一、IOC容器
1.IOC底层原理
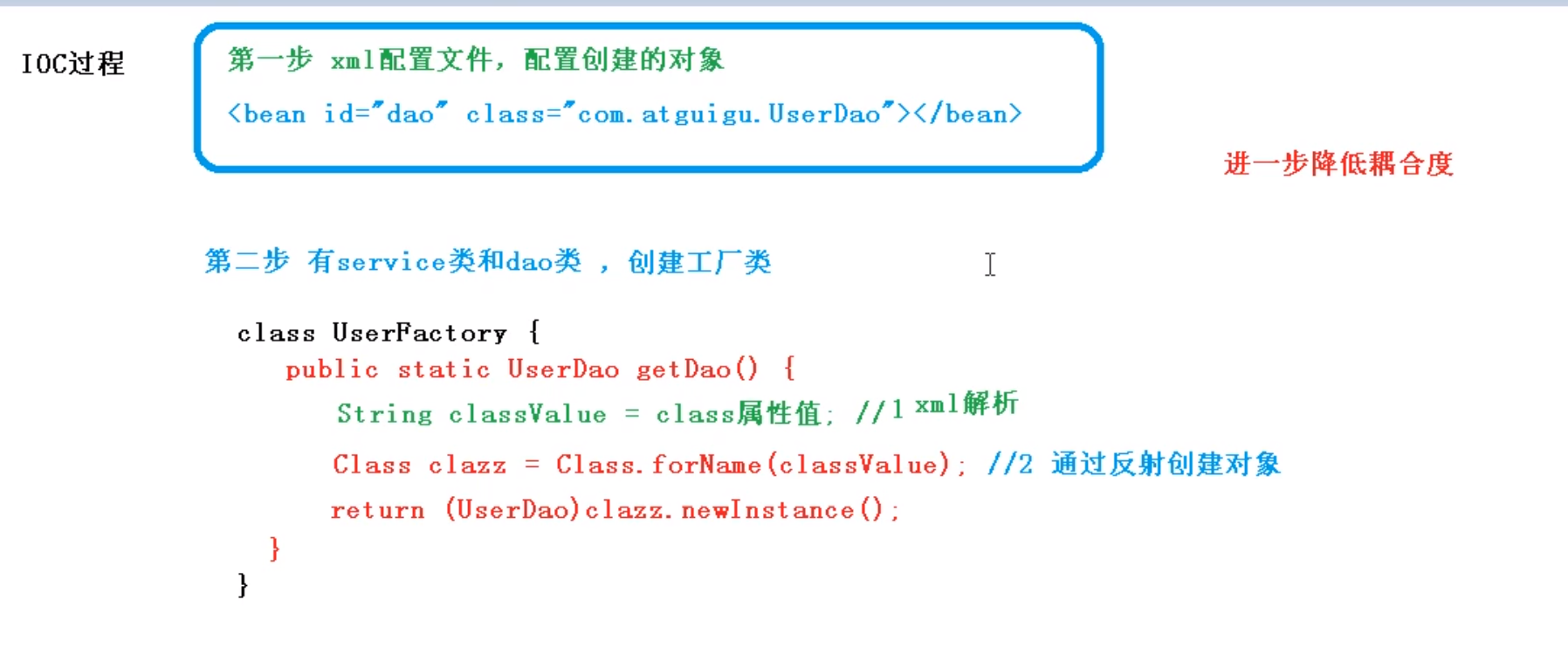
概念:控制反转,把对象创建和对象之间的调用过程,交给Spring进行管理。
目的:降低耦合度
为什么使用IOC?
原始new创建对象的方式耦合性太高了 修改一处就要整个修改
解决方案就是引入工厂模式
底层原理:XML解析,工厂模式,反射
IOC思想基于IOC容器完成 IOC容器底层就是对象工厂
Spring提供IOC容器实现的两种方式(两个接口)
(1)BeanFactory:IOC容器基本实现,是Spring内部的使用接口,不提供开发人员进行使用
加载配置文件时不会创建对象,在获取对象时才回去创建对象
(2)ApplicationContext:BeanFactory接口的子接口,提供更多更强大的功能,一般由开发人员进行使用
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
加载配置文件时候就会把在配置文件对象进行创建
IOC过程:
2.IOC接口(BeanFactory)
IOC操作Bean管理:
1.什么是Bean管理:指的是两个操作
(1)Spring创建对象
(2)Spring注入属性
2.Bean管理操作的两种方式
(1)基于XML配置文件方式实现
1.在spring配置文件中使用bean标签 标签中添加对应属性 就可以实现创建对象。
2.在bean标签中有很多常用属性:
id属性:唯一标识(不能使用特殊符号)
class属性:类全路径(包类路径)
<bean id="user" class="com.zzm.spring.User"></bean>
3.创建对象时,默认也是执行无参数构造方法完成对象创建。
(2)基于xml方式注入属性
1.DI:依赖注入,就是注入属性。
第一种注入方式:使用set方法注入
//创建Book类 public class Booke { private String bname; private String bauthor; public void setBname(String bname) { this.bname = bname; } public void setBauthor(String bauthor) { this.bauthor = bauthor; } public void show(){ System.out.println(bname+":::"+bauthor); } } //编写配置文件注入属性 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="book" class="com.zzm.Book"> <property name="bname" value="语文"></property> <property name="bauthor" value="小明"></property> </bean> </beans> //测试类查看结果 public class testbook { @Test public void testbook(){ ApplicationContext context1 = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml"); Booke book = context1.getBean("book", Book.class); book.show(); } }
//运行结果:语文:::小明
第二种注入方式:使用有参构造注入
(2)基于注解方式实现
//创建Orders类 public class Orders { private String oname; private String oaddress; public Orders(String oname, String oaddress) { this.oname = oname; this.oaddress = oaddress; } public void show(){ System.out.println(oname+":"+oaddress); } } //编辑xml配置文件 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="orders" class="com.zzm.Orders"> <constructor-arg name="oname" value="小明"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg name="oaddress" value="xx"></constructor-arg> </bean> </beans> //测试类查看结果 public class testuser { @Test public void testOrders(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml"); Orders orders = context.getBean("orders",Orders.class); orders.show(); } }
//运行结果:小明:xx
注入空值和特殊符号
//注入空值 <constructor-arg name="oname"> <null/> </constructor-arg> //注入特殊符号 <constructor-arg name="oname"> <value> <![CDATA[<<特殊>>]]> </value> </constructor-arg>
注入属性-外部bean
//service类 public class UserService { private UserDao userDao; public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; } public void add(){ System.out.println("userservice方法被调用"); userDao.update(); } }
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="userService" class="com.zzm.services.UserService"> <property name="userDao" ref="userDao"></property> </bean> <bean id="userDao" class="com.zzm.dao.UserDaoImpl"></bean> </beans>
注入属性-内部Bean
创建部门类
