B. Product

样例输入1
2 2 1000000007
样例输出1
128
样例输入2
233 131072 4894651
样例输出2
748517
样例输入3
1000000000 999999997 98765431
样例输出3
50078216solution:
把乘积的形式换位求和的形式 模 phi (P )
gcd用phi展开,用mu展开的话会很难搞
预处理一部分的d*f(d) f表示约数的个数,这个可以线性筛
筛phi的时候用杜教筛 phi * I = id
sigma i simg j [ gcd (i,j)==1 ] = (sigma i (2*phi(i)) )-1
CODE:
1 #include <set>
2 #include <map>
3 #include <deque>
4 #include <queue>
5 #include <stack>
6 #include <cmath>
7 #include <ctime>
8 #include <bitset>
9 #include <cstdio>
10 #include <string>
11 #include <vector>
12 #include <cstdlib>
13 #include <cstring>
14 #include <iostream>
15 #include <algorithm>
16 #include <unordered_map>
17 using namespace std;
18
19 typedef long long LL;
20 typedef pair<LL, LL> pLL;
21 typedef pair<LL, int> pLi;
22 typedef pair<int, LL> pil;;
23 typedef pair<int, int> pii;
24 typedef unsigned long long uLL;
25
26 #define lson rt<<1
27 #define rson rt<<1|1
28 #define lowbit(x) x&(-x)
29 #define name2str(name) (#name)
30 #define bug printf("*********
")
31 #define debug(x) cout<<#x"=["<<x<<"]" <<endl
32 #define FIN freopen("D://code//in.txt","r",stdin)
33 #define IO ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0)
34 #define long long
35 const double eps = 1e-8;
36 const int mod = 1000000007;
37 const int maxn = 1e7 + 3;
38 const double pi = acos(-1);
39 const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
40 const LL INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL;
41
42 bool v[maxn];
43 int n, m, p, cnt, MOD;
44 int isp[maxn/10], phi[maxn];
45 int sum[maxn], ssum[maxn];
46 unordered_map<int, int> dp1, dp2;
47 typedef long long ll;
48
49 int add(int x, int y) {
50 if(y < 0) x += y;
51 else x = x - MOD + y;
52 if(x < 0) x += MOD;
53 return x;
54 }
55
56
57 void init() {
58 phi[1] = ssum[1] = 1;
59 for(int i = 2; i < maxn; ++i) {
60 if(!v[i]) {
61 ssum[i] = 2;
62 phi[i] = i - 1;
63 isp[cnt++] = i;
64 }
65 for(int j = 0; j < cnt && i * isp[j] < maxn; ++j) {
66 v[i*isp[j]] = 1;
67 if(i % isp[j] == 0) {
68 phi[i*isp[j]] = phi[i] * isp[j];
69 int pp = 1, x = i;
70 while(x % isp[j] == 0) x /= isp[j], pp++;
71 ssum[i*isp[j]] = ssum[i] / pp * (pp + 1);
72 break;
73 }
74 phi[i*isp[j]] = phi[i] * (isp[j] - 1);
75 ssum[i*isp[j]] = ssum[i] * 2;
76 }
77 }
78 for(int i = 1; i < maxn; ++i) {
79 sum[i] = add(sum[i-1], phi[i]);
80 ssum[i] = add(1LL * ssum[i] * i % MOD, ssum[i-1]);
81 }
82 // for(int i=3e6-20;i<3e6;i++)cout<<ssum[i]<<" " ;puts("");
83
84 }
85
86
87
88 int getphi(int x) {
89 if(x < maxn) return sum[x];
90 if(dp1[x]) return dp1[x];
91 int ans = (1LL * x * (x + 1) / 2) % MOD;
92 for(int l = 2, r; l <= x; l = r + 1) {
93 r = x / (x / l);
94 int tmp = 1LL * (r - l + 1) * getphi(x/l) % MOD;
95 ans = add(ans, -tmp);
96 }
97 return dp1[x] = ans;
98 }
99
100 int qpow(int x, int n) {
101 int res = 1;
102 while(n) {
103 if(n & 1) res = 1LL * res * x % p;
104 x = 1LL * x * x % p;
105 n >>= 1;
106 }
107 return res;
108 }
109
110 int getnum(int x) {
111 if(x < 3e6) return ssum[x];
112 //if(dp2[x]) return dp2[x];
113 int ans = 0;
114 for(int l = 1, r; l <= x; l = r + 1) {
115 r = x / (x / l);
116 LL tmp1 = 1LL * ((x / l) + 1) * (x / l);
117 LL tmp2 = 1LL * (l + r) * (r - l + 1) / 2;
118 ans = add(ans, tmp1 * tmp2 / 2 % MOD);
119 }
120 return dp2[x] = ans;
121 }
122
123 signed main(){
124 scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &p);
125 MOD = p - 1;
126 init();
127 int ans2 = getnum(n);
128 int ans1 = 0;
129 for(int l = 1, r; l <= n; l = r + 1) {
