376. Wiggle Subsequence 自己没想出来,看了别人的分析. 主要是要分析出升序降序只跟临近的2个决定.虽然直觉上不是这样.
 View Code
View Code
455. 分发饼干 非常重要的一个题目,主要是要通过这个题目来彻底理解for 循环里面动态变化时候会发生的bug问题.问题本身是trivaial的.

class Solution: def findContentChildren(self, g, s): """ :type g: List[int] :type s: List[int] :rtype: int """ #做模拟即可 g.sort() s.sort() count=0 for i in g: for j in s: #注意for j in s:里面s是可以动态变动的.每一次都刷新s的取值. #总之:在for 循环里面修改s的值是很麻烦的一个事情,但是这里面代码没问题,因为每运行一次 #他遇到刷新也就是触发了remove时候马上break.不让后面麻烦的事情发生了,就可以. #这个麻烦的事情是什么呢.就是 if i<=j: s.remove(j) count+=1 break ''' a=[23,4324,32,42,34,32] for i in a: a.remove(a[0]) 这个代码他实际上只跑3次.也就是说for i in a:的本质是for i in range(len(a)): 他只认准index. i读取的数据是23,32,34!!!!!!!!!! ''' return count
392. 判断子序列

class Solution: def isSubsequence(self, s, t): """ :type s: str :type t: str :rtype: bool """ #显然从头到尾找s中字母在t中尽量小的index即可 for i in s: if i not in t: return False now=t.index(i) t=t[now+1:] return True
435. 无重叠区间 突然间的快乐,居然过了,因为被动态规划的全局变量恶心到了.好久都没ac了

# Definition for an interval. # class Interval: # def __init__(self, s=0, e=0): # self.start = s # self.end = e class Solution: def eraseOverlapIntervals(self, intervals): """ :type intervals: List[Interval] :rtype: int """ #二位平面里面的点或者一维里面的区间的讨论,最常用的预处理就是按照一个坐标排序,通常按照第一个排序,然后再跑 ''' 常用的对,对象组成的list进行排序的常用方法. class Interval: def __init__(self, s=0, e=0): self.start = s self.end = e a=[Interval(3,4),Interval(56,40),Interval(-89,400)] a=sorted(a, key=lambda x : x.start) print(a[0].start,a[0].end) print(a[1].start,a[1].end) print(a[2].start,a[2].end) ''' '''或者这样写,更简洁一点. class Interval: def __init__(self, s=0, e=0): self.start = s self.end = e a=[Interval(3,4),Interval(56,40),Interval(-89,400)] a.sort( key=lambda x : x.start) print(a[0].start,a[0].end) print(a[1].start,a[1].end) print(a[2].start,a[2].end) ''' if intervals==[]: return 0 intervals.sort(key=lambda x : x.start) def overlap(a,b): if a.start<b.start and a.end >b.start or b.start<a.start and b.end >a.start or a.start==b.start: return True return False last=intervals[0] count=0 for i in range(1,len(intervals)): #如果他跟前面一个香蕉了 if overlap(intervals[i],last): #那么从贪心角度为了后面尽量不发生相交事件,就要分析要保留之前最后一个区间还是现在这个新区间 #让last变成尾巴最短的那个 if intervals[i].end<last.end: last=intervals[i] count+=1 else: last=intervals[i] return count
课程liuyubobobo到这里结束了
再去找点书刷刷,还是继续放在这里.感觉方便查找
http://vdisk.weibo.com/s/zJQeg4_RK11_v?category_id=0&parents_ref=zJQeg4_RkvSaa
就砍这个了.
计算机程序设计艺术(第二卷).pdf 书名的逼格这么高
大概翻了一下,都是经典的历史和算法套路,可以休闲读一读,刷leecode还是核心
自我刷题过程:
4. 两个排序数组的中位数

class Solution: def findMedianSortedArrays(self, nums1, nums2): """ :type nums1: List[int] :type nums2: List[int] :rtype: float """#莫名其妙的hard a=nums1+nums2 a.sort() if len(a)%2==0: return (a[len(a)//2]+a[len(a)//2-1])/2 else: return a[len(a)//2]
5. 最长回文子串 内含非常重要的manacher算法的实现!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!