public class DeptDao { private String dname; public void setDname(String dname) { this.dname = dname; } @Override public String toString() { return "DeptDao{" + "dname='" + dname + '\'' + '}'; } }
创建员工类
public class ErpDao { private String name; private String gender; private DeptDao dept; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } public void setDept(DeptDao dept) { this.dept = dept; } public void show(){ System.out.println(name+gender+dept); } }
编辑bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="erp" class="com.zzm.dao.ErpDao"> <property name="name" value="zhangsan//"></property> <property name="gender" value="man//"></property> <property name="dept"> <bean id="dept" class="com.zzm.dao.DeptDao"> <property name="dname" value="anbao"></property> </bean> </property> </bean> </beans>
测试方法
@Test public void testErp(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml"); ErpDao erp = context.getBean("erp",ErpDao.class); erp.show(); }
3.IOC操作Bean管理(基于XML)
1)自动装配:根据指定装配规则(属性名称或属性类型),Sring自动将匹配的属性值进行注入
4.IOC操作Bean管理(基于注解)
1)注解:注解是代码特殊标记,格式:@注解名称(属性名称=属性值,属性名称=属性值......)
2)使用注解:注解可以作用在类上面 方法上 属性上
3)使用注解的目的:简化代码
Spring针对Bean管理中创建对象提供注解
1)@Component:泛指组件,当组件不好归类的时候,我们可以使用这个注解进行标注。
2)@Service:用于标注业务层组件
3)@Controller:用于标注控制层组件(如struts中的action)
4)@Repository:用于标注数据访问组件,即DAO组件.
上面四个注解功能是一样的 都可以用来创建bean实例(若不添加Value属性则被扫描的默认值为对象名的首字母小写)
基于注解方式实现对象创建
1)@Autowired:根据属性类型进行自动装配
2)@Qualifier:根据属性名称进行注入(若接口的实现类有多个 则无法使用Autowired进行注入 所有需要使用@Qualifier加创建对象时的Value属性)
3)@Resource:可以根据类型注入,也可以根据名称注入
4)@Value:注入普通类型属性
注解方式实现对象创建的步骤
1.修改XML配置文件(开启组件扫描)
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zzm.spring.dao"></context:component-scan>
2.创建Dao类并提添加注解
public interface UserDao { public void add(); } @Component public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ @Override public void add() { System.out.println("add..."); } }
3.创建Service类并添加注解(开启被扫描、自动装配)
@Service(value = "xx") public class UserService { @Autowired private UserDao userDao; public void show(){ System.out.println("sss"); userDao.add(); } }
4.测试代码
public class Tset { @Test public void testUserService(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); UserService userService = context.getBean("xx", UserService.class); userService.show(); } }
全注解开发
配置文件类:
@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.zzm.spring") public class ConfigSpring { }
UserDao接口和实现类
public interface UserDao { public void add(); } @Component public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ @Override public void add() { System.out.println("add方法被调用"); } }
UserService类
@Service(value = "aa") public class UserService { @Autowired private UserDao userDao; public void show(){ System.out.println("show方法被调用"); userDao.add(); } }
单元测试类
public class TestUser { @Test public void testUserDemo(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("com.zzm.spring"); UserService aa = context.getBean("aa",UserService.class); aa.show(); } }
AOP操作术语
1.连接点:类里面哪些方法可以被增强 这些方法称为连接点
2.切入点:实际被增强的方法叫切入点
3.通知(增强):实际增强的逻辑部分称为通知(增强)
4.切面:把通知应用到切入点的过程