状态转换都是有效的。另外,也可以自然地知道,每处理完一个模式时,FSA的当前状态都对应着此模式。因此,状态2,5,7,8分别对应模式he, she, his, hers,也就是2,5,7,8这4个状态对应的output表中的值。不过,到目前为止output表还未创建完成。
在下面的讨论中,我们用S’ = goto(S,C)表示状态S经由条件C转换到状态S‘,fail(S)表示状态S的fail表值,output(S)表示状态S的output表值。
goto表反映了有效的状态转换。而在fail表反映了转换失败时应回退到的状态。比如,设当前状态为2,当条件不是r时,状态转换就失败,必须回退到某一个合适的状态,这个状态就是状态2的fail值。而fail值的求法呢,和KMP算法中求next函数一样,可以用递推法来进行。
首先规定与状态0距离为1(即深度为1)的所有状态的fail值都为0。然后设当前状态是S1,求fail(S1)。我们知道,S1的前一状态必定是唯一的(从FSA图也可以看出),设S1的前一状态是S2,S2转换到S1的条件为C,测试S3 = goto(fail(S2), C),如果成功,则fail(S1) = goto(fail(S2), C),如果不成功,继续测试S4 = goto(fail(S3), C)是否成功,如此重复,直到转换到某个有效的状态Sn,令fail(S1) = Sn。
做为例子,我们来求状态3,4,5的fail值。首先,按照约定fail(3) == 0。接着求fail(4),由于goto(fail(3), h) == goto(0, h) == 1,所以fail(4) == 1。接着求fail(5),由于goto(fail(4), e) == goto(1, e) == 2,所以fail(5) == 2。在这里我们注意到,当FSA的状态转换到状态5时,不仅匹配了she,而且匹配了he,这意味着对两个状态S和S’,S>S’,如果fail(S) == S‘,则output(S)应添加output(S’)。这样一来,output表也构建完整了。fail表如下:
| 状态 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| fail值 | N/A | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 3 |
3个表构建完成后,就可以对输入串进行模式匹配了。设输入串为“ushers”,则匹配过程如下:
| 符号 | 状态转换 | 输出 |
| u | 0->0 | |
| s | 0->3 | |
| h | 3->4 | |
| e | 4->5 | she he |
| r | 5->2 2->8 | |
| s | 8->9 | hers |
注意,虽然扫描到符号r时经历了状态2,但那只是一个中间状态,之后立刻切换到状态8,因此并不输出output(2)的内容{he},这也避免了模式”he”的重复输出。
至此,我们已经构建了goto,fail,output 3个必需的表。这时构建的FSA也叫做非确定性有限状态机(Nondeterministic Finite State Automata: NFA),也就是说,当匹配过程中发生失配时,应根据fail表进行状态回退,但具体回退到哪个状态为止,是不确定的,需要一次或多次循环回溯。可以预见,NFA会影响模式匹配的效率。可以通过构建确定性有限状态机(Deterministic Finite State Automata: DFA)来弥补这个缺陷,它的原理是,在当前状态下,对于任意条件,都可以确定地给出下一状态,而不需要进行循环。
设当前状态是S,条件为C,问题是如何求得下一个确定状态S‘。如果goto(S, C)成功,则S’ = goto(S, C);否则,令S‘ = goto(fail(S), C),如果S’有效且不为0,则S‘就是那个确定状态,此时,应把S’ = goto(S, C)这个关系添加到goto表中。可以预见,DFA会提高匹配速度,但由于向goto表添加了更多的条目,会导致存储消耗增加。
做为例子,我们来求状态1的确定状态{S’}。首先fail(1)==0。当C==e或i时,S‘不变,分别是2,6。当C==h时,由于goto(0,h)==1,所以S’==1。当C==s时,由于goto(0, s)==3,所以S’==3。对于其他条件C,goto(0, C)==0。因此,我们需要往之前构建的goto表添加两项:1=goto(1, h), 3=goto(1,s)。
C++简单实现
下面,用简单的C++代码来实现前文所述的AC算法,包括NFA和DFA形式。
简单介绍一下宏定义、数据结构和各函数的作用:
| 名称 | 类型 | 说明 |
| AC_FAIL_STATE | 宏 | 无效/失败的跳转状态 |
| AC_UNDEF_FAIL | 宏 | 未定义的fail表值 |
| AC_CONT_SIZE | 宏 | 所有可能的条件,如果处理char字符,则范围是0-255 |
| ac_transition | 结构 | goto表项,不含当前状态,因为它等于数组下标 |
| FSAType | 枚举 | FSA类型,fail表创建后变为NFA,然后可以转换为DFA |
| ac_state_finder | 函数对象 | 用于查找当前状态下符合输入条件的goto表项 |
| ac_goto | 函数 | 实现S'=goto(S, C)逻辑,用于goto表创建和模式匹配过程 |
| ac_creat_goto_table | 函数 | 创建goto表 |
| ac_creat_fail_table | 函数 | 创建fail表,完成后将实现NFA |
| ac_convert_to_DFA | 函数 | 将NFA转换为DFA。会向goto表添加新项。完成后不再需要fail表 |
| ac_print_goto_table | 函数 | 打印所有状态及其对应的转换表、fail值(仅限NFA)、output值 |
| ac_search | 函数 | AC搜索函数 |
还有,NFA和DFA的创建过程中,需要用到类似图的广度优先搜索(Breadth-First-Search:BFS)算法,因此用到了队列(std::queue)容器。
1 // Author: 赵子清 2 // Blog: http://www.cnblogs.com/zzqcn 3 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <queue> 6 #include <algorithm> 7 #include <functional> 8 #include <string> 9 #include <cstdio> 10 using namespace std; 11 12 13 #define AC_FAIL_STATE -1 14 #define AC_UNDEF_FAIL -1 15 #define AC_CONT_SIZE 256 16 17 18 struct ac_transition 19 { 20 char condition; 21 int next; 22 }; 23 24 enum FSAType 25 { 26 FSA_NULL = 0, 27 FSA_NFA, 28 FSA_DFA 29 }; 30 31 32 struct ac_state_finder : 33 public binary_function<ac_transition, char, bool> 34 { 35 bool operator() (const ac_transition& t, char c) const 36 { 37 return (t.condition == c); 38 } 39 }; 40 41 42 vector<vector<ac_transition>> goto_table; 43 vector<vector<string>> output_table; 44 vector<int> fail_table; 45 FSAType fsa_type = FSA_NULL; 46 47 48 int ac_goto(int _state, char _cont); 49 int ac_creat_goto_table(const vector<string>& _ptns); 50 int ac_creat_fail_table(); 51 int ac_convert_to_DFA(); 52 int ac_print_goto_table(); 53 int ac_search(const string& _txt); 54 55 56 int main(int argc, char** argv) 57 { 58 string ss[4] = {"he", "she", "his", "hers"}; 59 vector<string> ptns(ss, ss+4); 60 string txt = "ushers"; 61 62 ac_creat_goto_table(ptns); 63 ac_creat_fail_table(); 64 ac_print_goto_table(); 65 ac_search(txt); 66 67 ac_convert_to_DFA(); 68 ac_print_goto_table(); 69 ac_search(txt); 70 71 return 0; 72 } 73 74 75 int ac_goto(int _state, char _cont) 76 { 77 vector<ac_transition>::const_iterator ret = 78 find_if(goto_table[_state].begin(), goto_table[_state].end(), 79 bind2nd(ac_state_finder(), _cont)); 80 if(goto_table[_state].end() == ret) 81 { 82 if(0 == _state) 83 return 0; 84 else 85 return AC_FAIL_STATE; 86 } 87 else 88 return ret->next; 89 } 90 91 92 int ac_creat_goto_table(const vector<string>& _ptns) 93 { 94 int state = 0; 95 int state_id = 0; 96 97 ac_transition t; 98 vector<ac_transition> ts; 99 vector<string> ss; 100 101 goto_table.push_back(ts); 102 output_table.push_back(ss); 103 state_id++; 104 105 for(vector<string>::const_iterator i = _ptns.begin(); i != _ptns.end(); ++i) 106 { 107 state = 0; 108 for(string::const_iterator j=i->begin(); j<i->end(); ++j) 109 { 110 int next_state = ac_goto(state, *j); 111 if(0 == next_state || AC_FAIL_STATE == next_state) 112 { 113 t.condition = *j; 114 t.next = state_id++; 115 goto_table[state].push_back(t); 116 117 goto_table.push_back(ts); 118 output_table.push_back(ss); 119 120 state = t.next; 121 } 122 else 123 state = next_state; 124 } 125 output_table[state].push_back(*i); 126 } 127 128 return 0; 129 } 130 131 132 int ac_creat_fail_table() 133 { 134 if(goto_table.empty()) 135 return -1; 136 137 fail_table.resize(goto_table.size()); 138 for(size_t i=0; i<goto_table.size(); ++i) 139 fail_table[i] = AC_UNDEF_FAIL; 140 141 queue<int> q; 142 for(vector<ac_transition>::const_iterator i = goto_table[0].begin(); 143 i != goto_table[0].end(); ++i) 144 { 145 fail_table[i->next] = 0; 146 q.push(i->next); 147 } 148 149 int state; 150 while(!q.empty()) 151 { 152 state = q.front(); q.pop(); 153 154 for(vector<ac_transition>::const_iterator i = goto_table[state].begin(); 155 i != goto_table[state].end(); ++i) 156 { 157 if(AC_UNDEF_FAIL != fail_table[i->next]) 158 continue; 159 160 q.push(i->next); 161 162 int prev_state = state, ret; 163 do 164 { 165 prev_state = fail_table[prev_state]; 166 ret = ac_goto(prev_state, i->condition); 167 } while (AC_FAIL_STATE == ret); 168 169 fail_table[i->next] = ret; 170 171 for(vector<string>::const_iterator j = output_table[ret].begin(); 172 j != output_table[ret].end(); ++j) 173 { 174 vector<string>::const_iterator sret = 175 find(output_table[i->next].begin(), output_table[i->next].end(), *j); 