class Solution: def longestPalindrome(self, s): """ :type s: str :rtype: str """ m='' #暴力法, ''' if s==s[::-1]: return s for i in range(len(s)): for j in range(i+1,len(s)+1): tmp=s[i:j] if tmp==tmp[::-1]: if len(tmp)>len(m): m=tmp return m ''' ''' 真正的解法:manaccher算法:求解一个str的所有回文子串 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008484167 下面我来用python实现它 ''' def manacher(s):#这个算法返回s这个数组 #比如[1,1,4]这个数组对应的[#1#1#4#]其中每一个字符 #作为中间字符所生成的半径,组成的数组:[1,2,3,2,2,1] #而这个半径-1其实就是最大的回文子串的长度,因为你填入了很多#. #补上# #为了方便补上边界左边补$右边补?(符号随意写2个不常用的不同符号即可) s_new=['?','#'] for i in s: s_new.append(i) s_new.append('#') s_new.append('!') s=s_new p=[0]*len(s)#要输出的数组 mx=0#最大的右边界 for i in range(1,len(s)-1): if i<mx: #启用之前的对称点来判断 p[i]=min(p[2*id-i],mx-i) else: p[i]=1 while s[i-p[i]]==s[i+p[i]]: #这里利用上面的补符号来判断越界. p[i]+=1 #更新mx和id if (mx<i+p[i]): id=i mx=i+p[i] find=max(p) id=p.index(find) right=id+find-1 left=id-find+1 jieguo=s[left:right] output='' for i in jieguo: if i !='#': output+=i return max(p)-1,output return manacher(s)[1] #经过我的修改里面的manacher函数返回最大回文子串的长度和他具体是什么,非常完美.借鉴了很多其他人的思路

好像是最后开着的灯一定是他的因子个数为奇数.所以答案是完全平方数.
我感觉:因为需要所有灯都按奇数次,所以按照一圈顺序都按一次即可. 这就是答案.

递推即可.T(1)=2 T(n)=T(n-1)+n 即可.

不容易说清楚,反正就是靠理解:
T(n)-T(n-1)等价于你拿一个新屏幕来跟已经存在的n-1条直线相交.看能投影多少份,也就等价于n-1个线把屏幕份多少份.带入上个题目.即可.
为什么空间新加多少个就等价于你拿n-1条直线切屏幕切多少份?
因为新添加一个屏幕就等价于你拿一个新屏幕来切已经存在的屏幕.空间中已经存在一条直线来把空间分割成2份了,就等价于你把心屏幕纷呈了多少个份.









f(n,m)=min(max(f(n-i,m),f(i,m-1))+1) max对i取遍1到n

比如a认识b:那么a一定不是明星. a不认识b:那么b一定不是明星
分布式的算法.提高常熟被.




398. 随机数索引 实践是检验真理的标准!

import random class Solution: def __init__(self, nums): """ :type nums: List[int] """ self.nums=nums def pick(self, target): """ :type target: int :rtype: int """ #来写pick函数,蓄水池抽样即可. a=[] count=0 for i in range(len(self.nums)): if self.nums[i] ==target: suiji=random.randint(1,count+1) if suiji==count+1: a=i count+=1 return a # Your Solution object will be instantiated and called as such: # obj = Solution(nums) # param_1 = obj.pick(target)

小明去考试,都不会,然后做5个纸条来随机残生4个选项,老师问为什么是5个,他说最后一个纸条是再扔一次.

根据上面思路是:发生正,背就选正,发生背,正就选正...其他扔出来的情况都作废重新扔即可.



这他妈也太难了.

