一 介绍
约束条件与数据类型的宽度一样,都是可选参数
作用:用于保证数据的完整性和一致性
主要分为:
PRIMARY KEY (PK) 标识该字段为该表的主键,可以唯一的标识记录 FOREIGN KEY (FK) 标识该字段为该表的外键 NOT NULL 标识该字段不能为空 UNIQUE KEY (UK) 标识该字段的值是唯一的 AUTO_INCREMENT 标识该字段的值自动增长(整数类型,而且为主键) DEFAULT 为该字段设置默认值 UNSIGNED 无符号 ZEROFILL 使用0填充
说明:
1. 是否允许为空,默认NULL,可设置NOT NULL,字段不允许为空,必须赋值
2. 字段是否有默认值,缺省的默认值是NULL,如果插入记录时不给字段赋值,此字段使用默认值
sex enum('male','female') not null default 'male'
age int unsigned NOT NULL default 20 必须为正值(无符号) 不允许为空 默认是20
3. 是否是key
主键 primary key
外键 foreign key
索引 (index,unique...)
二 not null与default
是否可空,null表示空,非字符串
not null - 不可空
null - 可空
默认值,创建列时可以指定默认值,当插入数据时如果未主动设置,则自动添加默认值
create table tb1(
nid int not null defalut 2,
num int not null)

==================not null==================== mysql> create table t1(id int); #id字段默认可以插入空 mysql> desc t1; +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ mysql> insert into t1 values(); #可以插入空 mysql> create table t2(id int not null); #设置字段id不为空 mysql> desc t2; +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | | NULL | | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ mysql> insert into t2 values(); #不能插入空 ERROR 1364 (HY000): Field 'id' doesn't have a default value ==================default==================== #设置id字段有默认值后,则无论id字段是null还是not null,都可以插入空,插入空默认填入default指定的默认值 mysql> create table t3(id int default 1); mysql> alter table t3 modify id int not null default 1; ==================综合练习==================== mysql> create table student( -> name varchar(20) not null, -> age int(3) unsigned not null default 18, -> sex enum('male','female') default 'male', -> hobby set('play','study','read','music') default 'play,music' -> ); mysql> desc student; +-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+------------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+------------+-------+ | name | varchar(20) | NO | | NULL | | | age | int(3) unsigned | NO | | 18 | | | sex | enum('male','female') | YES | | male | | | hobby | set('play','study','read','music') | YES | | play,music | | +-------+------------------------------------+------+-----+------------+-------+ mysql> insert into student(name) values('egon'); mysql> select * from student; +------+-----+------+------------+ | name | age | sex | hobby | +------+-----+------+------------+ | egon | 18 | male | play,music | +------+-----+------+------------+
三 unique

============设置唯一约束 UNIQUE=============== 方法一: create table department1( id int, name varchar(20) unique, comment varchar(100) ); 方法二: create table department2( id int, name varchar(20), comment varchar(100), constraint uk_name unique(name) ); mysql> insert into department1 values(1,'IT','技术'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into department1 values(1,'IT','技术'); ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry 'IT' for key 'name'

mysql> create table t1(id int not null unique); Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec) mysql> desc t1; +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | +-------+---------+------+-----+---------+-------+ row in set (0.00 sec)

create table service( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), host varchar(15) not null, port int not null, unique(host,port) #联合唯一 ); mysql> insert into service values -> (1,'nginx','192.168.0.10',80), -> (2,'haproxy','192.168.0.20',80), -> (3,'mysql','192.168.0.30',3306) -> ; Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.01 sec) Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> insert into service(name,host,port) values('nginx','192.168.0.10',80); ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '192.168.0.10-80' for key 'host'
四 primary key
primary key字段的值不为空且唯一
一个表中可以:
单列做主键
多列做主键(复合主键)
但一个表内只能有一个主键primary key