130 r = n / (n / l);
131 int tmp1 = getphi(n / l);
132 int tmp2 = add(getnum(r), -getnum(l-1));
133 ans1 = add(ans1, 1LL * tmp1 * tmp2 % MOD);
134 }
135 ans1 = 2LL * ans1 % MOD;
136 int ans = add(ans1, -ans2);
137 printf("%d
", qpow(m, ans));
138 return 0;
139 }
C. Angel's Journey
“Miyane!” This day Hana asks Miyako for help again. Hana plays the part of angel on the stage show of the cultural festival, and she is going to look for her human friend, Hinata. So she must find the shortest path to Hinata’s house.
The area where angels live is a circle, and Hana lives at the bottom of this circle. That means if the coordinates of circle’s center is (rx,ry)(rx, ry)(rx,ry) and its radius is rrr, Hana will live at (rx,ry−r)(rx, ry - r)(rx,ry−r).
Apparently, there are many difficulties in this journey. The area which is located both outside the circle and below the line y=ryy = ryy=ry is the sea, so Hana cannot pass this area. And the area inside the circle is the holy land of angels, Hana cannot pass this area neither.
However, Miyako cannot calculate the length of the shortest path either. For the loveliest Hana in the world, please help her solve this problem!
Input
Each test file contains several test cases. In each test file:
The first line contains a single integer T(1≤T≤500)T(1 le T le 500)T(1≤T≤500) which is the number of test cases.
Each test case contains only one line with five integers: the coordinates of center rxrxrx 、 ryryry, the radius rrr, thecoordinates of Hinata’s house xxx 、yyy. The test data guarantees that y>ryy > ryy>ry and (x,y)(x, y)(x,y) is out of the circle. (−102≤rx,ry,x,y≤102,0<r≤102)(-10^2 le rx,ry,x,y le 10^2,0 < r le 10^2)(−102≤rx,ry,x,y≤102,0<r≤102).
Output
For each test case, you should print one line with your answer (please keep 444 decimal places).
样例输入
2
1 1 1 2 2
1 1 1 1 3
样例输出
2.5708 3.8264
solution:
简单几何,注意危险区域是哪些
求出切点,特判切点的纵坐标是否小于 ry
CODE:
1 #include"bits/stdc++.h"
2 using namespace std;
3 const double pi = acos(-1);
4
5 double rx,ry,r;
6 double bx,by;
7 double s,t;
8 double diss(double a,double b,double c,double d)
9 {
10 return sqrt((a-c)*(a-c) + (b-d)*(b-d));
11 }
12
13 void work()
14 {
15 double d=diss(rx,ry,s,t);
16 double L1=sqrt(d*d-r*r);
17 bx=rx; by=ry-r;
18 double L2=diss(bx,by,s,t);
19 double th1=acos((d*d+r*r-L1*L1)/(2*d*r));
20 double th2=acos((d*d+r*r-L2*L2)/(2*d*r));
21 double th3=th2-th1;
22 // cout<<th1<<" "<<th2<<" "<<th3<<endl;
23 double tx,ty;
24 double ans;
25 if(s>rx)
26 {
27 tx=(0*cos(th3)-(-r)*sin(th3));
28 ty=(0*sin(th3)+(-r)*cos(th3));
29 //cout<<tx<<" "<<ty<<endl;
30 tx+=rx; ty+=ry;
31 // cout<<tx<<" "<<ty<<endl;
32 if(ty<ry)
33 ans=pi*r/2 + diss(rx+r,ry,s,t);
34 else ans=2*pi*r*th3/(2*pi) + diss(tx,ty,s,t);
35
36 }
37 else
38 {
39 tx=(0*cos(th3)-(-r)*sin(th3));
40 ty=(0*sin(th3)+(-r)*cos(th3));
41
42 tx=-tx; tx+=rx; ty+=ry;
43
44 if(ty<ry)
45 ans=pi*r/2 + diss(rx-r,ry,s,t);
46 else ans=2*pi*r*th3/(2*pi) + diss(tx,ty,s,t);
47 }
48 printf("%.4f
",ans);
49
50
51
52
53 }
54
55 int main()
56 {
57 int T;
58 for((cin>>T);T;T--)
59 {
60 cin>>rx>>ry>>r>>s>>t;
61 work();
62 }
63 }
M. Travel
There are nnn planets in the MOT galaxy, and each planet has a unique number from 1∼n1 sim n1∼n. Each planet is connected to other planets through some transmission channels. There are mmm transmission channels in the galaxy. Each transmission channel connects two different planets, and each transmission channel has a length.
