官方+白话讲解Executors、ThreadPoolExecutor线程池使用
Executors:JDK给提供的线程工具类,静态方法构建线程池服务ExecutorService,也就是ThreadPoolExecutor,使用默认线程池配置参数。
建议:对于大用户,高并发,不易掌控的项目,不建议使用Executors来创建线程池对象。
对于易于掌控且并发数不高的项目,可以考虑Executors。
ThreadPoolExecutor:线程池对象,实现ExecutorService接口,可以自定义线程池核心线程数、最大线程数、空闲时间、缓冲队列等。
建议:大用户,高并发,不易于掌控的项目,建议根据物理服务器配置,任务需求耗时,可能存在的并发量,自定义配置ThreadPoolExecutor线程信息。
一般项目会封装ThreadPoolExecutor工具类,因为需要考虑新手有时会乱用,也方便于统一灵活管理。
一、先说下Executors 创建线程池的三种策略
1.创建无边界缓存线程池:Executors.newCachedThreadPool()
无边界缓存界线程池:不限制最大线程数的线程池,且线程有空闲存活时长。
接着看下JDK Executors.newCachedThreadPool()源码:

源码可以可以看到,该方法创建了一个线程池为:核心线程数0,最大线程数Integer.MAX_VALUE(可以理解为无上限),线程空闲存活时长60,单位TimeUnit.SECONDS秒,缓冲队列是SynchronousQueue的线程池。
因为最大线程数没有上限,所以,大用户,高并发项目使用时一定要严谨配置。
关于SynchronousQueue缓冲队列的缓冲数是1,不过每次都被线程池创建取走,所以该缓冲对联永远isEmpty=true。具体细节先百度,后续有时间我再讲解。
2.创建有边界线程池:Executors.newFixedThreadPool(200)
有边界线程池:有最大线程数限制的线程池。
接着看下JDK Executors.newFixedThreadPool(200)源码:

源码可以可以看到,该方法创建了一个线程池为:核心线程数nThreads(200),最大线程数nThreads (200),线程空闲存活时长0,单位TimeUnit.SECONDS秒,缓冲队列是LinkedBlockingQueue的线程池。
LinkedBlockingQueue这里没有定义长度,也就是说这个缓冲队列的容量没有上限,大用户,高并发项目使用时一定要严谨配置。
3.创建单线程线程池:Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor()
单线程线程池:线程池里只有一个线程数,其他都存在缓冲队列里,
接着看下JDK Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor()源码:
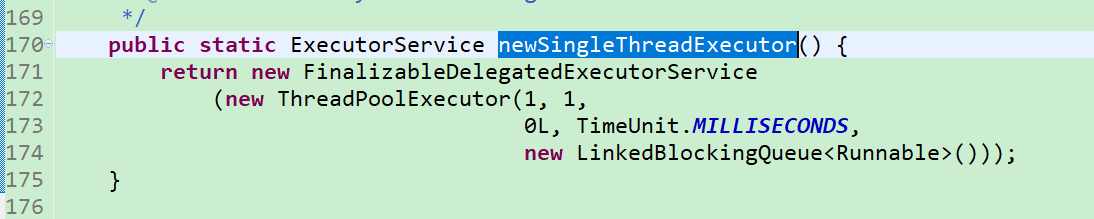
源码可以可以看到,该方法创建了一个线程池为:核心线程数1,最大线程数1,线程空闲存活时长0,单位TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS毫秒,缓冲队列是LinkedBlockingQueue的线程池。
LinkedBlockingQueue这里没有定义长度,也就是说这个缓冲队列的容量没有上限,大用户,高并发项目使用时一定要严谨配置。
使用场景:任务需要逐一调度执行。
二、ThreadPoolExecutor自定义配置线程池对象
通过上面的Executors,我们对创建线程池已经有了点了解。
下面直接看构造函数的源码,我把参数解释为白话文
/** * @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even * if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set
核心线程数,核心线程数永远小于等于最大线程数。
缓冲队列不满时,线程池的线程数用远小于等于核心线程数。
缓冲队列满时,线程池会在核心线程数的基础上再创建线程,但小于最大线程数
* @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the * pool
线程池最大线程数 * @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than * the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads * will wait for new tasks before terminating.
线程空闲存活时长 * @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument
线程存活时长单位 * @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are * executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable} * tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method.
缓冲队列,BlockingQueue接口的实现类,根据需求选择他的实现类即可,细节有必要去找度娘。
常用BlockingQueue有LinkedBlockingQueue和SynchronousQueue * @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor * creates a new thread
线程工厂,用来创建线程的,使用默认的就好 * @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked * because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached
缓冲队列已满且已经最大线程数,这时的处理策略
RejectedExecutionHandler下有多个实现类,根据所需决定
*/ public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) { if (corePoolSize < 0 || maximumPoolSize <= 0 || maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize || keepAliveTime < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ? null : AccessController.getContext(); this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize; this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize; this.workQueue = workQueue; this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime); this.threadFactory = threadFactory; this.handler = handler; }
在开发实战中,对于多线程颇为了解的,我建议根据硬件和软件需求结合,自定义创建ThreadPoolExecutor线程池。