============单列做主键=============== #方法一:not null+unique create table department1( id int not null unique, #主键 name varchar(20) not null unique, comment varchar(100) ); mysql> desc department1; +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | NO | UNI | NULL | | | comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ rows in set (0.01 sec) #方法二:在某一个字段后用primary key create table department2( id int primary key, #主键 name varchar(20), comment varchar(100) ); mysql> desc department2; +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | | comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ rows in set (0.00 sec) #方法三:在所有字段后单独定义primary key create table department3( id int, name varchar(20), comment varchar(100), constraint pk_name primary key(id); #创建主键并为其命名pk_name mysql> desc department3; +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | | comment | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | | +---------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ rows in set (0.01 sec)

==================多列做主键================ create table service( ip varchar(15), port char(5), service_name varchar(10) not null, primary key(ip,port) ); mysql> desc service; +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ | ip | varchar(15) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | port | char(5) | NO | PRI | NULL | | | service_name | varchar(10) | NO | | NULL | | +--------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+ rows in set (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into service values -> ('172.16.45.10','3306','mysqld'), -> ('172.16.45.11','3306','mariadb') -> ; Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec) Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0 mysql> insert into service values ('172.16.45.10','3306','nginx'); ERROR 1062 (23000): Duplicate entry '172.16.45.10-3306' for key 'PRIMARY'
五 auto_increment
约束字段为自动增长,被约束的字段必须同时被key约束

#不指定id,则自动增长 create table student( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), sex enum('male','female') default 'male' ); mysql> desc student; +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra | +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ | id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment | | name | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | | | sex | enum('male','female') | YES | | male | | +-------+-----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+ mysql> insert into student(name) values -> ('egon'), -> ('alex') -> ; mysql> select * from student; +----+------+------+ | id | name | sex | +----+------+------+ | 1 | egon | male | | 2 | alex | male | +----+------+------+ #也可以指定id mysql> insert into student values(4,'asb','female'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into student values(7,'wsb','female'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from student; +----+------+--------+ | id | name | sex | +----+------+--------+ | 1 | egon | male | | 2 | alex | male | | 4 | asb | female | | 7 | wsb | female | +----+------+--------+ #对于自增的字段,在用delete删除后,再插入值,该字段仍按照删除前的位置继续增长 mysql> delete from student; Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> select * from student; Empty set (0.00 sec) mysql> insert into student(name) values('ysb'); mysql> select * from student; +----+------+------+ | id | name | sex | +----+------+------+ | 8 | ysb | male | +----+------+------+ #应该用truncate清空表,比起delete一条一条地删除记录,truncate是直接清空表,在删除大表时用它 mysql> truncate student; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> insert into student(name) values('egon'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from student; +----+------+------+ | id | name | sex | +----+------+------+ | 1 | egon | male | +----+------+------+ row in set (0.00 sec)

#在创建完表后,修改自增字段的起始值 mysql> create table student( -> id int primary key auto_increment, -> name varchar(20), -> sex enum('male','female') default 'male' -> ); mysql> alter table student auto_increment=3; mysql> show create table student; ....... ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 mysql> insert into student(name) values('egon'); Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> select * from student; +----+------+------+ | id | name | sex | +----+------+------+ | 3 | egon | male | +----+------+------+ row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> show create table student; ....... ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 #也可以创建表时指定auto_increment的初始值,注意初始值的设置为表选项,应该放到括号外 create table student( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), sex enum('male','female') default 'male' )auto_increment=3; #设置步长 sqlserver:自增步长 基于表级别 create table t1( id int。。。 )engine=innodb,auto_increment=2 步长=2 default charset=utf8 mysql自增的步长: show session variables like 'auto_inc%'; #基于会话级别 set session auth_increment_increment=2 #修改会话级别的步长 #基于全局级别的 set global auth_increment_increment=2 #修改全局级别的步长(所有会话都生效) #!!!注意了注意了注意了!!! If the value of auto_increment_offset is greater than that of auto_increment_increment, the value of auto_increment_offset is ignored. 翻译:如果auto_increment_offset的值大于auto_increment_increment的值,则auto_increment_offset的值会被忽略 比如:设置auto_increment_offset=3,auto_increment_increment=2 mysql> set global auto_increment_increment=5; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> set global auto_increment_offset=3; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql> show variables like 'auto_incre%'; #需要退出重新登录 +--------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-------+ | auto_increment_increment | 1 | | auto_increment_offset | 1 | +--------------------------+-------+ create table student( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), sex enum('male','female') default 'male' ); mysql> insert into student(name) values('egon1'),('egon2'),('egon3'); mysql> select * from student; +----+-------+------+ | id | name | sex | +----+-------+------+ | 3 | egon1 | male | | 8 | egon2 | male | | 13 | egon3 | male | +----+-------+------+
六 foreign key
员工信息表有三个字段:工号 姓名 部门
公司有3个部门,但是有1个亿的员工,那意味着部门这个字段需要重复存储,部门名字越长,越浪费
解决方法:
我们完全可以定义一个部门表
然后让员工信息表关联该表,如何关联,即foreign key