The residents of the galaxy complete the interplanetary voyage by spaceship. Each spaceship has a level. The spacecraft can be upgraded several times. It can only be upgraded 111 level each time, and the cost is ccc. Each upgrade will increase the transmission distance by ddd and the number of transmissions channels by eee to the spacecraft. The spacecraft can only pass through channels that are shorter than or equal to its transmission distance. If the number of transmissions is exhausted, the spacecraft can no longer be used.
Alice initially has a 000-level spacecraft with transmission distance of 000 and transmission number of 000. Alice wants to know how much it costs at least, in order to transfer from planet 111 to planet nnn.
Input
Each test file contains a single test case. In each test file:
The first line contains nnn, mmm, indicating the number of plants and the number of transmission channels
The second line contains ccc, ddd, eee, representing the cost, the increased transmission distance, and the increased number of transmissions channels of each upgrade, respectively.
Next mmm lines, each line contains u,v,wu,v,wu,v,w, meaning that there is a transmission channel between uuu and vvv with a length of www.
(2≤n≤105,n−1≤m≤105,1≤u,v≤n,1≤c,d,e,w≤105)(2 le nle 10^5, n - 1 le m le 10^5,1 le u,v le n ,1 le c,d,e,w le 10^5)
(The graph has no self-loop , no repeated edges , and is connected)
Output
Output a line for the minimum cost. Output −1-1−1 if she can't reach.
样例输入
5 7
1 1 1
1 2 1
1 3 5
1 4 1
2 3 2
2 4 5
3 4 3
3 5 5
样例输出
5
solution:
二分一个升级的次数,只能走mid×d的路径,看此时的最短是时候小于mid×e
开long long
CODE:
1 #include"bits/stdc++.h"
2 using namespace std;
3 #define int long long
4
5 struct aa
6 {
7 int so;
8 int w;
9 };
10 const int N = 1e5+10;
11 vector<aa> v[N];
12 int n,m;
13 int c,d,e;
14 int deep[N];
15
16 int check(int mid)
17 {
18 int lim=mid*d;
19 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)deep[i] = 1e16;
20 deep[1]=0;
21 queue<int >q;
22 q.push(1);
23 while(!q.empty())
24 {
25 int t=q.front();q.pop();
26
27 for(auto i:v[t])
28 {
29 if(deep[i.so]!=1e16||i.w>lim)continue;
30 deep[i.so] = deep[t] + 1;
31 q.push(i.so);
32 }
33
34 }
35 //for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cout<<deep[i]<<" ";puts("");
36 return deep[n]<=e*mid;
37
38
39 }
40
41 signed main()
42 {
43 cin>>n>>m;cin>>c>>d>>e;
44 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
45 {
46 int a,b,c;cin>>a>>b>>c;
47 v[a].push_back({b,c});
48 v[b].push_back({a,c});
49 }
50
51 int l=1,r=8e7; int ans = 1;
52
53 while(l<=r)
54 {
55 int mid = l+r>>1;
56 if(check(mid))ans=mid,r=mid-1;
57 else l=mid+1;
58 }
59
60 cout<<ans*c;
61
62
63 }
L. Swap
There is a sequence of numbers of length nnn, and each number in the sequence is different. There are two operations:
- Swap the first half and the last half of the sequence (if nnn is odd, the middle number does not change)
- Swap all the numbers in the even position with the previous number (the position number starts from 111, and if nnn is odd, the last number does not change)
Both operations can be repeated innumerable times. Your task is to find out how many different sequences may appear (two sequences are different as long as the numbers in any one position are different).
