----android培训 、java培训 、期待与您交流!----
关键字finally:
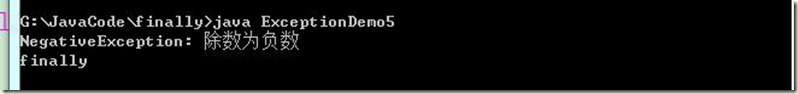
/* finally 代码块:定义一定执行的代码 ①通常用于关闭资源 ②某些代码一定要执行 */class NegativeException extends Exception { public NegativeException(String message) { super(message); } } class Arithmetic { public int div(int a,int b) throws NegativeException { if(b<0) throw new NegativeException("除数为负数"); return a/b; } } class ExceptionDemo5 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { int x=new Arithmetic().div(4,-1); } catch (NegativeException e) { System.out.println(e.toString()); return; //System.exit(0); //系统退出,JVM结束,finally不执行 } finally { System.out.println("finally"); } System.out.println("over"); } } /* finally作用: 示例: 连接数据库,对里面的数据进行一些操作,完成后必须断开(因为服务器的处理能力和资源有限) public void method() throws NoException { 连接数据库; 数据操作; //throw new SQLException(); //当数据库操作出现异常,无法断开连接 断开连接;//该动作,无论数据是否操作成功,一定要关闭资源 //因此把以上修改为 try { 连接数据库; 数据操作; } catch(SQLException) { DBA对数据库进行异常处理 throw new NoException(); } finally { 断开连接; } } throw new NoException(); 解析下为什么不抛new SQLException();? 这个类似异常练习中的电脑冒烟->抛给授课老师的无法上课 而不是电脑冒烟问题. 举个通俗易懂的例子:(有点牵强) 仓库管理员与销售人员 当仓库漏水了(仓库中的货出问题了),总不能跟销售说 仓库漏水(异常)了,哥们去解决下(处理异常) 而是给销售说现在没货 仓库管理员也不能 不回复销售人员(不抛) 让销售人员郁闷 以上运用了分层思想-->各司其职 */
finally与continue和break:
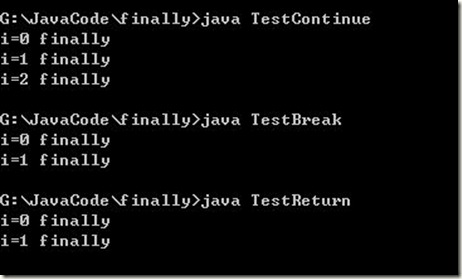
class TestContinue { public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=0;i<3;++i) { try { if(i==1) continue; } finally { System.out.println("i="+i+" finally"); } } } } class TestBreak { public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=0;i<3;++i) { try { if(i==1) break; } finally { System.out.println("i="+i+" finally"); } } } } class TestReturn { public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=0;i<3;++i) { try { if(i==1) return; } finally { System.out.println("i="+i+" finally"); } } } } /* 总结: finally语句块: ①总是在程序退出方法之前被执行. ②总是在循环被跳过(continue)或中断(break)之前被执行 */
异常在字父类覆盖中的体现:
/*异常在字父类覆盖中的体现:
1.子类在覆盖父类时,如果父类的方法抛出异常,
那么子类的覆盖父类方法,只能抛出父类的异常
或该异常的子类或不抛
2.如果父类方法抛出多个异常,那么子类在覆盖该方法时,只能抛出父类异常的子集(子类可以不抛)3.如果父类或者接口的方法中没有异常抛出,那么子类在覆盖方法时,也不可以抛出异常.
如果子类方法中发生了异常,就必须要进行处理,绝对不能抛.
特殊:(针对RuntimeException)
如果是RuntimeException可以不用处理,进行throw.
