装饰器
现在你写了一个函数,在你的程序里多次调用,后期你需要给函数扩展功能,根据开闭原则:可以扩展功能,加入新的代码,但不能修改原有写好的代码。所以你需要在不改变函数调用方式和不修改函数内代码的情况下,给函数增加功能。
以给shop()函数添加计算函数执行时间为例:
import time, random
# shop()原来的代码如下
def shop():
print("shopping...")
time.sleep(random.random())
你需要这样写才能完成你的功能:
start = time.time()
shop()
stop = time.time()
print("this process run %.5f s" % (stop - start))
为了容易调用,你决定将它封装为一个函数:
start = time.time()
shop()
stop = time.time()
print("this process run %.5f s" % (stop - start))
但是这样来看,你修改了函数的调用方式,你现在需要调用inner 才能完成功能。如果强行将shop=inner(),shop(),会发生循环调用,然后报错,怎样才能让shop()不会自己调用自己呢?
让shop这个函数名与调用 () 不在同一层名称空间,只有通过闭包的方式才能拿到一次,然后执行shop。同时在执行的那一层可以添加新功能。即:
def timer():
func=shop
def inner():
start = time.time()
func()
stop = time.time()
print("this process run %.5f s" % (stop - start))
return inner
shop=timer()
shop()
看到么,函数里,func = shop 就相当于上一篇博客里那张图中的x=1一样,我们通过闭包的方式完成了传值!!记住,闭包也是一种传值方式!
但是还不够,这样的功能被写死了,只能计算shop()的时间,我们之前在函数参数那一节学过用第一种用变量传值的方式,还记得么?用到这里就是:
def timer(func):
def inner():
start = time.time()
stop = time.time()
print("this process run %.5f s" % (stop - start))
return inner
shop=timer(shop) # 前一个shop是变量名,第二个shop是函数(一个地址,shop函数的代码地址)作为vaule传给timmer里的形参func
shop()
这样就完成了一个装饰器
装饰器思路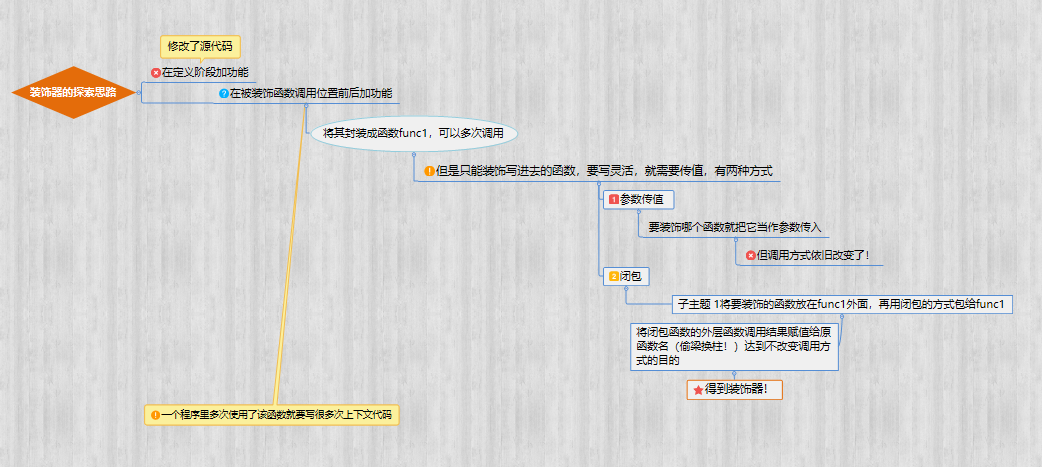
现在思考下,这个装饰器有没有不足?
1.用装饰器实际上是“偷梁换柱”将被装饰函数换成了inner,如果被装饰函数有参数传入,而inner现在不能接收参数,就会报错了。
2.如果被装饰函数有返回值,用目前的装饰器接收不到。
所以进一步完善下:
def timer(func):
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
stop = time.time()
print("this process run %.5f s" % (stop - start))
return res
return inner
到这里,想必你已经能总结出一个装饰器的固定模板了,那就是:
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
# 添加功能
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
# 添加功能
return res
return inner
最后,给你一个快捷使用装饰器的方式,在编程中,将某种代码简化,固定成形的语法被称为语法糖,装饰器这里就有一颗语法糖,无参装饰器的完整使用方法如下:
import time, random
def timer(func):
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
res = func(*args, **kwargs)
stop = time.time()
print("this process run %.5f s" % (stop - start))
return res
return inner
# 语法糖
@timer
def shop():
print("shopping...")
time.sleep(random.random())
shop()
试试再给shop()和与之同样的pay()加上认证的功能吧
import time import random status_dict = {"user": None, "login": False} db = 'info.txt' def auth(auth_source="text"): def auth_status(func): def wrapper(*args, **kwargs): if status_dict["user"] and status_dict.get("login"): return func if auth_source == "text": uname = input("输入用户名》》") upwd = input("输入密码》》") with open(db, 'rt', encoding='utf8') as f: for line in f: info_dict = eval(line.strip()) if uname == info_dict.get("name") and upwd == info_dict.get("pwd"): print("login successful") status_dict["user"] = uname status_dict["login"] = True res = func(*args, **kwargs) return res else: print("username or pwd error!") elif auth_source == " mySQL": print("没有数据") else: print("没有数据") return wrapper return auth_status def timer(func): def inner(*args, **kwargs): start = time.time() res = func(*args, **kwargs) stop = time.time() print("this process run %.5f s" % (stop - start)) return res return inner @timer def shop(): print("shopping...") time.sleep(random.random()) shop() @auth(auth_source="text") @timer def pay(): print("paying...") pay() 认证与计时装饰器
当你想新增的功能需要接收一个参数时,需要写成三层的有参装饰器。