Input
Each test file contains a single test case. In each test file:
The first line contains an integer nnn, indicating the length of the sequence (1≤n≤10000)(1 le n le 10000)(1≤n≤10000).
The second line contains nnn different numbers.
Output
Output the number of different sequences.
样例输入1
3
2 5 8
样例输出1
6
样例输入2
4
1 2 3 4
样例输出2
4
solution:
找规律。。
读错题意了,幸好不是比赛,要不把队友演了 qaq
PS:这种题我做不了,交给两个ljj和ljn了
CODE:
1 #include"bits/stdc++.h"
2 using namespace std;
3 #define int long long
4
5 int work(int n)
6 {
7 string s;
8 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)s+='a'+i-1;
9 set<string > ss;
10 ss.insert(s);
11 queue<string > q;
12 q.push(s);
13 while(!q.empty())
14 {
15 string y=q.front();q.pop();
16 // cout<<y<<endl;
17 for(int i=1;i<y.length();i+=2)
18 swap(y[i],y[i-1]);
19 if(!ss.count(y))q.push(y),ss.insert(y);
20 for(int i=1;i<y.length();i+=2)
21 swap(y[i],y[i-1]);
22
23 int len = y.length();
24 if(len%2==0)
25 {
26 for(int i=1;i<=len/2;i++)
27 swap(y[i-1],y[len/2+i-1]);
28 }
29 else
30 {
31 for(int i=1;i<=len/2;i++)
32 swap(y[i-1],y[len/2+i]);
33 }
34
35 if(!ss.count(y))q.push(y),ss.insert(y);
36 // cout<<y<<endl;
37 }
38 cout<<n<<" "<<ss.size()<<endl;
39
40 }
41 signed main()
42 { /*for(int i=1;i<=26;i++)
43
44 {
45 work(i);
46 }*/
47
48 int n;cin>>n;
49 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){int x;cin>>x;} if(n==1)
50 {
51 puts("1");return 0;
52 }
53 if(n==2){puts("2");return 0;}
54 else if(n==3){puts("6");return 0;}
55 if(n%4==0)cout<<4;
56 else if(n%4==1)cout<<n*2;
57 else if(n%4==2)cout<<n;
58 else if(n%4==3)cout<<12;
59 else cout<<4;
60 }
D. Miku and Generals
“Miku is matchless in the world!” As everyone knows, Nakano Miku is interested in Japanese generals, so Fuutaro always plays a kind of card game about generals with her. In this game, the players pick up cards with generals, but some generals have contradictions and cannot be in the same side. Every general has a certain value of attack power (can be exactly divided by 100100100 ), and the player with higher sum of values will win. In this game all the cards should be picked up.
This day Miku wants to play this game again. However, Fuutaro is busy preparing an exam, so he decides to secretly control the game and decide each card's owner. He wants Miku to win this game so he won't always be bothered, and the difference between their value should be as small as possible. To make Miku happy, if they have the same sum of values, Miku will win. He must get a plan immediately and calculate it to meet the above requirements, how much attack value will Miku have?
As we all know, when Miku shows her loveliness, Fuutaro's IQ will become 000 . So please help him figure out the answer right now!
Input
Each test file contains several test cases. In each test file:
The first line contains a single integer T(1≤T≤10) T(1 le T le 10)T(1≤T≤10) which is the number of test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains two integers: the number of generals N(2≤N≤200)N(2 le N le 200)N(2≤N≤200) and thenumber of pairs of generals that have contradictions M(0≤M≤200)M(0 le M le 200)M(0≤M≤200).
The second line contains NNN integers, and the iii-th integer is cic_ici, which is the attack power value of the iii-th general (0≤ci≤5×104)(0 le c_i le 5 imes 10^4)(0≤ci≤5×104).
The following MMM lines describe the contradictions among generals. Each line contains two integers AAA and BBB , which means general AAA and BBB cannot be on the same side (1≤A,B≤N)(1 le A , B le N)(1≤A,B≤N).