红黑树 再设计一个随机返回一个数的操作.
答案:数组加哈希表加红黑树.3个组合来实现
哈希来做数组元素下表和红黑树里面元素之间的联系.
数组里面删除是把最后一个元素跟第一个元素来做交换然后删除最后一个元素.数组是为了random函数而存储的数据.
其他操作都是用红黑树来实现.
Trie树,双数组Trie树.
大数据面试: 最重要的hash分桶法.

解法:1.假设内存是无线的.那么我们用哈希表来处理.

总结一下:也就是1.把100G文件切分成1000份 2.每一份做hash处理即可.
首先需要明确做估计:ipv4的地址是4个256乘法.也就是256**4=16G内存
1G=2^30次方个byte
1个int需要4个byte
他是把哈希之后的哈希值进行分桶.这个很巧妙把16G给拆成100份来存储.
伪代码就是:

data=100G内容 a=[] for i in range(100): a.append({}) for i in data: index=hash(i)%100 if i not in a[index]: a[index][i]=0 a[index][i]+=1 return max(max(a[index][i].value))
直接上面的方法,在建立一个堆即可.用小根堆,来存topk.如果要存入的数据比小根堆的堆顶要大,就把堆顶弹出去,然后新数据入堆.
堆:用于解决topk的问题
双堆:维护中位数!!!!!!!!!!!

还是没想明白自己再想想.
双堆算中位数:复杂度是:n/2*logn 就比排序算法快了一半,空间开销都一样都是O(N).
https://blog.csdn.net/liuyuan185442111/article/details/48396413
其实深入理解这个题目之后:发现他说的意思是维护中位数.也就是随时插入进去一个数,都要立马读出中位数.是这个时间,而不计算堆建立的时间.
这个过程排序需要nlogn,但是大小堆方法.只需要插入进去一个数logn,然后比较一下就出来了.所以是logn时间复杂度.比nlogn快多了.
还是有必要实现一下的.但是python没有大根堆,真是烦,自己写又麻烦.知道用相反数可以建立.

还是哈希分桶法. 因为是整数,所以可以用int的取值范围来做分割即可.

都是哈希分桶法.加堆.

哈希分桶法亦然实用!!!!!!
只不过bitmanp更好一点.
一个整数表示的最大范围是大概是40亿多,算是40亿那就是40*10^8*4字节大概是4g*4=16g,100亿就是16*2.5大概是40g。
100亿个整数=1*10^10*4个字节
1个G=10^9个字节.
所以100亿个数是40个G
而int总共是2^32个.也就是40亿个数.他消耗字节2^32*4=160亿个字节
1G有10亿个字节.
所以需要空间是16个G.
总之:需要记住的是1.记录所有整数需要16个G 2.1G存储2.5亿个数. 3.100亿个数需要40个G

我想到的方法是bitmap改成3进制.
老师的答案是用bitmap里面2个数位来存一个状态,00表示没出现过,01表示出现过1次,11表示出现过大于2次,10表示出现过2次.
3进制效率不行.所以还是老师的答案对.