176 if(output_table[i->next].end() == sret) 177 output_table[i->next].push_back(*j); 178 } 179 } 180 } 181 182 fsa_type = FSA_NFA; 183 184 return 0; 185 } 186 187 188 int ac_convert_to_DFA() 189 { 190 if(fsa_type != FSA_NFA) 191 return -1; 192 193 if(goto_table.empty() || fail_table.empty()) 194 return -1; 195 196 queue<int> q; 197 for(vector<ac_transition>::const_iterator i = goto_table[0].begin(); 198 i != goto_table[0].end(); ++i) 199 { q.push(i->next); } 200 201 int state; 202 while(!q.empty()) 203 { 204 state = q.front(); q.pop(); 205 206 for(size_t c=0; c<AC_CONT_SIZE; ++c) 207 { 208 int next_state = ac_goto(state, c); 209 if(next_state != AC_FAIL_STATE && next_state != 0) 210 q.push(next_state); 211 else 212 { 213 next_state = ac_goto(fail_table[state], c); 214 if(next_state != AC_FAIL_STATE && next_state != 0) 215 { 216 ac_transition t; 217 t.condition = c; 218 t.next = next_state; 219 goto_table[state].push_back(t); 220 } 221 } 222 } 223 } 224 225 fail_table.clear(); 226 fsa_type = FSA_DFA; 227 228 return 0; 229 } 230 231 232 void OutputMatch(int _state, size_t _pos) 233 { 234 for(vector<string>::const_iterator i = output_table[_state].begin(); 235 i != output_table[_state].end(); ++i) 236 { 237 printf("%d %s : %d ", _state, i->c_str(), _pos - i->length()); 238 } 239 } 240 241 int ac_search(const string& _txt) 242 { 243 if(goto_table.empty() || FSA_NULL == fsa_type) 244 return -1; 245 246 int state = 0; 247 string::size_type i; 248 for(i=0; i<_txt.length(); ++i) 249 { 250 char c = _txt[i]; 251 if(output_table[state].size() > 0) 252 OutputMatch(state, i); 253 254 if(FSA_NFA == fsa_type) 255 { 256 while(AC_FAIL_STATE == ac_goto(state, c)) 257 state = fail_table[state]; 258 state = ac_goto(state, c); 259 } 260 else if(FSA_DFA == fsa_type) 261 { 262 state = ac_goto(state, c); 263 if(AC_FAIL_STATE == state) 264 state = 0; 265 } 266 } 267 268 if(output_table[state].size() > 0) 269 OutputMatch(state, i); 270 271 return 0; 272 } 273 274 275 int ac_print_goto_table() 276 { 277 if(goto_table.empty()) 278 return -1; 279 280 int state_id = 0; 281 for(vector<vector<ac_transition>>::const_iterator i = goto_table.begin(); 282 i != goto_table.end(); ++i, ++state_id) 283 { 284 printf("%d: ", state_id); 285 286 if(FSA_NFA == fsa_type) 287 printf("%d ", fail_table[state_id]); 288 289 for(vector<ac_transition>::const_iterator j = i->begin(); 290 j != i->end(); ++j) 291 { 292 printf("%c->%d ", j->condition, j->next); 293 } 294 295 for(vector<string>::const_iterator j = output_table[state_id].begin(); 296 j != output_table[state_id].end(); ++j) 297 { 298 printf("(%s) ", j->c_str()); 299 } 300 printf(" "); 301 } 302 printf(" "); 303 304 return 0; 305 }
输出结果:
0: -1 h->1 s->3 1: 0 e->2 i->6 2: 0 r->8 (he) 3: 0 h->4 4: 1 e->5 5: 2 (she) (he) 6: 0 s->7 7: 3 (his) 8: 0 s->9 9: 3 (hers) 5 she : 1 5 he : 2 9 hers : 2
0: h->1 s->3 1: e->2 i->6 h->1 s->3 2: r->8 h->1 s->3 (he) 3: h->4 s->3 4: e->5 h->1 i->6 s->3 5: h->1 r->8 s->3 (she) (he) 6: s->7 h->1 7: h->4 s->3 (his) 8: s->9 h->1 9: h->4 s->3 (hers) 5 she : 1 5 he : 2 9 hers : 2
参考资料:
【1】《Efficient String Matching: An Aid to Bibliographic Search》 - Alfred V. Aho & Margaret J. Corasick, 贝尔实验室