The input data guarantees that the solution exists.
Output
For each test case, you should print one line with your answer.
Hint
In sample test case, Miku will get general 222 and 333 .
样例输入
1
4 2
1400 700 2100 900
1 3
3 4
样例输出
2800
solution:
矛盾的关系中,每一个联通的矛盾关系图可以分成两部分
最后会出现许多的两部分,
现在答案变成了,每个两部分中取一个,使得差值最小
记sum为所有的价值之和,则当最优时取得sum/2 价值的物品
dp求的所有能取到的价值
从sum/2向后取第一个合法的价值
开始val全除100,输出的时候在×100
CODE:
1 #include"bits/stdc++.h"
2 using namespace std;
3
4 struct aa
5 {
6 int x,y;
7 };
8 vector<aa>w;
9 vector<int >v[300];
10 int val[300];
11 int n,m;
12 int vis[300];
13 vector<int >v1,v2;
14 int dp[210][300100];
15 void dfs(int x,int f)
16 {
17 // cout<<x<<endl;
18 vis[x]=f;
19 if(f==1)v1.push_back(x);
20 else v2.push_back(x);
21 for(auto i:v[x])if(!vis[i])
22 {
23 dfs(i,f==1?2:1);
24 }
25
26 }
27 void work()
28 {
29 memset(vis,0,sizeof vis);
30 w.clear();
31
32 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
33 {
34 //cout<<i<<endl;
35 if(!vis[i])
36 {
37 v1.clear(); v2.clear();
38 dfs(i,1);
39 int s1=0,s2=0;
40 for(auto j:v1)s1+=val[j];
41 for(auto j:v2)s2+=val[j];
42 w.push_back({s1,s2});
43 }
44 }
45 //for(auto i:w)cout<<i.x<<" "<<i.y<<endl;
46 int sze=w.size();
47 dp[0][0]=1;
48 for(int i=0;i<sze;i++)
49 {
50 int x=w[i].x,y=w[i].y;
51 for(int j=0;j<=100000;j++)
52 {
53 if(dp[i][j])
54 {
55 if(j+x<=100000)dp[i+1][j+x] = 1;
56 if(j+y<=100000)dp[i+1][j+y] = 1;
57 }
58 }
59 }
60 int tot=0;
61 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)tot+=val[i];
62 tot= (tot+1)/2;
63 for(int i=tot;i<=100000;i++)
64 if(dp[sze][i])
65 {
66 cout<<i*100<<endl;
67 return ;
68 }
69 }
70 int main()
71 {
72
73 int T;
74
75 for(cin>>T;T;T--)
76 {
77 cin>>n>>m;memset(dp,0,sizeof dp);
78 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)v[i].clear();
79 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>val[i],val[i]/=100;
80 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
81 {
82 int l,r;cin>>l>>r;v[l].push_back(r); v[r].push_back(l);
83 }
84 work();
85 }
86 }
J.And And And
A tree is a connected graph without cycles. You are given a rooted tree with nnn nodes, labeled from 1ton1 to n1ton. The tree is rooted at node 111. The parent of the iii-th node is faif_{a_i}fai. The edge weight between the iii-th node and faif_{a_i}fai is wiw_iwi
- E(u,v)E(u, v)E(u,v) is a set of all the nodes through a path which is from uuu to vvv, including uuu and vvv. For example,
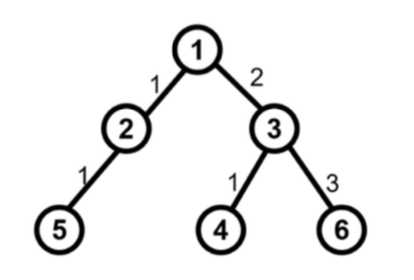
E(5,3)={5,2,1,3},E(4,6)={4,3,6},E(2,5)={2,5}E(5,3) = {5, 2, 1, 3}, E(4,6) = {4, 3, 6}, E(2,5) = {2,5}E(5,3)={5,2,1,3},E(4,6)={4,3,6},E(2,5)={2,5}
- X(u,v)X(u, v)X(u,v) represents the XOR of all edge weights on the path from uuu to vvv
For example, in the case given above,
X(1,5)=1X(1,5) = 1X(1,5)=1 xorxorxor 1=01=01=0,X(4,6)=1X(4,6) = 1X(4,6)=1 xorxorxor 3=23=23=2,X(2,5)=1X(2,5) = 1X(2,5)=1,X(3,5)=2X(3,5) = 2X(3,5)=2 xorxorxor 111 xorxorxor 111 =2=2=2You need to calculate the answer to the following formula:
∑u=1n∑v=1n∑u′∈E(u,v)∑v′∈E(u,v)[u<v][u′<v′][X(u′,v′)=0]displaystylesum_{u=1}^n displaystylesum_{v=1}^n displaystylesum_{u' in E(u,v)} displaystylesum_{v' in E(u,v)} [u < v][ u' < v'][X(u',v')=0]u=1∑nv=1∑nu′∈E(u,v)∑v′∈E(u,v)∑[u<v][u′<v′][X(u′,v′)=0]
The answer modulo 100000000710000000071000000007
- XOR is equivalent to '^' in c / c++ / java / python. If both bits in the compared position of the bit patterns are 000 or 111, the bit in the resulting bit pattern is 000, otherwise 111.