query 查询
我思路是:哈希桶,分a1,....an ,b1,....bn .然后ai,bj的交取并即刻.
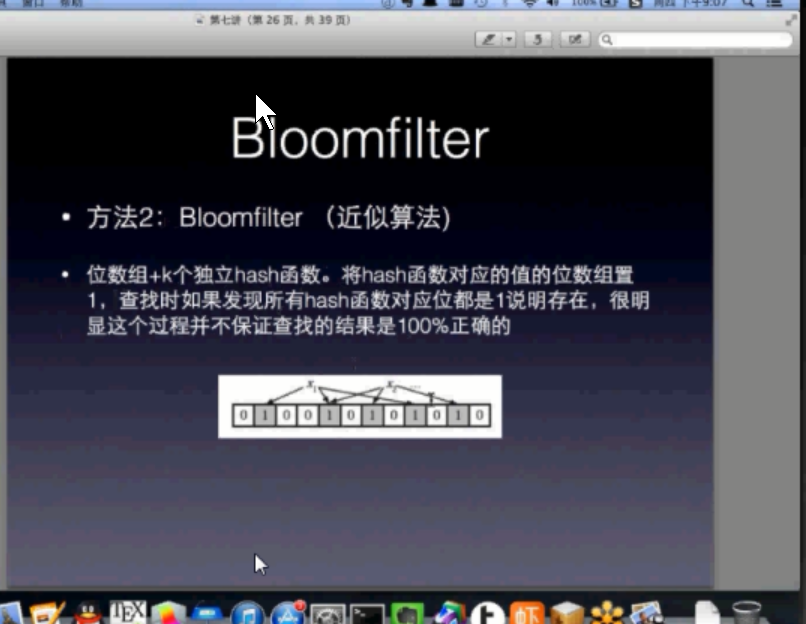
是一种高效的近似求交算法. bloomfilter
比如我要查询x是否存在.那么用k个哈希函数对x做映射.分别得到x1,....xk.(哈希函数尽可能选的都互相非常不像)
然后我们把一个数据叫存在等价于他左哈希之后的数位x1,...xk都是1.
这样我们不停的存储一个数的哈希位是否是1.得到一个01串即可表示在这个集合中一个元素是否存在!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!(道理其实和bitmap一样,只不过更深入复杂一点来获取
一个编码.) 他导致的可能会false positive.即没有的记成了有.
然后对于我们这个问题而言:可以这么做:
把a建立bloomfilter的0,1子串.然后这k个哈希函数作用到b里面的b1.
b1生成代码比如31位为1,36位为1.然后我们看上面这个子串里面31位是不是1,36位是不是1.
如果都是1我们说她是a交b.否则说不是.
显然会false positive.因为我们说是,可能这个并不是a里面的b1元素来提供的这些位上的1.
但是没啥太大毛病,因为当k取得足够多,和特殊的时候,错误率是有一个数学上的下界的.
显然是一个近似查询过程.1.哈希函数可能会在一点取值相同. 2.同一个哈希函数把x ,y映射到同一个值.
为什么用k个就是为了避免一个哈希函数映射2个元素可能值相同.多个更保险.

Trie 树,更牛逼.比如1000万个文字.
你平衡二叉树是O(logn),Trie树是O(1).因为字母26个.他看做是超多个分支的树.
处理字符串很常用!!!!!!!!!!
Trie树实现: 别人的代码,我加点注释而已,非常巧妙
但是其实本质就是多级字典的深度遍历.找到即可.

#coding=utf-8 #字典嵌套牛逼,别人写的,这样每一层非常多的东西,搜索就快了,树高26.所以整体搜索一个不关多大的单词表 #还是O(1). ''' Python 字典 setdefault() 函数和get() 方法类似, 如果键不存在于字典中,将会添加键并将值设为默认值。 说清楚就是:如果这个键存在字典中,那么这句话就不起作用,否则就添加字典里面这个key的取值为后面的默认值. 简化了字典计数的代码.并且这个函数的返回值是做完这些事情之后这个key的value值. dict.setdefault(key, default=None) Python 字典 get() 函数返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回默认值。 dict.get(key, default=None) ''' class Trie: root = {} END = '/' #加入这个是为了区分单词和前缀,如果这一层node里面没有/他就是前缀.不是我们要找的单词. def add(self, word): #从根节点遍历单词,char by char,如果不存在则新增,最后加上一个单词结束标志 node = self.root for c in word: node=node.setdefault(c,{}) #利用嵌套来做,一个trie树的子树也是一个trie树. #利用setdefault的返回值是value的特性,如果找到了key就进入value #没找到,就建立一个空字典然后 node[self.END] = None #当word都跑完了,就已经没有字了.那么当前节点也就是最后一个字母的节点 #加一个属性标签end.这个end里面随意放一个value即可.因为我们判定只是 #判定end这个key是否在字典里面. def find(self, word): node = self.root for c in word: if c not in node: return False node = node[c] return self.END in node a=Trie() (Trie.END)#python这个也是吊,类方法和类属性:自动也是对象的方法或者属性! a.add('a') a.add('ab') a.add('abc') a.add('c') a.add('ca') a.add('cad') print(a.find('cat')) #测试一下非常好使!
7. 反转整数