#表类型必须是innodb存储引擎,且被关联的字段,即references指定的另外一个表的字段,必须是主键 create table department( id int primary key, name varchar(20) not null )engine=innodb; #dpt_id外键,关联父表(department主键id),同步更新,同步删除 create table employee( id int primary key, name varchar(20) not null, dpt_id int, constraint fk_name foreign key(dpt_id) references department(id) on delete cascade on update cascade )engine=innodb; #先往父表department中插入记录 insert into department values (1,'欧德博爱技术有限事业部'), (2,'艾利克斯人力资源部'), (3,'销售部'); #再往子表employee中插入记录 insert into employee values (1,'egon',1), (2,'alex1',2), (3,'alex2',2), (4,'alex3',2), (5,'李坦克',3), (6,'刘飞机',3), (7,'张火箭',3), (8,'林子弹',3), (9,'加特林',3) ; #删父表department,子表employee中对应的记录跟着删 mysql> delete from department where id=3; mysql> select * from employee; +----+-------+--------+ | id | name | dpt_id | +----+-------+--------+ | 1 | egon | 1 | | 2 | alex1 | 2 | | 3 | alex2 | 2 | | 4 | alex3 | 2 | +----+-------+--------+ #更新父表department,子表employee中对应的记录跟着改 mysql> update department set id=22222 where id=2; mysql> select * from employee; +----+-------+--------+ | id | name | dpt_id | +----+-------+--------+ | 1 | egon | 1 | | 3 | alex2 | 22222 | | 4 | alex3 | 22222 | | 5 | alex1 | 22222 | +----+-------+--------+

表1 foreign key 表2
则表1的多条记录对应表2的一条记录,即多对一
利用foreign key的原理我们可以制作两张表的多对多,一对一关系
多对多:
表1的多条记录可以对应表2的一条记录
表2的多条记录也可以对应表1的一条记录
一对一:
表1的一条记录唯一对应表2的一条记录,反之亦然
分析时,我们先从按照上面的基本原理去套,然后再翻译成真实的意义,就很好理解了
、、
三张表:出版社,作者信息,书
一对多(或多对一):一个出版社可以出版多本书
关联方式:foreign key

=====================多对一===================== create table press( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) ); create table book( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), press_id int not null, foreign key(press_id) references press(id) on delete cascade on update cascade ); insert into press(name) values ('北京工业地雷出版社'), ('人民音乐不好听出版社'), ('知识产权没有用出版社') ; insert into book(name,press_id) values ('九阳神功',1), ('九阴真经',2), ('九阴白骨爪',2), ('独孤九剑',3), ('降龙十巴掌',2), ('葵花宝典',3) ;
多对多:一个作者可以写多本书,一本书也可以有多个作者,双向的一对多,即多对多
关联方式:foreign key+一张新的表