Input
Each test file contains a single test case. In each test file:
The first line contains one integer n(1≤n≤105)n(1 le n le 10^5)n(1≤n≤105) — the number of nodes in the tree.
Then n−1n - 1n−1 lines follow. iii-th line contains two integers fai(1≤fai<i)f_{a_i}(1 le f_{a_i} < i)fai(1≤fai<i), wi(0≤wi≤1018)w_i(0 le w_i le 10^{18})wi(0≤wi≤1018) —The parent of the iii-th node and the edge weight between the iii-th node and fai(if_{a_i} (ifai(i start from 2)2)2).
Output
Print a single integer — the answer of this problem, modulo 100000000710000000071000000007.
样例输入1
2
12
样例输出1
0
样例输入2
5
1 0
2 0
3 0
4 0
样例输出2
35
solution:
感觉像是套路
树上贡献->考虑每一个贡献点的贡献-> 分类讨论
像这里分为了在一个链和不在一个链的情况
CODE:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h>
2 using namespace std;
3 #define ll long long
4 const int maxn=1e5+5;
5 const int mod=1e9+7;
6 int n,u,num[maxn];
7 ll w,ans;
8 struct node
9 {
10 int v;
11 ll w;
12 node(int _v=0,ll _w=0):v(_v),w(_w) {}
13 };
14 vector<node> G[maxn];
15 unordered_map<ll,int> ump;
16 int dfsnum(int now)
17 {
18 num[now]++;
19 for(node tt:G[now]) num[now]+=dfsnum(tt.v);
20 return num[now];
21 }
22 int tmp=0;
23 void dfs(int now,ll s) //统计到根同链 ump[s]:当前点往上到根所有点右端点数和 tmp:单个点右端的点数
24 {
25 ans=(ans+num[now]*1ll*ump[s])%mod;
26
27 for(node tt:G[now])
28 {
29 //tmp=(tmp+num[now]-num[tt.v])%mod;
30 int t=0;t += n-num[tt.v];
31 ump[s]=(ump[s]+t)%mod;
32 dfs(tt.v,s^tt.w);
33 ump[s]=(ump[s]-t)%mod;
34 // tmp=(tmp-num[now]+num[tt.v])%mod;
35 }
36 }
37 void dfs1(int now,ll s)
38 {
39 ans=(ans+num[now]*1ll*ump[s])%mod;
40 for(node tt:G[now]) dfs1(tt.v,s^tt.w);
41 ump[s]=(ump[s]+num[now])%mod;
42 }
43 int main()
44 {
45 // freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
46 scanf("%d",&n);
47 for(int i=2; i<=n; i++)
48 {
49 scanf("%d %lld",&u,&w);
50 G[u].push_back(node(i,w));
51 }
52 dfsnum(1);//计算每个点子树节点数
53 dfs(1,0);//计算同链的
54 ump.clear();
55 dfs1(1,0);//计算不同链的
56 cout<<(ans+mod)%mod;
57 return 0;
58 }
E. Tree
Ming and Hong are playing a simple game called nim game. They have nnn piles of stones numbered 111 to nnn ,the iii-th pile of stones has aia_iai stones. There are n−1n - 1n−1 bidirectional roads in total. For any two piles, there is a unique path from one to another. Then they take turns to pick stones, and each time the current player can take arbitrary number of stones from any pile. Of course, the current player should pick at least one stone. Ming always takes the lead. The one who takes the last stone wins this game. Ming and Hong are smart enough so they will make optimal operations every time.
m events will take place. Each event has a type called optoptopt ( the value of opt is among {1,2,3} {1,2,3 }{1,2,3} ).