class Solution: def reverse(self, x): """ :type x: int :rtype: int """ if x>=0: x=str(x) x=x[::-1] x=int(x) if x in range(-2**31,2**31-1): return x else: return 0 else: return -self.reverse(-x)
8. 字符串转整数 (atoi)

class Solution: def myAtoi(self, str): """ :type str: str :rtype: int """ str=str.lstrip() a='' if str=='': return 0 if str[0] in '+-': a+=str[0] for i in range(1,len(str)): if str[i] in '0123456789': a+=str[i] else: break elif str[0] in '0123456789': a+=str[0] for i in range(1,len(str)): if str[i] in '0123456789': a+=str[i] else: break else: return 0 try: a=int(a) if a>2**31-1: return 2**31-1 if a<-2**31: return -2**31 else: return a except: return 0
9. 回文数

class Solution: def isPalindrome(self, x): """ :type x: int :rtype: bool """ x=str(x) return x==x[::-1]
10. 正则表达式匹配 注意对re.fullmatch的学习

import re class Solution: def isMatch(self, s, p): """ :type s: str :type p: str :rtype: bool """ a=re.fullmatch(p,s) if a==None: return False else: return True
14. 最长公共前缀

class Solution: def longestCommonPrefix(self, strs): """ :type strs: List[str] :rtype: str """ if len(strs)==1: return strs[0] if strs==[]: return '' aa=float('inf') for i in strs: if len(i)<aa: aa=len(i) a='' b=0 while b!=aa: for i in range(len(strs)): if strs[i][b]!=strs[0][b]: return a b+=1 a+=strs[0][b-1] return strs[0][:aa]
6. Z字形变换

import copy class Solution: def convert(self, s, numRows): """ :type s: str :type numRows: int :rtype: str """ if s=='': return '' if numRows==1: return s if numRows>len(s): return s a=[0]*len(s) output=[] for i in range(numRows): output.append(copy.copy(a)) hang=0 lie=0 i=0 while i<len(s): if hang==0 and len(s)-i>=numRows: for j in range(numRows): output[hang+j][lie]=s[i+j] hang+=numRows i+=numRows continue if hang==0 and len(s)-i<numRows: xin=len(s)-i for j in range(xin): output[hang+j][lie]=s[i+j] hang+=xin i+=xin continue if hang>=numRows: hang-=2 lie+=1 if hang==0: #这一步也解决冲突 continue output[hang][lie]=s[i] i+=1 else: print('**********') print(s[i]) print(hang,lie) hang-=1 lie+=1 if hang==0:#这个步解决前面冲突 continue output[hang][lie]=s[i] i+=1 #拍平函数即可 def paiping(a): b=[] for i in a: b+=i return b output=paiping(output) tmp='' for i in output: if i!=0: tmp+=i print(tmp) return tmp
15. 三数之和

import copy class Solution: def threeSum(self, nums): """ :type nums: List[int] :rtype: List[List[int]] """ #貌似哈希方法没法解,只能对撞指针. nums.sort() old_nums=nums.copy() output=[] for i in range(len(old_nums)): if i!=0 and old_nums[i]==old_nums[i-1]: #这个为了驱虫 continue nums=old_nums[i+1:] target=-old_nums[i] ii=0 jj=len(nums)-1 while 1: if ii>=jj: break if nums[ii]+nums[jj]>target : jj-=1 continue if nums[ii]+nums[jj]<target: ii+=1 continue if nums[ii]+nums[jj]==target : if ii==0:#这里面各种if else也是为了驱虫 output.append([-target,nums[ii],nums[jj]]) ii+=1 else: if nums[ii]==nums[ii-1]: ii+=1 else: output.append([-target,nums[ii],nums[jj]]) ii+=1 return output
16. 最接近的三数之和