=====================多对多===================== create table author( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) ); #这张表就存放作者表与书表的关系,即查询二者的关系查这表就可以了 create table author2book( id int not null unique auto_increment, author_id int not null, book_id int not null, constraint fk_author foreign key(author_id) references author(id) on delete cascade on update cascade, constraint fk_book foreign key(book_id) references book(id) on delete cascade on update cascade, primary key(author_id,book_id) ); #插入四个作者,id依次排开 insert into author(name) values('egon'),('alex'),('yuanhao'),('wpq'); #每个作者与自己的代表作如下 egon: 九阳神功 九阴真经 九阴白骨爪 独孤九剑 降龙十巴掌 葵花宝典 alex: 九阳神功 葵花宝典 yuanhao: 独孤九剑 降龙十巴掌 葵花宝典 wpq: 九阳神功 insert into author2book(author_id,book_id) values (1,1), (1,2), (1,3), (1,4), (1,5), (1,6), (2,1), (2,6), (3,4), (3,5), (3,6), (4,1) ;
#两张表:学生表和客户表
一对一:一个学生是一个客户,一个客户有可能变成一个学校,即一对一的关系
关联方式:foreign key+unique

#一定是student来foreign key表customer,这样就保证了: #1 学生一定是一个客户, #2 客户不一定是学生,但有可能成为一个学生 create table customer( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null ); create table student( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null, class_name varchar(20) not null default 'python自动化', level int default 1, customer_id int unique, #该字段一定要是唯一的 foreign key(customer_id) references customer(id) #外键的字段一定要保证unique on delete cascade on update cascade ); #增加客户 insert into customer(name) values ('李飞机'), ('王大炮'), ('守榴弹'), ('吴坦克'), ('赢火箭'), ('战地雷') ; #增加学生 insert into student(name,customer_id) values ('李飞机',1), ('王大炮',2) ;
练习:账号信息表,用户组,主机表,主机组

#用户表 create table user( id int not null unique auto_increment, username varchar(20) not null, password varchar(50) not null, primary key(username,password) ); insert into user(username,password) values ('root','123'), ('egon','456'), ('alex','alex3714') ; #用户组表 create table usergroup( id int primary key auto_increment, groupname varchar(20) not null unique ); insert into usergroup(groupname) values ('IT'), ('Sale'), ('Finance'), ('boss') ; #主机表 create table host( id int primary key auto_increment, ip char(15) not null unique default '127.0.0.1' ); insert into host(ip) values ('172.16.45.2'), ('172.16.31.10'), ('172.16.45.3'), ('172.16.31.11'), ('172.10.45.3'), ('172.10.45.4'), ('172.10.45.5'), ('192.168.1.20'), ('192.168.1.21'), ('192.168.1.22'), ('192.168.2.23'), ('192.168.2.223'), ('192.168.2.24'), ('192.168.3.22'), ('192.168.3.23'), ('192.168.3.24') ; #业务线表 create table business( id int primary key auto_increment, business varchar(20) not null unique ); insert into business(business) values ('轻松贷'), ('随便花'), ('大富翁'), ('穷一生') ; #建关系:user与usergroup create table user2usergroup( id int not null unique auto_increment, user_id int not null, group_id int not null, primary key(user_id,group_id), foreign key(user_id) references user(id), foreign key(group_id) references usergroup(id) ); insert into user2usergroup(user_id,group_id) values (1,1), (1,2), (1,3), (1,4), (2,3), (2,4), (3,4) ; #建关系:host与business create table host2business( id int not null unique auto_increment, host_id int not null, business_id int not null, primary key(host_id,business_id), foreign key(host_id) references host(id), foreign key(business_id) references business(id) ); insert into host2business(host_id,business_id) values (1,1), (1,2), (1,3), (2,2), (2,3), (3,4) ; #建关系:user与host create table user2host( id int not null unique auto_increment, user_id int not null, host_id int not null, primary key(user_id,host_id), foreign key(user_id) references user(id), foreign key(host_id) references host(id) ); insert into user2host(user_id,host_id) values (1,1), (1,2), (1,3), (1,4), (1,5), (1,6), (1,7), (1,8), (1,9), (1,10), (1,11), (1,12), (1,13), (1,14), (1,15), (1,16), (2,2), (2,3), (2,4), (2,5), (3,10), (3,11), (3,12) ;
作业:
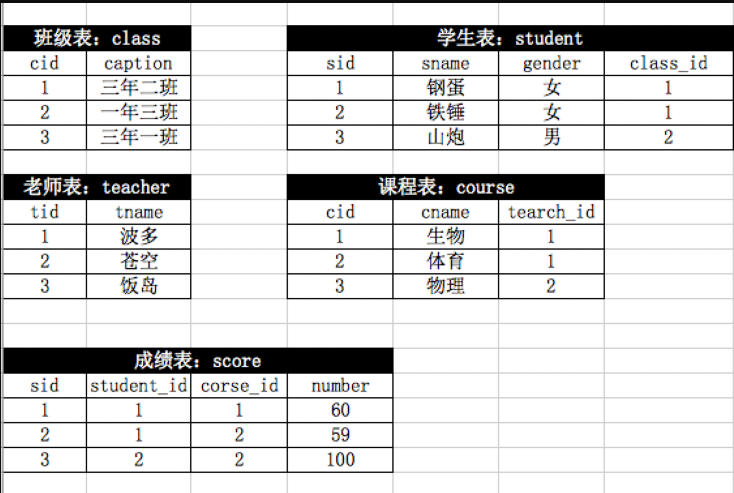
七、总结