If optoptopt is 111, modify the numbers of stones of piles on the path from 1 to sss by the following way: change aia_iai to ai∣ta_i|tai∣t . ( s,ts,ts,t will be given).
If optoptopt is 222 , modify the numbers of stones of piles on the path from 1 to sss by the following way: change aia_iai to ai&ta_i&tai&t. (s,ts,ts,t will be given).
If optoptopt is 333 , they play nim game. Firstly, take the piles on the path from 1 to SSS into consideration. At the same time create a new pile with t stones and take it into consideration. Now they have taken +1 + 1+1 piles into consideration. Then they play nim game on these S+1S + 1S+1 piles. You need to figure out if Ming is going to win the game. Amazingly, after playing nim game, the numbers of stones of each pile on the path from 111 to sss will return to the original numbers.
Input
Each test file contains a single test case. In each test file:
The first line contains two integers,nnn and mmm.
The next line contains nnn integers, aia_iai.
The next n - 1 lines, each line contains two integers, b, c, means there is a bidirectional road between pile b and pile c.
Each of the following mmm lines contains 333 integers, optoptopt, sss and ttt.
If optoptopt is 111, change all the stone numbers of piles on the path from 111 to sss in the first way (ai(a_i(ai to ai∣t)a_i|t)ai∣t)
If optoptopt is 222, change all the stone numbers of piles on the path from 111 to sss in the second way (ai(a_i(ai to ai&t)a_i&t)ai&t).
If optoptopt is 333, we query whether Ming will win when given sss and ttt as parameters in this round.
It is guaranteed:1≤n,m≤105 1 le n,m le 10^51≤n,m≤105,
0≤ai≤1090 le a_i le 10^90≤ai≤109,
1≤opt≤3,1≤s≤105,0≤t≤109.1 le opt le 3, 1 le s le 10^5, 0 le t le 10^9.1≤opt≤3,1≤s≤105,0≤t≤109.
Output
If optoptopt is 333, print a line contains one word “YES” or “NO” (without quotes) , representing whether Ming will win the game.
样例输入
6 6
0 1 0 3 2 3
2 1
3 2
4 1
5 3
6 3
1 3 0
2 3 1
1 1 0
3 5 0
2 4 1
3 3 1
样例输出
YES
NO
solution:
感觉题解跟巧妙
a和t的范围是1e9,可以按每一个2进制的每一位考虑
就是开32个线段树 复杂度只是多了一个log
对于某一位,如果奇数个1异或,答案为1,偶数个1异或,答案为0
所以问题就变为求路径上1的个数
对于操作1,就是或操作,本质就是将某些位强制变为1
对于操作2,就是与操作,本质就是将某些位强制变为0
CODE:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h>
2 #define N 100010
3 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
4 #define eps 1e-10
5 #define pi 3.141592653589793
6 #define P 1000000007
7 #define LL long long
8 #define pb push_back
9 #define fi first
10 #define se second
11 #define cl clear
12 #define si size
13 #define lb lower_bound
14 #define ub upper_bound
15 #define mem(x) memset(x,0,sizeof x)
16 #define sc(x) scanf("%d",&x)
17 #define scc(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)
18 #define sccc(x,y,z) scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z)