class Solution: def threeSumClosest( self,nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: int """ #取定一个数,还是对撞指针. if nums==[-1,2,1,-4]: return 2 nums.sort() output=float('inf') for i in range(len(nums)): targett=target-nums[i] #找距离target最近的(2个数的和) ii=0 tmp=nums[i+1:] jj=len(tmp)-1 while 1: if ii>=jj: break if tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]==targett: if abs(tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]-targett)<output: output=abs(tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]-targett) save=tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]+nums[i] jj-=1 continue else: jj-=1 continue if tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]>targett: if abs(tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]-targett)<output: output=abs(tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]-targett) save=tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]+nums[i] jj-=1 continue else: jj-=1 continue if tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]<targett: if abs(tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]-targett)<output: output=abs(tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]-targett) save=tmp[ii]+tmp[jj]+nums[i] ii+=1 continue else: ii+=1 return save
18. 四数之和 去重很烦,但是本身这个题目效率要求不高,所以多次排序去重可以

class Solution: def fourSum( self,nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: List[List[int]] """ #建立两个数之和这个哈希表 k={} for i in range(len(nums)): for j in range(i+1,len(nums)): k.setdefault(nums[i]+nums[j],set([])) k[nums[i]+nums[j]].add((i,j)) #然后拼起来,得到index数组output output=[] for ii in k: tmptarget=target-ii if tmptarget not in k: continue first=k[ii] second=k[tmptarget] for i in first: for j in second: tmp=list(i)+list(j) if len(set(tmp))!=4: continue tmp.sort() if tmp not in output: output.append(tmp) #切换成内容 for i in output: for ii in range(len(i)): i[ii]=nums[i[ii]] for i in range(len(output)): output[i].sort() output2=[] for i in output: if i not in output2: output2.append(i) return output2
22. 括号生成 网上人都好强,做出来的人这么多,我没想出来,看到
拿到题的第一反应想到的是这道题是典型的递归,但是好长时间过去了依然不知道怎么递归。参考学长博客:http://blog.csdn.net/wwh578867817/article/details/46392701,得到规律左半括号永远大于等于右半括号。
才收到的启发写出来的代码:

class Solution: def generateParenthesis(self, n): """ :type n: int :rtype: List[str] """ output=[] def add_one(listme): listout=[] for i in listme: if i.count('(')>i.count(')') and i.count('(')<n: listout.append(i+'(') listout.append(i+')') continue if i.count('(')>i.count(')') and i.count('(')==n: listout.append(i+')') else: listout.append(i+'(') return listout i=0 a=[''] while i<2*n: a=add_one(a) i+=1 return a
25. k个一组翻转链表

# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution: def reverseKGroup(self, head, k): """ :type head: ListNode :type k: int :rtype: ListNode """ #使用数组套路来解这个链表题 #虽然套路但是多练练没坏处 old_head=head a=[] while head!=None: a.append(head) head=head.next i=0 while 1: if i+k-1 <len(a):#说明k长的子数组都存在 left=i right=i+k-1 while left<=right: a[left],a[right]=a[right],a[left] left+=1 right-=1 i=i+k else: break for i in range(len(a)-1): a[i].next=a[i+1] if a==[]: return None a[len(a)-1].next=None return a[0]
28. 实现strStr()

class Solution: def strStr(self, haystack, needle): """ :type haystack: str :type needle: str :rtype: int """ if needle not in haystack: return -1 return haystack.index(needle)
29. 两数相除

class Solution: def divide(self, dividend, divisor): """ :type dividend: int :type divisor: int :rtype: int """ if dividend==0: return 0 if dividend>0 and divisor >0: a= dividend//divisor if dividend<0 and divisor >0: a= -(-dividend//divisor) if dividend>0 and divisor<0: i=0 while dividend+divisor>=0: dividend+=divisor i+=1 a=-i if dividend<0 and divisor <0: a= (-dividend)//(-divisor) if a<-2**31: return -2**31 if a>2**31-1: return 2**31-1 else: return a