如果父类方法没有throws,而子类也可以throws RuntimeException(或其子类).*/
//为什么子类不能抛其它异常?
class AException extends Exception
{
}
class BException extends AException
{
}
class CException extends Exception { }class Father
{
void show() throws AException
{class Son extends Father
}
}
{
void show() throws AException//或BException都可以
{ //如果在这里抛了CException 不行
//复写 //如果Son中真有C异常->内部处理(不抛)
}
}
class Test
{
void method(Father f)
{
try
{
f.show();//代码① 调用父类的show()-->处理
//代码② 调用子类的show()
}
catch (AException e)//代码② 接收new CException()-->无法处理
{ //早期的程序不能处理后期程序产生的新异常
}
}
}
class FxException
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//new Test().method(new Father());//①
new Test().method(new Son());//②
}
}
异常练习:
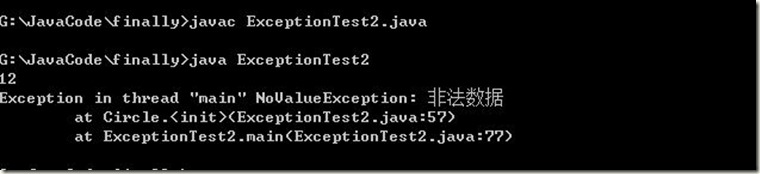
/* 有一个圆形和长方形. 都可以获取面积.对于面积如果出现非法的数值, 视为是获取面积出现的问题. 问题通过异常来表示 现有对这个程序进行基本设计. */ //自定义异常 class NoValueException extends RuntimeException { public NoValueException(String message) { super(message); } } //把面积视为一个扩展功能(抽象类也可以) interface Shape { public abstract void getArea(); } //长方形 class Rec implements Shape { private int len,wid; Rec(int len,int wid) { if(len<0||wid<0) throw new NoValueException("出现非法值"); //可以抛RuntimeException但是异常不具体 //另外如果我想对该异常进行其它描述呢,需要在NoValueException中描述 this.len=len; this.wid=wid; } public void getArea() { System.out.println(len*wid); } } //圆形 class Circle implements Shape { private int radius; public static final double PI=3.14;//共享数据 public Circle(int radius) { if(radius<0) throw new NoValueException("非法数据"); this.radius=radius; } public void getArea() { System.out.println(PI*radius*radius); } } class ExceptionTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { new Rec(3,4).getArea(); //如果长方形的长或宽发生问题,下面关于 //长方形的一些计算已经丧失意义了因此 //继承RuntimeException new Circle(-8).getArea(); System.out.println("Over"); } }
try..catch几种格式总结:
//第一个格式: try{} catch(){}catch(){}… //以上或对应多个catch /*catch语句可以有多个,用来匹配多个异常,匹配上多个中一个后,执行catch语句块时候仅仅执行匹配上的异常*///第二个格式: try{} catch(){} finally{} //第三个格式: try{} finally{} */ //小例子: //① class Demo { public void method() { throw new Exception();//不可以通过编译->Exception为被检测异常-->必须在函数上声明 } } //② class Demo { public void method() { try { throw new Exception();//可以通过编译-->问题已解决 } catch(Exception e) { } } } //③ class Demo { public void method() { try { throw new Exception();//可以通过编译-->问题已解决 } catch(Exception e) { try { throw e; } catch(Exception e)//依然可以 { } } } } //④ class Demo { public void method() throws Exception { try { throw new Exception(); } finally { //关闭资源或一定会执行的代码 } } } /* 总结:catch用于处理异常,如果没有catch代表该异常没有处理过,如果该异常是检测时异常,那么必须声明 (前面总结过) */
经典例子:
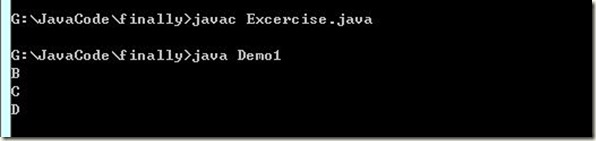
//关于异常两个例子对比 //throw下面不能有语句,有则编译不通过 //例一: class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { try { showExce();//可能出现异常,因此下面的语句有可能执行到 System.out.println("A"); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("B"); } finally { System.out.println("C"); } System.out.println("D"); } public static void showExce() throws Exception { throw new Exception(); } } //例二 class Demo2 { public static void func() { try { throw new Exception(); //System.out.println("A");//"无法访问的语句", } //上面已经出现异常一定执行不到 catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("B"); } } public static void main(String[] args) { try { func(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("C"); } System.out.println("D"); } }