19 using namespace std;
20 vector<int> a[N];
21 int n,m,cnt,rt,tg,son[N],top[N],id[N],fa[N],d[N],sz[N],rk[N],w[N];
22 struct node
23 {
24 int s,lz;
25 } f[35][N<<2];
26 void dfs1(int x,int ffa)
27 {
28 sz[x]=1;
29 for(auto i:a[x]) if (i!=ffa)
30 {
31 fa[i]=x;
32 d[i]=d[x]+1;
33 dfs1(i,x);
34 sz[x]+=sz[i];
35 if (sz[i]>sz[son[x]]) son[x]=i;
36 }
37 }
38 void dfs2(int x,int t)
39 {
40 top[x]=t;
41 id[x]=++cnt;
42 rk[cnt]=x;
43 if (!son[x]) return;
44 dfs2(son[x],t);
45 for (auto i:a[x]) if (i!=son[x] && i!=fa[x]) dfs2(i,i);
46 }
47
48 inline void pushdown(int x,int l,int r,int t)
49 {
50 if (f[rt][x].lz)
51 {
52 f[rt][x<<1].lz=f[rt][x].lz;
53 f[rt][x<<1].s=(t-l+1)*(f[rt][x].lz==1);
54 f[rt][x<<1|1].lz=f[rt][x].lz;
55 f[rt][x<<1|1].s=(r-t)*(f[rt][x].lz==1);
56 f[rt][x].lz=0;
57 }
58 }
59
60 void updata(int x,int l,int r,int fl,int fr)
61 {
62 if (l>=fl && r<=fr)
63 {
64 f[rt][x].lz=tg;
65 f[rt][x].s=(r-l+1)*(f[rt][x].lz==1);
66 }
67 else
68 {
69 int t=l+r>>1;
70 pushdown(x,l,r,t);
71 if (fl<=t) updata(x<<1,l,t,fl,fr);
72 if (fr>t) updata(x<<1|1,t+1,r,fl,fr);
73 f[rt][x].s=f[rt][x<<1].s+f[rt][x<<1|1].s;
74 }
75
76
77 }
78
79 int query(int x,int l,int r,int fl,int fr)
80 {
81 if (l==fl && r==fr) return f[rt][x].s;
82 int t=l+r>>1;
83 pushdown(x,l,r,t);
84 if (fr<=t)return query(x<<1,l,t,fl,fr);
85 else if (fl>t)return query(x<<1|1,t+1,r,fl,fr);
86 else
87 return query(x<<1,l,t,fl,t)+query(x<<1|1,t+1,r,t+1,fr);
88 }
89
90 int sum(int x,int y)
91 {
92 int ans=0;
93 while(top[x]!=top[y])
94 {
95 if (d[top[x]]<d[top[y]]) swap(x,y);
96 ans+=query(1,1,n,id[top[x]],id[x]);
97 x=fa[top[x]];
98 }
99 if (d[x]>d[y]) swap(x,y);
100 ans+=query(1,1,n,id[x],id[y]);
101 return ans;
102 }
103 void change(int x,int y)
104 {
105 while(top[x]!=top[y])
106 {
107 if (d[top[x]]<d[top[y]]) swap(x,y);
108 updata(1,1,n,id[top[x]],id[x]);
109 x=fa[top[x]];
110 }
111 if (d[x]>d[y]) swap(x,y);
112 updata(1,1,n,id[x],id[y]);
113 }
114
115 int main()
116 {
117 scc(n,m);
118 for (int i=1; i<=n; i++) sc(w[i]);
119 for (int i=1,x,y; i<n; i++)
120 {
121 scc(x,y);
122 a[x].pb(y),a[y].pb(x);
123 }
124 dfs1(1,-1);
125 dfs2(1,1);
126 for (int i=1; i<=n; i++)
127 for(rt=0; rt<33; rt++)
128 {
129 if ((w[i]>>rt)&1) tg=1;
130 else tg=2;
131 change(i,i);
132 }
133
134 for (int i=1,op,x,y; i<=m; i++)
135 {
136 sccc(op,x,y);
137 if (op==1)
138 {
139 for(rt=0; rt<33; rt++)if ((y>>rt)&1)
140 {
141 tg=1;
142 change(1,x);
143 }
144 }
145 else if (op==2)
146 {
147 for(rt=0; rt<33; rt++)if (!((y>>rt)&1))
148 {
149 tg=2;
150 change(1,x);
151 }
152 }
153 else
154 {
155 int fg=0;
156 for(rt=0; rt<33; rt++)
157 {
158 int t=sum(1,x)&1;
159 if (t!=((y>>rt)&1))
160 {
161 fg=1;
162 break;
163 }
164 }
165 if (fg) puts("YES");
166 else puts("NO");
167 }
168 }
169 }