一、继承相关概念
1、语法:

2、定义:

3、优缺点:

4、相关概念:

5、相关内置函数:

6、继承内存图:
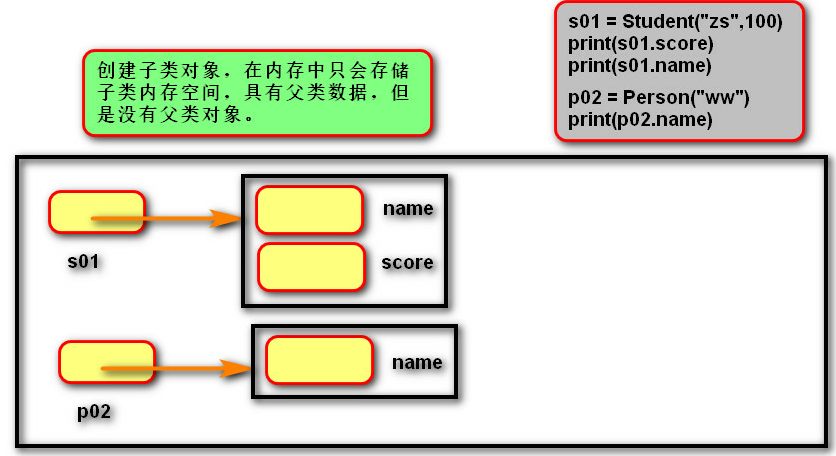
7、多继承:

二、多态相关概念
1、定义及作用:

2、重写概念:

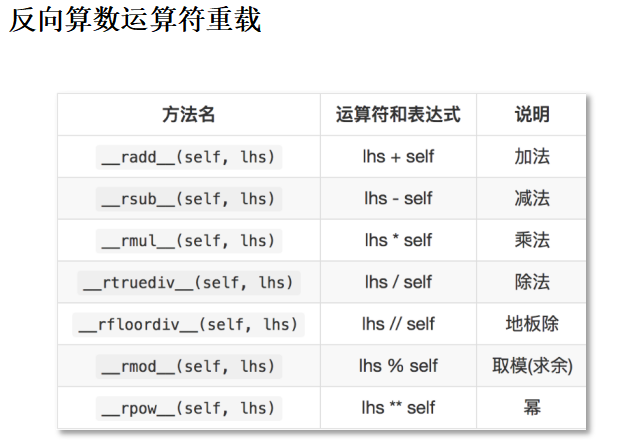
3、运算符重载:
定义:让自定义的类生成的对象(实例)能够使用运算符进行操作。



三、基础技能代码:
代码1:
""" 继承语法 -- 方法 财产 皇位 #练习1:定义父类--宠物, 行为:吃 # 定义子类--狗, 行为:防守xx # 定义子类--鸟, 行为:飞 #创建相应对象,调用相应方法.测试isinstance,issubclass函数 #14:35 """ # 学生 与 老师 在某种概念上是统一的 # 学生是 人 # 老师是 人 # class Person: def say(self): print("说") class Student(Person): def study(self): print("学习") class Teacher(Person): def teach(self): print("教") s01 = Student() s01.study() # 可以直接使用父类成员 s01.say() p02 = Person() p02.say() # 父类不能使用子类成员 # p02.study() t03 = Teacher() t03.teach() # 不能使用"兄弟"类成员 # t03.study() # 判断一个对象是否"兼容"一个类型 print(isinstance(s01,Person)) # True print(isinstance(s01,Student)) # True print(isinstance(s01,object)) # True print(isinstance(s01,Teacher)) # False print(isinstance(p02,Student)) # False # 判断一个类是否"兼容"一个类型 print(issubclass(Student,Person)) # True print(issubclass(Student,Teacher)) # False print(issubclass(Student,(Teacher,Person))) # True print(issubclass(Student,Student)) # True
代码2:
""" 继承语法 -- 数据 # 练习: 定义父类--宠物, 数据:名字 # 定义子类--狗, 数据:工作 # 创建相应对象,画出内存图 """ class Person: def __init__(self,name): self.name = name class Student(Person): def __init__(self,name,score): # 通过函数,调用父类方法 super().__init__(name) self.score = score class Teacher(Person): def __init__(self,name,salary): super().__init__(name) self.salary = salary s01 = Student("zs",100) print(s01.score) print(s01.name) p02 = Person("ww") print(p02.name)
代码3:
""" 继承 -- 设计思想 面向对象设计原则 练习:exercise01.py 1. 开闭原则 开放 关闭 对扩展 对修改 允许增加新功能 不允许改变(增加/删除/修改)以前的代码 2. 依赖倒置(抽象) 使用抽象(父类),而不使用具体(子类). """ # 老张开车去东北 # 变化:飞机 # 火车 # 汽车 # ....... class Person: def __init__(self, name): self.name = name # def go_to(self, str_type, str_pos): # if str_type == "汽车": # Car().run(str_pos) # elif str_type =="飞机": # Airplane().fly(str_pos) # # elif xxxxx: def go_to(self, vehicle, str_pos): """ 写代码期间: 使用的是交通工具的,而不是汽车,飞机等 所以无需判断具体类型 运行期间: 传递具体的对象(汽车,飞机) :param vehicle: :param str_pos: :return: """ # 如果传入的对象,不是交通工具,则退出. if not isinstance(vehicle,Vehicle): print("传入的不是交通工具") return vehicle.transport(str_pos) # class Car: # def run(self, str_pos): # print("行驶到", str_pos) # # # class Airplane: # def fly(self, str_pos): # print("飞到", str_pos) class Vehicle: """ 交通工具 """ def transport(self, str_pos): # 人为创造一个错误() raise NotImplementedError() # print("儿子们,必须有这个方法啊") class Car(Vehicle): def transport(self, str_pos): print("行驶到", str_pos) class Airplane(Vehicle): def transport(self, str_pos): print("飞到", str_pos) # .... p01 = Person("老张") # p01.go_to("汽车", "东北") p01.go_to(Airplane(),"东北")
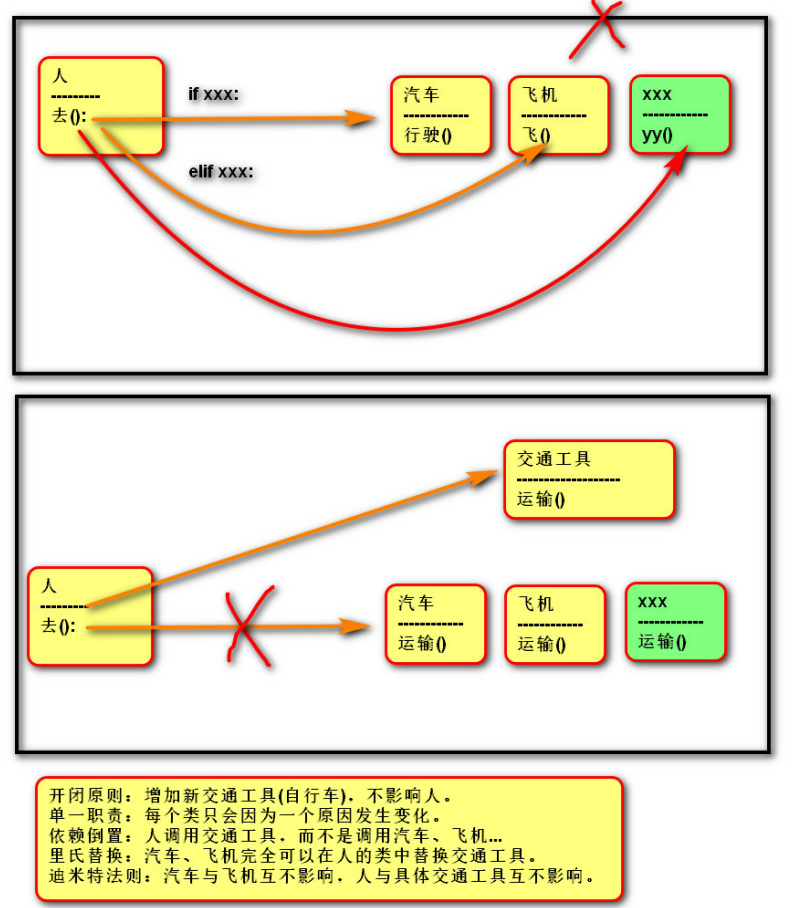
四、具体实例:
练习1:
# 练习:手雷爆炸了,可能伤害敌人,玩家.还有可能伤害未知事物(鸭子,树,房子). # 要求:如果增加了新的事物,手雷代码不变. 17:15 class Grenade: """ 手雷 """ def __init__(self, atk): self.atk = atk def explode(self, *args): """ 爆炸 :return: """ for item in args: if not isinstance(item, Damageable): print("类型不兼容") return item.damage(self.atk) class Damageable: """ 可以受伤 """ def __init__(self, hp): self.hp = hp def damage(self, value): # 约束子类必须具有当前方法 # raise NotImplementedError() self.hp -= value class Player(Damageable): def damage(self, value=0): # self.hp -= value super().damage(value) print("碎屏") class Enemy(Damageable): def damage(self, value): # self.hp -= value super().damage(value) print("播放动画") g01 = Grenade(10) p02 = Player(100) e03 = Enemy(50) g01.explode(p02, e03)
练习2:
""" 有若干个图形(圆形,矩形........) 每种图形,都可以计算面积. 定义图形管理器,记录所有图形,提供计算总面积的方法. 要求:增加新的图形,不改变图形管理器代码. """ class GraphicManager: def __init__(self): # 记录所有图形 self.__graphics = [] def add_graphic(self,g): if not isinstance(g,Graphic): return self.__graphics.append(g) def get_total_area(self): """ 计算总面积 :return: """ total_area = 0 for item in self.__graphics: total_area += item.get_area() return total_area class Graphic: """ 图形 """ def get_area(self): pass class Circle(Graphic): """ 圆形 """ def __init__(self,radius): self.radius = radius def get_area(self): return self.radius ** 2 * 3.14 class Rectangle(Graphic): """ 矩形 """ def __init__(self, length,width): self.length = length self.width = width def get_area(self): return self.length * self.width manager = GraphicManager() manager.add_graphic("ok") manager.add_graphic(Rectangle(2,3)) manager.add_graphic(Circle(5)) # 加断点,调试 print(manager.get_total_area())
练习3:
# 1. 定义父类:武器,数据:攻击力,行为:购买(所有子类都一样).攻击(不知道怎么攻击) # 定义子类:枪,数据:射速,行为:攻击 # 定义子类:手雷,数据:爆炸范围,行为:攻击 # 创建相应对象,调用相应方法. # 画出内存图 class Weapon: """ 武器 """ def __init__(self,atk): self.atk = atk def buy(self): print("购买武器") def attack(self): # 子类如果没有当前方法,就会报错 raise NotImplementedError() class Gun(Weapon): """ 枪 """ def __init__(self,atk,speed): super().__init__(atk) self.att_speed = speed def attack(self): print("开枪啦") class Grenade(Weapon): """ 手雷 """ def __init__(self, atk, range): super().__init__(atk) self.explode_range = range def attack(self): print("爆炸啦") g01 = Gun(10,0.1) g01.buy() g01.attack() grenade01 = Grenade(50,10) grenade01.buy() grenade01.attack()
练习4:
# 2. 一家公司,有如下几种岗位: # 普通员工:底薪 # 程序员:底薪 + 项目分红 # 销售员:底薪 + 销售额 # 定义员工管理器,记录所有员工,提供计算总薪资方法. # 要求:增加新岗位,员工管理器代码不做修改. # 体会:依赖倒置 class EmployeeManager: """ 员工管理器 """ def __init__(self): self.__all_employee = [] def add_employee(self, employee): if not isinstance(employee, Employee): return self.__all_employee.append(employee) def get_total_salary(self): """ 计算总薪资 :return: """ total_salary = 0 for item in self.__all_employee: # 编码期间:item 认为是员工 # 运行期间:item 实际是具体员工 total_salary += item.get_salary() return total_salary class Employee: """ 员工类 作用:代表具体员工,隔离员工管理器与具体员工的变化. """ def __init__(self, name, salary): self.name = name self.base_salary = salary def get_salary(self): return self.base_salary class Programmer(Employee): """ 程序员 """ def __init__(self, name, salary, bonus): super().__init__(name, salary) self.bonus = bonus def get_salary(self): # return self.base_salary + self.bonus # 扩展重写 return super().get_salary() + self.bonus class Salesmen(Employee): """ 销售员 """ def __init__(self, name, salary, sale_value): super().__init__(name, salary) self.sale_value = sale_value def get_salary(self): return super().get_salary() + self.sale_value * 0.05 manager = EmployeeManager() manager.add_employee(Employee("zs",3000)) manager.add_employee(Programmer("xp",4000,10)) manager.add_employee(Programmer("xx",99999,6135138)) manager.add_employee(Salesmen("pp",3000,500)) re = manager.get_total_salary() print(re) #练习:老王转岗 # 销售 --> 程序员 lw = Salesmen("老王",3000,500) lw = Programmer("老王",8000,100000) # 重新创建新对象,替换引用.好比是开除"老王",招聘新"老王" # 要求:对象部分改变,而不是全部改变.
练习5:
class Employee: """ 员工类 """ def __init__(self, name,job): self.name = name # 成员变量的类型是岗位 self.job = job def calculate_salary(self): """ 使用岗位,计算薪资. :return: """ return self.job.get_salary() class Job: """ 岗位 """ def __init__(self,salary): self.base_salary = salary def get_salary(self): return self.base_salary class Programmer(Job): """ 程序员 """ def __init__(self,salary, bonus): super().__init__(salary) self.bonus = bonus def get_salary(self): # return self.base_salary + self.bonus # 扩展重写 return super().get_salary() + self.bonus class Salesmen(Job): """ 销售员 """ def __init__(self,salary, sale_value): super().__init__(salary) self.sale_value = sale_value def get_salary(self): return super().get_salary() + self.sale_value * 0.05 #练习:老王转岗 # 销售 --> 程序员 # 继承关系 # lw = Salesmen("老王",3000,500) # lw = Programmer("老王",8000,100000) # 重新创建新对象,替换引用.好比是开除"老王",招聘新"老王" # 要求:对象部分改变,而不是全部改变. lw = Employee("老王",Salesmen(3000,500)) print(lw.calculate_salary()) # 转岗 lw.job = Programmer(8000,100000) print(lw.calculate_salary())
练习6:
""" 内置可重写函数 """ class Wife: def __init__(self,name,age): self.name = name self.age = age def __str__(self): # 返回给人看 return "奴家叫:%s,年芳:%d"%(self.name,self.age) def __repr__(self): # 返回给解释器看 return 'Wife("%s",%d)'%(self.name,self.age) w01 = Wife("金莲",25) print(w01)# 将对象转换为字符串 # re = eval("1 + 5") # print(re) # w02 = eval('Wife("金莲",25)') # w03 = eval(input("")) #创建了新对象 w02 = eval(w01.__repr__()) print(w02) w01.name ="莲莲" print(w02.name)
练习7:
# 练习: 重写 StudentModel 类 __str__ 方法 与__repr__方法 # 创建学生对象,创建学生对象列表.分别print class StudentModel: def __init__(self, name="", age=0, score=0, id=0): self.id = id self.name = name self.age = age self.score = score def __str__(self): return "我的编号是:%d,姓名是:%s,年龄是:%d,成绩是:%d."%(self.id,self.name,self.age,self.score) def __repr__(self): return 'StudentModel("%s",%d,%d)'%(self.name,self.age,self.score) s01 = StudentModel("zs",24,100) s02 = eval(s01.__repr__()) print(s02) print(s01) list01 = [s01,s02] print(list01)
练习8:
""" 运算符重载 """ # print("a" + "b") class Vector: """ 向量 """ def __init__(self, x): self.x = x def __str__(self): return "向量的x变量是:%s"%self.x # 对象 + def __add__(self, other): return Vector(self.x + other) # + 对象 def __radd__(self, other): return Vector(self.x + other) # 累加:在原有对象基础上进行操作,不创建新对象. def __iadd__(self, other): self.x += other return self def __lt__(self, other): return self.x < other v01 = Vector(10) v02 = v01 + 5 # print(v02) # 练习:实现向量类 与 整数 做 减法/乘法运算 17:25 v03 = 5 + v01 # print(v03) v04 = v01 + v02 # print(v04) # 练习:实现整数 与 向量 做 减法/乘法运算 # 向量 向量 list01 = [1] list02 = list01 + [2] print(list01) list01 += [2] print(list01) print(id(v01)) # 累加含义:在原有对象基础上,增加新值 v01 += 1 print(v01) print(id(v01)) # 练习:实现向量类 与 整数 做 累计减法/累计乘法运算 print(v01 < 2)