1 not null 与default create table student2( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(5), sex enum('male','female') not null default 'female' ); insert into student2(name) values('alex'); create table student3( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(5), age int not null default 30 ); insert into student3(name) values('alex'); 2 unique #单列唯一 create table teacher( id int not null unique, name char(10) ); insert into teacher values(1,'egon'); insert into teacher values(1,'alex'); #多列唯一 #255.255.255.255 create table services( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(10), host char(15), port int, constraint host_port unique(host,port) ); insert into services values('ftp','192.168.20.17',8080); insert into services values('httpd','192.168.20.17',8081); #auto_increment_offset:偏移量 create table dep( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(10) ); insert into dep(name) values('IT'),('HR'),('SALE'),('Boss'); create table dep1( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(10) )auto_increment=10; insert into dep1(name) values('IT'),('HR'),('SALE'),('Boss'); #auto_increment_increment:步长 create table dep2( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(10) ); set session auto_increment_increment=2; #会话级,只对当前会话有效 set global auto_increment_increment=2; #全局,对所有的会话都有效 insert into dep1(name) values('IT'),('HR'),('SALE'),('Boss'); #auto_increment_offset:偏移量+auto_increment_increment:步长 注意:如果auto_increment_offset的值大于auto_increment_increment的值,则auto_increment_offset的值会被忽略 set session auto_increment_offset=2; set session auto_increment_increment=3; show variables like '%auto_in%'; create table dep3( id int primary key auto_increment, name char(10) ); insert into dep3(name) values('IT'),('HR'),('SALE'),('Boss'); #foreign key #!!!先建被关联的表,并且被关联的字段必须唯一 create table dep( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(50), comment varchar(100) ); create table emp_info( id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), dep_id int, constraint fk_depid_id foreign key(dep_id) references dep(id) on delete cascade on update cascade ); #先给被关联的表初始化记录 insert into dep values (1,'欧德博爱技术有限事业部','说的好...'), (2,'艾利克斯人力资源部','招不到人'), (3,'销售部','卖不出东西'); insert into emp_info values (1,'egon',1), (2,'alex1',2), (3,'alex2',2), (4,'alex3',2), (5,'李坦克',3), (6,'刘飞机',3), (7,'张火箭',3), (8,'林子弹',3), (9,'加特林',3) ;
